Maine State Taxes

Maine, known for its picturesque landscapes and vibrant communities, has a unique approach to state taxes that impacts its residents and businesses alike. Understanding the intricacies of Maine's tax system is crucial for individuals and companies looking to navigate the state's financial landscape. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the specifics of Maine state taxes, providing an in-depth analysis of its various components and their implications.
Understanding Maine’s Tax Structure

Maine’s tax system is designed to generate revenue for the state’s operations and services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and more. It consists of a combination of income, sales, and property taxes, each playing a significant role in funding the state’s initiatives.
Income Tax
Income tax is a crucial component of Maine’s tax revenue. The state imposes a progressive tax rate, meaning the tax rate increases as income rises. This progressive structure ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger proportion of their income to the state. For the tax year 2023, Maine’s income tax rates range from 5.8% to 7.15% across seven tax brackets. These brackets are adjusted annually to account for inflation and ensure fairness.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 - $24,000 (single filers) / $36,000 (joint filers) | 5.8% |
| $24,001 - $48,000 (single) / $36,001 - $72,000 (joint) | 6.5% |
| $48,001 - $84,000 (single) / $72,001 - $126,000 (joint) | 6.75% |
| $84,001 - $132,000 (single) / $126,001 - $180,000 (joint) | 6.85% |
| $132,001 - $180,000 (single) / $180,001 - $240,000 (joint) | 6.95% |
| $180,001 - $240,000 (single) / $240,001 - $360,000 (joint) | 7.05% |
| $240,001+ (single) / $360,001+ (joint) | 7.15% |
It's important to note that Maine offers several tax credits and deductions to reduce the tax burden on residents. These include the Property Tax Fairness Credit, which provides relief for homeowners, and the Earned Income Tax Credit, benefiting low- to moderate-income earners. Additionally, Maine allows itemized deductions for certain expenses, such as medical costs and charitable contributions.
Sales and Use Tax
Maine imposes a sales and use tax on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. The state’s general sales tax rate is 5.5%, with additional local option taxes ranging from 0% to 1.5%, depending on the municipality. This means that the total sales tax rate can vary across different regions of Maine.
Maine's sales tax applies to a wide range of goods, including clothing, electronics, and groceries. However, there are some notable exceptions and exemptions. For instance, most non-prepared food items are exempt from sales tax, as are prescription drugs and medical devices. Additionally, Maine offers tax holidays, during which certain items, such as school supplies and clothing, are exempt from sales tax for a specified period.
In addition to the sales tax, Maine also levies a use tax on items purchased outside the state but used or consumed within Maine. This ensures that residents and businesses pay their fair share of taxes, regardless of where they make their purchases.
Property Tax
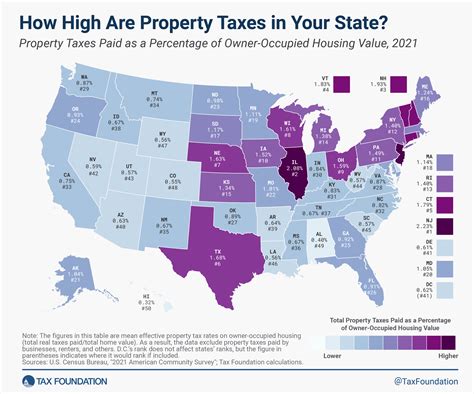
Property tax is a significant source of revenue for Maine’s local governments, including cities, towns, and school districts. The property tax rate varies across the state, as it is set by each individual municipality. On average, Maine’s property tax rate is around 1.48%, but it can range from 0.7% to over 2% in some areas.
Maine's property tax system is based on the assessed value of real estate, which is determined by the local tax assessor. The assessed value is then multiplied by the applicable tax rate to calculate the annual property tax bill. It's important for property owners to stay informed about their assessment and any changes to the tax rate, as these can impact their financial obligations.
Tax Incentives and Programs

