Miami Dade Taxes
Miami-Dade County, often referred to as the "Magic City," is a vibrant and bustling metropolis located in the southeastern corner of Florida. With its diverse culture, stunning beaches, and thriving economy, it has become a popular destination for residents and tourists alike. However, like any other county, Miami-Dade also has its fair share of taxes and regulations that impact its residents and businesses.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Miami-Dade Taxes, exploring the various tax structures, rates, and regulations that shape the financial landscape of this dynamic county. From property taxes to sales taxes and unique local taxes, we will provide an in-depth analysis to help you navigate the tax system effectively.
Understanding the Miami-Dade Tax System

The tax system in Miami-Dade County is a complex interplay of state, county, and municipal regulations. It is essential to understand the different levels of taxation to comprehend the overall tax burden in the region.
State Taxes
Florida, known for its favorable tax climate, has a straightforward state tax structure. The state imposes a 6% sales tax on most goods and services, which is a standard rate across the state. Additionally, there is a state corporate income tax of 5.5% for C-corporations and a 5.5% income tax on pass-through entities like S-corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships.
Florida also has a tangible personal property tax, which applies to certain business assets. This tax is typically calculated based on the asset's assessed value and the applicable tax rate, which can vary depending on the county.
County Taxes
Miami-Dade County, being one of the most populous counties in Florida, has its own set of taxes and regulations. The county imposes a county sales tax in addition to the state sales tax, bringing the total sales tax rate to 7% in Miami-Dade County. This additional county tax is used to fund various county services and infrastructure projects.
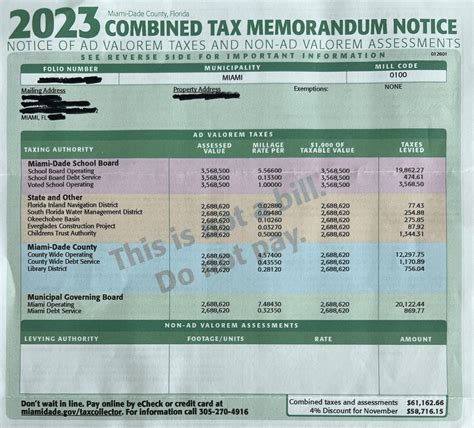
Furthermore, Miami-Dade County has a property tax system that plays a significant role in the county's finances. Property taxes are levied on both real estate and tangible personal property, and the rates can vary depending on the location and type of property.
| Tax Category | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Residential Property Tax | 1.1595% |
| Commercial Property Tax | 1.7456% |
| Tangible Personal Property Tax | 1.25% |

Municipal Taxes
Within Miami-Dade County, there are numerous cities and municipalities, each with their own set of taxes and regulations. For instance, the city of Miami imposes a municipal sales tax of 1%, bringing the total sales tax rate within the city to 8%. Other municipalities may have different tax structures, so it is essential to research the specific taxes applicable to your area.
Additionally, some municipalities have unique taxes, such as a tourist development tax or a resort tax, which are often imposed on short-term rentals and hotels to fund tourism-related projects and infrastructure.
Miami-Dade Property Taxes: A Closer Look

Property taxes are a significant component of the tax landscape in Miami-Dade County. Let’s explore the intricacies of property taxation in this vibrant county.
Assessment and Valuation
The property tax system in Miami-Dade County is based on the assessed value of the property. The Miami-Dade Property Appraiser’s Office is responsible for determining the assessed value of both real estate and tangible personal property.
The assessed value is typically a percentage of the property's just value, which is the estimated fair market value. The assessment percentage can vary depending on the property type and location. For instance, the assessment percentage for homestead properties (primary residences) is 10%, while for non-homestead properties, it is 25%.
Taxable Value and Exemptions
Once the assessed value is determined, it is multiplied by the applicable tax rate to arrive at the taxable value. This taxable value is then used to calculate the property tax liability.
