Alabama Tax Rate
Understanding the Alabama tax system is essential for individuals and businesses operating within the state. With a diverse range of taxes, from income tax to sales tax, it is crucial to navigate the intricacies of the Alabama tax landscape to ensure compliance and optimize financial strategies.
A Comprehensive Guide to Alabama’s Tax Structure

The tax system in Alabama encompasses various taxes, each with its own set of rules and rates. This guide will provide an in-depth analysis of the state’s tax landscape, offering valuable insights for taxpayers and business owners.
Income Tax in Alabama
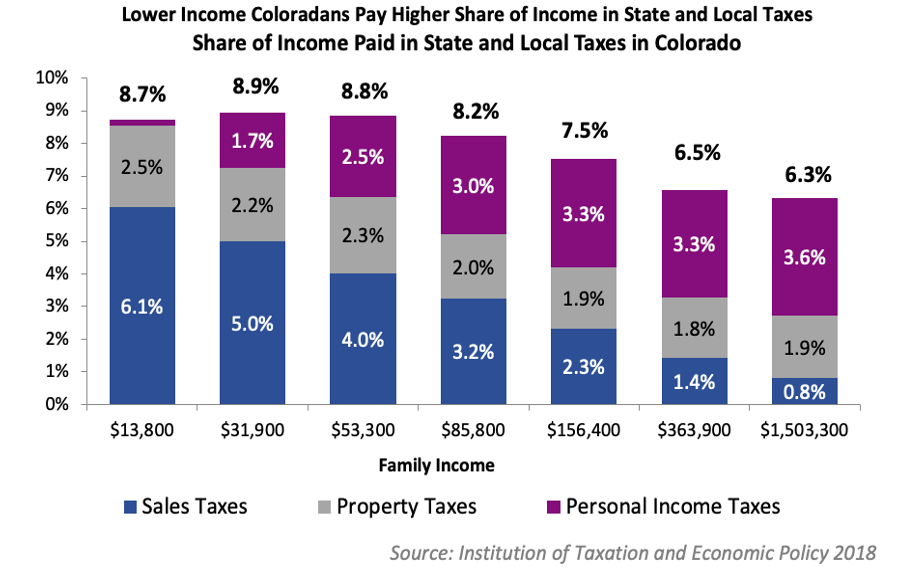
Income tax is a significant component of the Alabama tax system. As of 2023, the state operates a flat tax rate structure, meaning all taxpayers, regardless of their income level, are subject to the same tax rate. The current Alabama income tax rate stands at 2%, which is applied to taxable income. This flat rate simplifies the tax filing process, making it more predictable for taxpayers.
It's important to note that Alabama does not impose a municipal income tax, which sets it apart from some other states. This absence of local income tax can be advantageous for individuals and businesses, as it reduces the overall tax burden.
To illustrate, let's consider an example. John, a resident of Alabama, has a taxable income of $50,000 for the year. With the Alabama flat income tax rate of 2%, John's income tax liability would amount to $1,000. This straightforward calculation makes it easier for taxpayers to estimate their tax obligations.
Sales and Use Tax
Sales and use tax is another crucial aspect of the Alabama tax system. The state’s sales tax rate is currently set at 4%, which is applicable to most tangible personal property and certain services. However, it’s important to note that local governments can impose additional sales tax rates, resulting in varying total sales tax rates across the state.
For instance, the city of Birmingham has a local sales tax rate of 5%, bringing the total sales tax rate in the city to 9% (state rate + local rate). On the other hand, the city of Huntsville has a local sales tax rate of 3%, resulting in a total sales tax rate of 7% in that area.
To provide a clearer picture, let's calculate the sales tax for a purchase in Birmingham. If an individual buys a television for $1,000, the sales tax applicable would be $90 (9% of $1,000). This breakdown highlights the impact of local tax rates on overall sales tax obligations.
| Sales Tax Rates in Alabama | State Rate | Local Rate | Total Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birmingham | 4% | 5% | 9% |
| Huntsville | 4% | 3% | 7% |
Property Tax
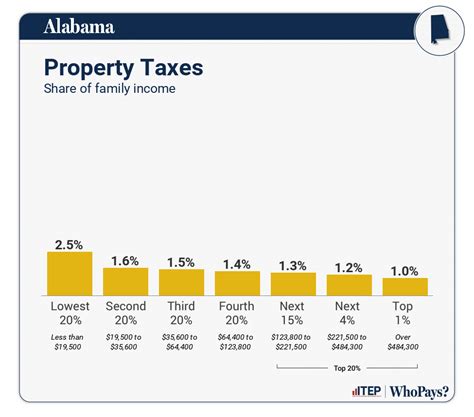
Property tax is an essential revenue source for local governments in Alabama. The state’s property tax system is primarily administered by counties and municipalities, resulting in diverse tax rates and assessment methods.