Maine recognizes the importance of encouraging economic growth and supporting its businesses. As such, the state offers various tax incentives and programs to attract and retain businesses, create jobs, and stimulate the economy.
Business Tax Incentives
Maine provides a range of tax incentives to businesses, depending on their industry, location, and employment goals. These incentives can take the form of tax credits, deductions, or even full or partial exemptions from certain taxes. For example, the Research and Development Tax Credit offers a credit for businesses conducting research and development activities within Maine.
Additionally, Maine's New Markets Tax Credit Program provides tax credits to investors who contribute to the development of economically distressed areas within the state. This program aims to encourage investment in underserved communities, promoting economic growth and job creation.
Tax Abatement Programs
Maine also offers tax abatement programs, which provide a reduction in property taxes for qualifying businesses. These programs are typically targeted at specific industries or development projects, aiming to encourage economic development and job creation. For instance, the Maine Forest Products Tax Abatement Program provides a reduced property tax rate for forest product manufacturers, helping to support this important industry in the state.
Startup and Small Business Support
Maine understands the challenges faced by startups and small businesses, and as such, provides various support programs. These initiatives aim to reduce the tax burden on small businesses, offering tax credits and deductions for research and development, job creation, and more. Additionally, Maine’s Small Business Tax Fairness Act ensures that small businesses are not disproportionately impacted by tax increases.
Tax Filing and Compliance
Understanding the tax filing process and compliance requirements is crucial for individuals and businesses operating in Maine. The state provides resources and guidance to ensure taxpayers can meet their obligations accurately and efficiently.
Individual Tax Filing
Maine residents must file their state income tax returns annually, typically by April 15th. The state offers both paper and electronic filing options, with the latter being the preferred method due to its efficiency and accuracy. The Maine Revenue Services website provides detailed instructions and forms for individual tax filing, ensuring residents can navigate the process seamlessly.
It's important for individuals to keep accurate records of their income, deductions, and credits to ensure they can complete their tax returns correctly. Maine offers e-file options for individuals, making the filing process more convenient and reducing the risk of errors.
Business Tax Filing
Businesses operating in Maine are subject to various tax obligations, including income tax, sales and use tax, and potentially other taxes depending on their industry and activities. The specific filing requirements and deadlines vary based on the type of business and its tax obligations.
Maine Revenue Services provides comprehensive guidance and resources for businesses to ensure they understand their tax responsibilities. This includes instructions for registering for tax accounts, filing tax returns, and making tax payments. The state also offers online tools and resources to help businesses estimate their tax liabilities and manage their tax obligations effectively.
Future Implications and Tax Policy Changes
Maine’s tax policies are subject to ongoing evaluation and potential changes, driven by economic conditions, legislative priorities, and the state’s fiscal needs. Understanding the potential implications of these changes is crucial for individuals and businesses planning their financial strategies.
Proposed Tax Reforms
In recent years, there have been discussions and proposals for tax reforms in Maine. These include suggestions to simplify the tax code, reduce tax rates, and provide additional tax relief to certain sectors or individuals. For instance, there have been proposals to eliminate or reduce the state’s income tax for certain low-income earners, as well as to streamline the sales tax system.
These proposed reforms aim to make Maine's tax system more competitive, attractive to businesses, and fairer for residents. However, it's important to note that tax policy is a complex and often politically charged topic, and proposed reforms may face challenges and modifications before implementation.
Economic Impact of Tax Changes
Changes to Maine’s tax policies can have significant economic implications. For instance, reducing tax rates can stimulate economic growth by providing individuals and businesses with more disposable income to spend or invest. On the other hand, increasing taxes can generate additional revenue for the state, which can be used to fund important services and initiatives.
It's crucial for Maine's policymakers to carefully consider the potential impacts of tax changes on different sectors and income levels. Balancing the need for revenue with the goal of fostering economic growth and maintaining a competitive business environment is a delicate task.
What are the tax filing deadlines in Maine?
+
The deadline for individual income tax returns in Maine is typically April 15th. However, if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. For businesses, the filing deadlines vary depending on the type of business and tax obligations. It’s important to consult the Maine Revenue Services website or seek professional advice for specific deadlines.
Are there any tax incentives for renewable energy projects in Maine?
+
Yes, Maine offers several tax incentives for renewable energy projects. The state provides tax credits for investments in renewable energy equipment, such as solar panels and wind turbines. Additionally, there are tax abatements available for renewable energy development projects. These incentives aim to encourage the adoption of clean energy technologies and support Maine’s environmental goals.
How does Maine’s sales tax apply to online purchases?
+
Maine imposes a sales tax on online purchases, including those made from out-of-state retailers. This is known as the “Amazon Law,” which requires online retailers with no physical presence in Maine to collect and remit sales tax on purchases shipped to the state. This ensures that online shoppers pay their fair share of sales tax, just as they would for in-store purchases.