Miami-Dade County offers several property tax exemptions to eligible homeowners. These exemptions can significantly reduce the taxable value of a property, resulting in lower property tax bills. Some common exemptions include:
- Homestead Exemption: This exemption is available to homeowners who use the property as their primary residence. It provides a $50,000 exemption on the assessed value of the property, reducing the taxable value.
- Senior Exemption: Residents aged 65 or older may be eligible for an additional $50,000 exemption if their household income is below a certain threshold.
- Military Exemption: Active-duty military personnel and veterans may qualify for exemptions based on their service status.
Calculating Property Taxes
To calculate the property tax liability, the taxable value is multiplied by the applicable tax rate. The tax rate is set by the county and can vary based on the property’s location and the services it receives.
For instance, let's consider a residential property in Miami-Dade County with an assessed value of $300,000. With a homestead exemption of $50,000, the taxable value would be $250,000. If the applicable tax rate is 1.1595%, the annual property tax liability would be approximately $2,898.75 ($250,000 x 1.1595%).
Sales and Use Taxes in Miami-Dade County
Sales and use taxes are a significant source of revenue for the county and play a crucial role in funding various public services and infrastructure projects.
Sales Tax Rates
As mentioned earlier, the total sales tax rate in Miami-Dade County is 7%, consisting of the 6% state sales tax and the 1% county sales tax. This rate applies to most goods and services sold within the county.
It is important to note that certain items, such as groceries, prescription drugs, and certain medical devices, are exempt from sales tax. Additionally, there are specific exemptions for businesses, such as the resale exemption, which allows businesses to purchase goods tax-free if they intend to resell them.
Use Tax
The use tax is a complementary tax to the sales tax and is applicable when goods are purchased from out-of-state vendors and brought into Miami-Dade County for use or consumption. The use tax rate is typically the same as the sales tax rate, ensuring that there is no tax advantage for purchasing goods outside the county.
Online Sales and Marketplace Facilitator Laws
With the rise of e-commerce, Miami-Dade County, like many other jurisdictions, has implemented laws to ensure that online sales are properly taxed. Marketplace facilitator laws require online marketplaces and third-party sellers to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the county.
This ensures that even online purchases are subject to the applicable sales tax, providing a level playing field for local businesses and helping to fund essential county services.
Unique Local Taxes and Fees
In addition to the standard taxes, Miami-Dade County has several unique local taxes and fees that residents and businesses should be aware of.
Resort Tax
The resort tax, also known as the bed tax, is a tax imposed on short-term rentals and hotels within Miami-Dade County. This tax is typically added to the rental rate and is used to fund tourism-related projects and infrastructure.
The resort tax rate can vary depending on the location and type of accommodation. For instance, in the city of Miami, the resort tax rate is 6%, while in other parts of the county, it may be lower.
Transportation Taxes
Miami-Dade County has a transportation tax to fund public transportation projects and infrastructure. This tax is often added to the cost of certain transportation-related items, such as vehicle registrations, fuel, and parking fees.
The transportation tax helps improve the county's transportation network, making it more efficient and accessible for residents and visitors.
Environmental Impact Fees
In an effort to promote environmental sustainability, Miami-Dade County has implemented environmental impact fees on certain activities and developments. These fees are designed to offset the environmental impact of new construction and encourage sustainable practices.
For instance, there may be fees associated with new construction projects to fund stormwater management, wetland preservation, and other environmental initiatives.
Tax Incentives and Programs

Miami-Dade County, like many other counties, offers various tax incentives and programs to attract businesses and promote economic development.
Enterprise Zones
Enterprise zones are designated areas within the county that offer tax incentives to businesses that locate or expand within these zones. These incentives can include reduced tax rates, tax credits, and other financial benefits.
The goal of enterprise zones is to stimulate economic growth in specific areas by making it more attractive for businesses to operate there.
