Nys Tax Status
In the world of business and finance, understanding tax obligations is crucial, especially when it comes to navigating the intricate tax landscape of a state like New York. The New York State Tax Status refers to the various regulations, rates, and requirements that businesses and individuals must adhere to when dealing with taxes in this bustling state. This article aims to delve into the specifics of New York's tax status, providing a comprehensive guide for those looking to comprehend and manage their tax responsibilities effectively.
Understanding New York’s Tax Structure
New York, often referred to as the Empire State, boasts a robust economy and a diverse tax system to match. The state’s tax structure is designed to fund a wide range of public services and infrastructure projects, making it a critical aspect of the state’s fiscal policy. The New York State Tax Status encompasses several key components, each with its own set of rules and implications.
Income Tax
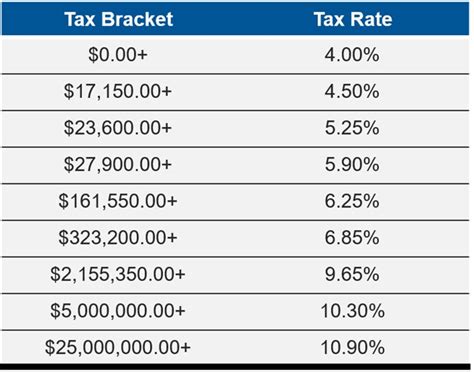
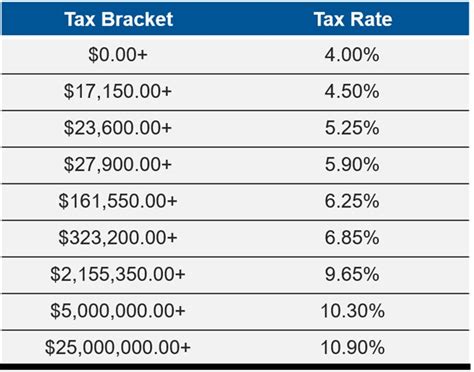
New York imposes a progressive income tax system, meaning the tax rate increases as income rises. This system is designed to ensure that those with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their earnings to the state’s revenue. The income tax rates in New York range from approximately 4% to 8.82%, depending on the taxpayer’s income bracket. It’s important to note that New York City and some other localities may also levy additional income taxes, creating a complex web of tax rates.
| Income Bracket (NYS) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $8,400 | 4% |
| $8,401 - $11,100 | 4.5% |
| $11,101 - $13,050 | 5.5% |
| $13,051 - $21,000 | 6% |
| $21,001 - $161,550 | 6.5% |
| $161,551 - $2,143,050 | 6.85% |
| $2,143,051 and above | 8.82% |

Sales and Use Tax
The New York State Tax Status also includes a sales and use tax, which applies to the retail sale, lease, or rental of most goods, as well as some services. The base sales tax rate in New York is 4%, but this can vary significantly depending on the county and city where the sale takes place. For instance, New York City imposes an additional 4.5% tax, resulting in a combined rate of 8.5% in most areas of the city.
| Location | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| New York City | 8.5% |
| Nassau County | 8.625% |
| Suffolk County | 8.625% |
| Other Counties | 4% - 4.75% |
Certain items, such as groceries, clothing, and prescription drugs, are exempt from sales tax or have reduced rates in New York. Additionally, the state offers various tax incentives and credits to encourage specific behaviors or support certain industries.
Corporate Taxes
New York levies a corporate income tax on the income of corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), and other business entities. The tax rate is 6.5%, but there are various deductions and credits available to reduce the taxable income. For instance, New York offers a net operating loss carryover provision, allowing businesses to offset future taxable income with past losses.
Furthermore, New York has a franchise tax, which applies to both domestic and foreign corporations doing business in the state. This tax is based on the corporation's entire net income and can be calculated using various methods, depending on the nature of the business.
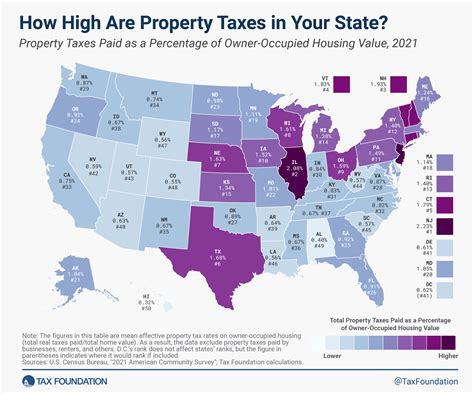
Property Tax
Property taxes in New York are primarily determined at the local level, with rates varying widely across the state. On average, the effective property tax rate in New York is approximately 1.75%, which ranks among the highest in the nation. These taxes are used to fund local services such as schools, fire departments, and public safety initiatives.
Tax Filing and Compliance
Understanding the New York State Tax Status is only half the battle; the other crucial aspect is ensuring compliance with the state’s tax laws. This involves timely filing of tax returns, accurate reporting of income and expenses, and proper payment of taxes owed.
Tax Forms and Filing Deadlines
New York offers a variety of tax forms depending on the type of tax being filed. For instance, Form IT-201 is used for individual income tax returns, while Form CT-6 is used for corporate tax filings. It’s essential to use the correct form and to file it by the specified deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
The due date for most tax returns in New York aligns with the federal deadline, which is typically April 15th. However, certain types of taxes, such as estimated tax payments, have different deadlines. For example, estimated tax payments are due on April 15th, June 15th, September 15th, and January 15th of the following year.
Taxpayer Assistance and Resources
The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance provides extensive resources to help taxpayers navigate the complex tax landscape. This includes online tax guides, tax forms, and publications, as well as a helpline for taxpayers seeking assistance. Additionally, the department offers various payment options, including online payments, direct debit, and payment plans for those struggling to pay their tax liabilities.
Penalties and Interest
Failure to comply with New York’s tax laws can result in significant penalties and interest. For instance, late filing of tax returns can incur a penalty of up to 5% of the unpaid tax per month, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, late payment of taxes can result in interest charges of up to 9% per year.
Conclusion: Navigating the Empire State’s Tax Landscape
The New York State Tax Status is a multifaceted and dynamic system, requiring a deep understanding of various tax types, rates, and regulations. From income and sales taxes to corporate and property taxes, each aspect has its own set of rules and implications. Navigating this complex landscape requires diligence, attention to detail, and a willingness to stay updated with the latest tax laws and regulations.
By understanding the New York State Tax Status and leveraging the resources provided by the state's Department of Taxation and Finance, businesses and individuals can ensure compliance, minimize their tax liabilities, and contribute effectively to the state's economy.
How can I determine my New York State tax bracket for income tax purposes?
+You can determine your New York State tax bracket by referring to the state’s tax tables, which are based on your taxable income. These tables outline the specific tax rates for each income bracket. It’s important to note that New York’s tax brackets are not linear; the tax rate increases as income rises.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available for small businesses in New York?
+Yes, New York offers a variety of tax incentives and credits to support small businesses. These can include tax credits for job creation, research and development, and energy efficiency improvements. It’s advisable to consult with a tax professional or refer to the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance’s website for a comprehensive list of available incentives.
What happens if I miss the tax filing deadline in New York?
+Missing a tax filing deadline in New York can result in penalties and interest charges. The state may impose a late filing penalty of up to 5% of the unpaid tax per month, with a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest on unpaid taxes can accrue at a rate of up to 9% per year. It’s important to file as soon as possible to minimize these charges.