New California Gas Tax
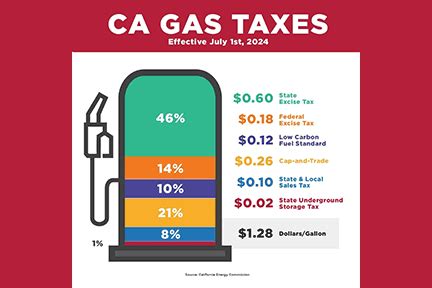
In the state of California, a new gas tax has been implemented, aiming to revolutionize transportation funding and infrastructure development. This comprehensive tax reform, officially known as the Road Repair and Accountability Act, or SB 1, was signed into law in 2017. With its implementation, California takes a significant step towards addressing the challenges of maintaining and improving its vast network of roads and highways.
The new California gas tax is a complex system designed to provide a stable and sustainable source of revenue for critical transportation projects. It aims to tackle the state's aging infrastructure, congestion issues, and environmental concerns, all while ensuring a fair contribution from various stakeholders.
Understanding the California Gas Tax
The California gas tax reform is a multi-faceted approach, incorporating various elements to achieve its goals. It consists of a series of new and adjusted taxes and fees, each targeting specific aspects of transportation funding.
Gasoline and Diesel Taxes
At the core of the reform is an increase in the taxes on gasoline and diesel. These taxes are now based on the price of fuel, with a higher tax rate applied to more expensive fuels. For instance, the tax on regular gasoline is set at 39.5 cents per gallon, while premium fuels can face a tax of up to 47.5 cents per gallon. This variable tax rate ensures that the tax burden is proportional to the price of fuel, making it more equitable.
| Fuel Type | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Regular Gasoline | 39.5 cents/gallon |
| Premium Gasoline | 47.5 cents/gallon |
| Diesel Fuel | 46.5 cents/gallon |
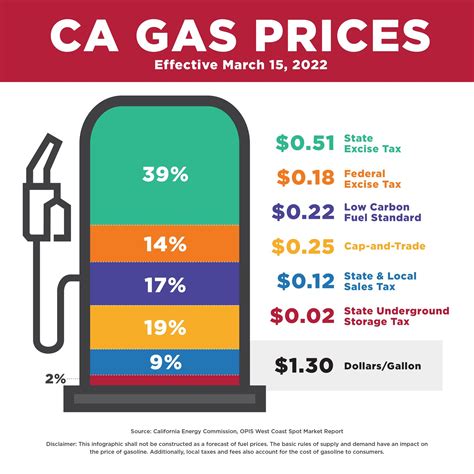
This approach, known as a "price-based" or "price-linked" tax, helps to ensure that the tax revenue keeps pace with inflation and fuel price fluctuations. It also encourages the use of more efficient, less costly fuels, as consumers may opt for cheaper alternatives to save on fuel costs and tax.
Vehicle Registration Fees
In addition to fuel taxes, the new California gas tax reform includes adjustments to vehicle registration fees. These fees are now based on the value of the vehicle, with higher fees for more expensive cars. This “value-based” fee structure aims to ensure that those with more valuable vehicles contribute more to transportation funding.
| Vehicle Value | Registration Fee |
|---|---|
| Up to $5,000 | $108 |
| $5,001 - $10,000 | $132 |
| $10,001 - $20,000 | $156 |
| Over $20,000 | $180 |
By linking registration fees to vehicle value, the state can ensure a more progressive funding system, where those with more expensive vehicles, which typically have a larger environmental and infrastructure impact, contribute proportionally more.
Other Fees and Taxes
The California gas tax reform also introduces or increases several other fees and taxes related to transportation. These include a new annual fee for zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs), an increase in the Heavy Vehicle Fee for commercial trucks, and a new “Cap and Trade” program, which puts a limit on greenhouse gas emissions and allows companies to trade emission allowances.
| Fee/Tax | Description |
|---|---|
| Zero-Emission Vehicle Fee | Annual fee of $100 for ZEVs to help fund transportation infrastructure. |
| Heavy Vehicle Fee | Increased fees for commercial trucks based on weight to account for road wear. |
| Cap and Trade Program | Limits greenhouse gas emissions and allows trading of emission allowances. |
These additional measures aim to capture revenue from various transportation-related activities, ensuring a comprehensive and fair funding approach.
Funding Distribution and Allocation

The revenue generated from the new California gas tax is distributed among various transportation-related projects and initiatives. The distribution process is carefully designed to address a range of infrastructure needs, from road repairs to public transit improvements.
