Montana Property Tax

Understanding property taxes is essential for homeowners and prospective buyers alike. This article delves into the intricacies of property taxation in the state of Montana, offering a comprehensive guide to help navigate the process effectively.
Montana Property Tax System: An Overview
Montana's property tax system is a vital component of the state's revenue stream, playing a significant role in funding essential public services. The system is designed to ensure that property owners contribute their fair share towards maintaining and improving local infrastructure, schools, and other community amenities.
The assessment and collection of property taxes in Montana are governed by a set of rules and regulations that aim to provide fairness and transparency. Here's a closer look at how the system operates and what it entails for property owners in the state.
Property Assessment Process
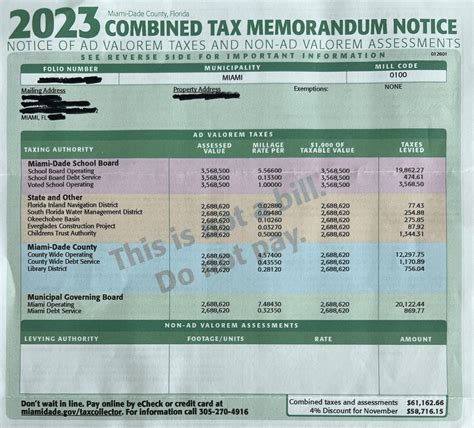
Property assessment is the first critical step in the taxation process. In Montana, this task is carried out by county assessors, who are responsible for determining the value of each property within their jurisdiction. The assessed value is then used as the basis for calculating the property tax liability.
Assessors consider various factors when determining a property's value, including its size, location, age, and recent sales data. They aim to assess properties at their full and true market value, which is the price for which a property would likely sell on the open market.
Once the assessment is complete, property owners receive a notice of assessment, which details the estimated value of their property. This notice serves as a crucial document for property owners, providing transparency and allowing them to review and, if necessary, appeal the assessed value.
| Assessment Timeline | Key Dates |
|---|---|
| Assessments Mailed | Late May - Early June |
| Appeal Deadline | 30 days after assessments are mailed |

Property Tax Rates and Calculation
Montana utilizes a mill levy system to determine property tax rates. A mill is a unit of measurement representing one-tenth of a cent, and mill levies are used to calculate the tax rate for each property. These mill levies are set by various taxing jurisdictions, including counties, cities, school districts, and special districts.
To calculate the property tax liability, the assessed value of the property is multiplied by the applicable mill levy rate. This results in the taxable value, which is then used to determine the actual tax amount owed. The formula can be simplified as follows:
Taxable Value = Assessed Value x Mill Levy Rate
The mill levy rates can vary significantly depending on the location of the property and the specific taxing jurisdictions it falls under. For instance, properties in rural areas may have lower mill levies compared to those in urban centers.
| Example Mill Levy Rates | Jurisdiction | Mill Levy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| County | X County | 50 mills |
| City | Y City | 40 mills |
| School District | Z School District | 70 mills |
Tax Rates and Property Types
It's important to note that Montana offers different tax rates for different property types. For instance, residential properties often have lower tax rates compared to commercial or industrial properties. This differentiation is designed to encourage homeownership and provide a more affordable living environment for residents.
Additionally, Montana provides certain tax exemptions and credits to eligible homeowners. These can include homestead credits, veteran's exemptions, and disabled homeowner credits, which can significantly reduce the property tax burden for qualifying individuals.
Payment Options and Deadlines
Property tax payments in Montana are typically due twice a year, with specific deadlines set by the county treasurer's office. Late payments may incur penalties and interest, so it's essential to stay informed about these deadlines and make timely payments.
Property owners have several payment options, including online payments, in-person payments at the treasurer's office, and even payment plans for those facing financial difficulties. It's advisable to explore these options and choose the one that best suits your circumstances.
| Payment Deadlines | Key Dates |
|---|---|
| First Half Payment | Early November |
| Second Half Payment | Early May |
The Impact of Property Taxes on Homeownership

Property taxes are an essential aspect of homeownership, and understanding their impact is crucial for anyone considering purchasing or owning property in Montana.
Factors Influencing Property Tax Bills
Several factors contribute to the amount of property tax an owner pays. Apart from the property's assessed value and the applicable mill levy rates, other factors come into play.
For instance, the age of the property can impact the tax bill. Older properties may have a lower assessed value due to depreciation, which can result in lower taxes. Conversely, newer properties may have higher assessed values, leading to higher tax liabilities.
Improvements or renovations to a property can also affect its assessed value. Adding a new room, updating the kitchen, or enhancing the landscaping can increase the property's value, which in turn increases the tax bill. It's important for homeowners to be aware of these potential changes and plan their finances accordingly.
Additionally, market conditions play a significant role. In a strong real estate market, property values tend to rise, leading to higher assessments and, subsequently, higher taxes. Conversely, in a weak market, property values may decrease, resulting in lower tax bills.
Managing Property Tax Burdens
For homeowners, managing property tax burdens is a crucial aspect of financial planning. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Appeal Assessments: If you believe your property's assessed value is too high, you can appeal the assessment. This process can help reduce your tax liability if the appeal is successful.
- Tax Exemptions and Credits: Explore the various tax exemptions and credits offered by the state. Qualifying for these can significantly reduce your tax burden.
- Payment Plans: If you're facing financial difficulties, consider setting up a payment plan with the county treasurer's office. This can help manage the tax burden over a more extended period.
- Budgeting and Planning: Incorporate property taxes into your annual budget. By setting aside funds specifically for taxes, you can ensure you have the necessary funds when payment deadlines approach.
Conclusion: Navigating Montana's Property Tax System
Montana's property tax system, while comprehensive, can be navigated effectively with the right knowledge and strategies. Understanding the assessment process, tax rates, and payment options is crucial for homeowners and prospective buyers alike.
By staying informed about the various factors that influence property taxes and employing effective management strategies, homeowners can ensure they're contributing their fair share while also protecting their financial interests. It's an essential aspect of responsible homeownership and a critical component of the state's revenue system.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often are properties assessed for tax purposes in Montana?
+
Properties in Montana are typically assessed once every two years. However, some counties may assess properties more frequently, especially in areas with rapidly changing property values.
Can I appeal my property assessment if I disagree with the value assigned to my property?
+
Absolutely! Property owners have the right to appeal their assessments if they believe the value assigned to their property is inaccurate. The process usually involves submitting an appeal to the county assessor’s office with supporting evidence, such as recent sales data or appraisals.
What happens if I miss the deadline to pay my property taxes?
+
Missing the deadline to pay your property taxes can result in penalties and interest charges. It’s important to stay informed about the payment deadlines and make timely payments to avoid additional costs.
Are there any tax exemptions or credits available for homeowners in Montana?
+
Yes, Montana offers a range of tax exemptions and credits to eligible homeowners. These can include homestead credits, veteran’s exemptions, and disabled homeowner credits. It’s advisable to explore these options and determine if you qualify.
Can I pay my property taxes online in Montana?
+
Most counties in Montana offer online payment options for property taxes. You can typically access these payment portals through the county treasurer’s website. However, it’s important to note that some counties may have different payment methods, so it’s best to check with your local treasurer’s office for specific instructions.