Tax Exempt Bonds
Miami-Dade County, in partnership with the state, offers tax-exempt bonds to finance certain projects and initiatives. These bonds are often used for infrastructure development, such as building schools, hospitals, and other public facilities.
The tax-exempt status of these bonds makes them attractive to investors, as the interest earned is typically exempt from federal and state income taxes.
Economic Development Incentives
The county actively promotes economic development by offering a range of incentives to businesses. These incentives can include property tax abatements, sales tax exemptions, and job creation grants.
By providing these incentives, Miami-Dade County aims to attract new businesses, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth throughout the region.
Tax Compliance and Resources
Navigating the tax system can be complex, and it is essential to stay compliant with the various tax regulations. Miami-Dade County provides several resources to help taxpayers understand their obligations and ensure compliance.
Taxpayer Assistance
The Miami-Dade County Tax Collector’s Office offers assistance to taxpayers, providing information on tax rates, due dates, and payment options. They also offer online tools and resources to help taxpayers calculate their tax liabilities and understand the tax system.
Tax Forms and Publications
The county provides a wide range of tax forms and publications to guide taxpayers through the process. These resources cover various tax types, including property taxes, sales taxes, and business taxes. They are available online and at local government offices.
Tax Appeals and Disputes
If you have a disagreement with your tax assessment or believe there has been an error, Miami-Dade County has a process in place for tax appeals. The Value Adjustment Board (VAB) is an independent body that hears and decides on tax disputes.
You can file an appeal with the VAB if you believe your property assessment is inaccurate, or if you have concerns about your tax liability. The VAB will review your case and make a decision based on the evidence presented.
Future Outlook and Tax Policy Changes
The tax landscape in Miami-Dade County is subject to change, and staying informed about potential policy shifts is crucial for residents and businesses.
Proposed Tax Reforms
There are ongoing discussions and proposals for tax reforms within the county. These reforms aim to simplify the tax system, reduce tax burdens, and promote economic growth.
One proposed reform is to reduce the county sales tax to make Miami-Dade County more competitive with neighboring counties. This reduction could potentially boost economic activity and attract more businesses and tourists.
Impact of Economic Trends
The economic health of the county plays a significant role in tax policy. During periods of economic growth, the county may have the flexibility to offer tax incentives and reduce tax burdens. Conversely, during economic downturns, tax rates may need to be adjusted to maintain essential services.
Miami-Dade County has a diverse economy, with a strong focus on tourism, real estate, and international trade. The county's ability to adapt to economic trends and implement strategic tax policies will be crucial for its long-term prosperity.
Conclusion: Navigating Miami-Dade Taxes
Understanding the tax system in Miami-Dade County is essential for both residents and businesses. With a range of taxes, from property taxes to sales taxes and unique local taxes, it is crucial to stay informed and compliant.
By exploring the various tax structures, rates, and incentives, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and effectively manage their tax obligations. Miami-Dade County offers a vibrant and dynamic environment, and by navigating the tax system wisely, residents and businesses can thrive in this magical city.
How often do property taxes change in Miami-Dade County?
+Property taxes in Miami-Dade County are assessed annually. The Property Appraiser’s Office determines the assessed value of properties each year, and this value is used to calculate the property tax liability. Changes in the assessed value can occur due to various factors, including market conditions and improvements made to the property.
Are there any tax breaks for renewable energy installations in Miami-Dade County?
+Yes, Miami-Dade County offers a property tax exemption for renewable energy installations. This exemption applies to solar energy systems, wind energy systems, and other eligible renewable energy sources. By installing these systems, homeowners can reduce their property tax liability, making it a more attractive option for environmentally conscious residents.
What is the deadline for filing tax returns in Miami-Dade County?
+The deadline for filing tax returns in Miami-Dade County aligns with the state of Florida’s tax filing deadline. For most individuals and businesses, the deadline is typically April 15th of each year. However, it is essential to check with the Miami-Dade County Tax Collector’s Office for any specific deadlines or extensions that may apply.