Road Maintenance and Repair
A significant portion of the gas tax revenue, approximately 60%, is allocated towards road maintenance and repair. This includes funding for pavement preservation, bridge repairs, and other critical infrastructure maintenance tasks. By prioritizing road maintenance, the state aims to improve road safety and reduce congestion caused by deteriorated roads.
Public Transit and Active Transportation
Around 20% of the gas tax revenue is directed towards public transit and active transportation initiatives. This funding supports projects such as bus rapid transit, light rail expansion, and improvements to pedestrian and bicycle infrastructure. By investing in these alternatives to personal vehicle use, the state aims to reduce traffic congestion and encourage more sustainable transportation choices.
Local Road Projects
Another 10% of the gas tax revenue is set aside for local road projects. This funding is distributed to cities and counties based on a formula that considers factors such as population, road mileage, and vehicle miles traveled. Local governments can use this funding for a variety of road-related projects, from street repairs to traffic signal upgrades.
Traffic Safety and Environmental Initiatives
The remaining 10% of the gas tax revenue is dedicated to traffic safety and environmental initiatives. This includes funding for projects such as traffic signal synchronization, traffic calming measures, and the development of complete streets, which prioritize the safety and accessibility of all users, including pedestrians and cyclists.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The new California gas tax is designed with a strong focus on environmental sustainability. By encouraging the use of more efficient fuels and vehicles, the tax system helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. The revenue generated from the gas tax also supports the development of sustainable transportation options, such as electric vehicle infrastructure and public transit improvements.
Furthermore, the "Cap and Trade" program introduced as part of the gas tax reform provides a mechanism to limit greenhouse gas emissions and promote the adoption of cleaner technologies. This program not only generates revenue for transportation funding but also contributes to California's overall environmental goals.
Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Promotion
A notable aspect of the gas tax reform is its encouragement of zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) adoption. While ZEVs are subject to an annual fee, this fee is significantly lower than the fuel taxes paid by traditional vehicles. This difference in fees makes ZEVs more cost-effective over time, encouraging consumers to consider these environmentally friendly options.
Additionally, the revenue generated from the ZEV fee is directed towards transportation infrastructure, further supporting the development of a sustainable transportation system.
Community Engagement and Transparency
The implementation of the new California gas tax is accompanied by a strong emphasis on community engagement and transparency. The California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) and other state agencies involved in transportation planning and funding have made efforts to engage with the public, local governments, and stakeholders to ensure the effective and equitable distribution of funds.
Caltrans maintains a dedicated website, www.roadwork.ca.gov, where the public can track the progress of transportation projects funded by the gas tax. This website provides transparency and allows citizens to see how their tax dollars are being utilized for infrastructure improvements.
Public Outreach and Education
To ensure public understanding and support, the state has launched an extensive public outreach and education campaign. This campaign includes television, radio, and digital advertisements, as well as community workshops and events, to explain the new gas tax and its benefits to the state’s transportation infrastructure.
By actively engaging with the public, the state aims to build trust and ensure that citizens are aware of the purpose and impact of the gas tax.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Transportation Funding Solution
The new California gas tax represents a significant shift in the state’s approach to transportation funding. By implementing a multi-faceted tax and fee system, California is able to generate stable and sustainable revenue for its vast transportation needs. The reform addresses the challenges of maintaining and improving the state’s infrastructure while promoting environmental sustainability and fair contribution from all stakeholders.
As California continues to implement and refine the gas tax reform, the state is poised to set a new standard for transportation funding and infrastructure development, offering a model for other states and regions to follow.
FAQ
What is the purpose of the new California gas tax?
+
The new California gas tax aims to provide a stable and sustainable source of revenue for transportation projects, including road repairs, public transit improvements, and environmental initiatives.
How is the revenue from the gas tax distributed?
+
The revenue is distributed among various transportation-related projects, with a focus on road maintenance, public transit, local road projects, and traffic safety initiatives.
How does the gas tax encourage environmental sustainability?
+
The tax system encourages the use of more efficient fuels and vehicles, and the revenue generated supports the development of sustainable transportation options, such as electric vehicle infrastructure.
What is the “Cap and Trade” program, and how does it work?
+
The “Cap and Trade” program limits greenhouse gas emissions and allows companies to trade emission allowances. It generates revenue for transportation funding and contributes to California’s environmental goals.
How can I track the progress of transportation projects funded by the gas tax?
+
You can track the progress of these projects on the www.roadwork.ca.gov website, which provides transparency and updates on infrastructure improvements.