The property tax rate in Alabama is typically expressed as a "mills," which is equivalent to one-tenth of a cent. The millage rate, which is determined by local authorities, is applied to the assessed value of the property to calculate the tax liability.
For instance, if a homeowner in Alabama has a property assessed at a value of $200,000 and the millage rate is set at 25 mills, the annual property tax liability would be calculated as follows: $200,000 x 0.025 = $5,000. This example illustrates how the property tax rate and assessed value impact the overall tax obligation.
Other Taxes in Alabama
Alabama imposes various other taxes to generate revenue and fund specific initiatives. These taxes include:
- Gasoline Tax: Alabama levies a tax on gasoline, which is used to fund transportation infrastructure. The current rate is 18 cents per gallon, with an additional 4 cents per gallon dedicated to county roads and bridges.
- Motor Vehicle Sales Tax: A tax is applied to the purchase of motor vehicles, with the rate varying based on the vehicle's value. This tax is collected at the time of registration and is used to support transportation-related projects.
- Lodging Tax: Alabama imposes a tax on hotel and lodging accommodations, with the rate ranging from 4% to 11% depending on the location. This tax is a significant revenue source for local tourism initiatives.
Tax Strategies and Planning

Navigating the Alabama tax landscape requires careful planning and an understanding of the state’s tax rules. Here are some key considerations for effective tax planning:
Utilizing Tax Credits and Deductions
The Alabama Department of Revenue offers various tax credits and deductions that can reduce tax liabilities. These include credits for education expenses, energy-efficient improvements, and tax deductions for charitable contributions.
For instance, the Alabama Income Tax Credit for Contributions to Public Schools allows taxpayers to claim a credit of up to $50 for contributions made to eligible public schools. This credit can be a valuable tool for taxpayers looking to reduce their tax burden while supporting local education initiatives.
Business Tax Considerations
Businesses operating in Alabama face unique tax challenges. It is crucial for businesses to understand the state’s tax regulations, including sales tax collection and remittance requirements, to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
One important consideration for businesses is the Alabama Business Privilege Tax. This tax is imposed on businesses based on their net worth, with rates ranging from 0.15% to 0.55% depending on the business's classification. The tax is calculated on the business's net worth, which is determined by subtracting liabilities from assets.
Estate and Inheritance Tax
Alabama does not impose an estate or inheritance tax, which provides an advantage for residents and businesses. This absence of estate taxes can simplify the process of transferring assets and property, making Alabama an attractive state for wealth management and estate planning.
Conclusion: Navigating Alabama’s Tax Landscape
The Alabama tax system, with its diverse range of taxes and rates, requires a comprehensive understanding for effective financial planning. From the flat income tax rate to the varying local sales tax rates, taxpayers and businesses must stay informed to optimize their tax strategies.
By staying up-to-date with Alabama's tax regulations and utilizing available tax credits and deductions, individuals and businesses can navigate the state's tax landscape successfully. Whether it's understanding property tax assessments or planning for business tax obligations, knowledge is key to ensuring compliance and maximizing financial outcomes.
What is the Alabama income tax rate for 2023?
+
The Alabama income tax rate for 2023 is a flat 2%, which is applied to taxable income.
Are there any local income taxes in Alabama?
+
No, Alabama does not impose any local income taxes, which is unique compared to some other states.
How does the Alabama sales tax rate vary across the state?
+
The state sales tax rate is 4%, but local governments can add additional rates, resulting in varying total sales tax rates across Alabama. For example, Birmingham has a total rate of 9%, while Huntsville has a total rate of 7%.
What is the Alabama property tax rate structure?
+
The property tax rate in Alabama is expressed in “mills,” with the millage rate determined by local authorities. The millage rate is applied to the assessed value of the property to calculate the tax liability.
Does Alabama have an estate or inheritance tax?
+
No, Alabama does not impose an estate or inheritance tax, which can provide advantages for residents and businesses in terms of asset and property transfers.