Ma Income Tax Rate

The Massachusetts income tax rate is an important factor for residents and businesses to consider when managing their financial affairs. Understanding the state's tax system is crucial for effective tax planning and ensuring compliance with the law. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the Ma Income Tax Rate, covering its structure, rates, deductions, and the impact it has on individuals and businesses within the state.
Understanding the Ma Income Tax Rate

The Commonwealth of Massachusetts imposes an income tax on various sources of income earned by individuals, trusts, estates, and businesses operating within the state. This tax system plays a significant role in funding public services, infrastructure, and state programs. The income tax rate in Massachusetts is progressive, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates, promoting fairness and contributing to a robust economy.
Income Tax Rates for Individuals
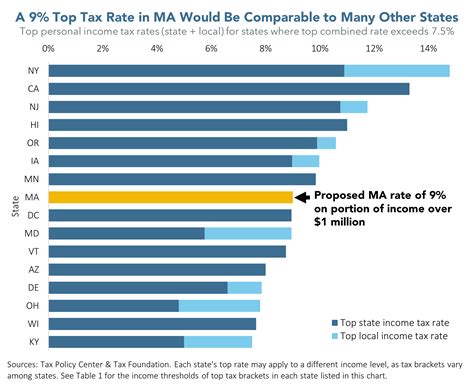
For individuals filing their taxes in Massachusetts, the income tax rate varies based on their taxable income. As of the latest tax year, the state offers a five-bracket progressive tax system with the following rates:
| Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|
| 5.05% | $0 - $9,999 |
| 5.2% | $10,000 - $24,999 |
| 5.95% | $25,000 - $49,999 |
| 7.05% | $50,000 - $150,000 |
| 8.95% | $150,000 and above |

These rates apply to both single and joint filers, ensuring that taxpayers with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion to the state's revenue.
Income Tax for Businesses
Massachusetts also imposes an income tax on businesses operating within its borders. The tax rates for businesses vary depending on the entity’s legal structure and the nature of its operations. Here’s a breakdown of the income tax rates for different business entities:
- Corporations: Massachusetts imposes a flat tax rate of 8.8% on corporate income. This rate applies to both resident and non-resident corporations conducting business in the state.
- Limited Liability Companies (LLCs): LLCs are taxed as pass-through entities, meaning that the income is passed through to the owners or members, who then pay individual income taxes on their share of the profits. The income tax rates for LLC members are the same as those for individuals, as outlined above.
- Partnerships and S Corporations: Similar to LLCs, partnerships and S corporations are also pass-through entities. The income from these entities is distributed to the partners or shareholders, who then pay individual income taxes on their respective shares.
Deductions and Exemptions
Massachusetts offers various deductions and exemptions to reduce the tax burden on individuals and businesses. These provisions help promote financial stability and provide relief to taxpayers. Here are some notable deductions and exemptions available in Massachusetts:
- Personal Exemption: Individuals can claim a personal exemption of $4,350 for themselves and an additional exemption for each dependent. This exemption reduces the taxable income, providing a financial benefit to taxpayers with dependents.
- Standard Deduction: Massachusetts allows taxpayers to claim a standard deduction, which reduces their taxable income further. The standard deduction amount varies based on the taxpayer's filing status. For the current tax year, the standard deduction amounts are as follows:
- Single: $4,350
- Married Filing Jointly: $8,700
- Head of Household: $6,525
- Itemized Deductions: Taxpayers can opt for itemized deductions instead of the standard deduction if it results in a more substantial reduction of their taxable income. Itemized deductions include expenses such as medical costs, charitable contributions, state and local taxes, mortgage interest, and certain investment expenses.
- Business Deductions: Businesses operating in Massachusetts can take advantage of various deductions to lower their taxable income. These deductions include business expenses, depreciation, and certain employee benefit costs. Additionally, businesses may be eligible for tax credits and incentives to promote economic development and job creation.
Impact of Ma Income Tax Rate
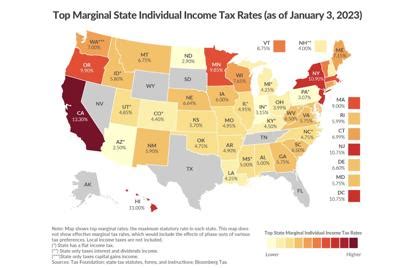
The Ma Income Tax Rate has a significant impact on the financial landscape of the state. It influences the cost of doing business, personal finances, and overall economic growth. Here’s a closer look at the impact of the income tax rate:
Economic Growth and Revenue
The progressive income tax system in Massachusetts aims to promote economic growth by encouraging investment and job creation. By taxing higher incomes at higher rates, the state generates substantial revenue to support public services, infrastructure development, and social programs. This revenue is vital for maintaining a robust economy and providing essential services to residents.
Tax Burden on Individuals
For individuals, the Ma Income Tax Rate can significantly impact their financial planning and disposable income. The progressive nature of the tax system means that those with higher incomes pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes. While this promotes fairness, it also means that individuals with lower incomes may have a greater financial burden relative to their income level.
Business Competitiveness
The income tax rate for businesses is a crucial factor in determining the competitiveness of Massachusetts as a business destination. The flat tax rate of 8.8% for corporations is higher than some neighboring states, which may influence businesses’ decisions to locate or expand within the state. However, Massachusetts offers various tax incentives and credits to attract and retain businesses, making it an attractive option for certain industries.
Tax Planning and Compliance
Understanding the Ma Income Tax Rate is essential for effective tax planning and compliance. Taxpayers must carefully calculate their taxable income, deductions, and exemptions to ensure accurate tax filings. Failure to comply with tax regulations can result in penalties and legal consequences. Consulting with tax professionals or utilizing tax preparation software can help individuals and businesses navigate the complexities of the tax system.
Conclusion
The Ma Income Tax Rate plays a critical role in shaping the financial landscape of Massachusetts. Its progressive structure ensures a fair and equitable tax system, while also generating revenue to support the state’s infrastructure and services. Individuals and businesses must stay informed about the tax rates, deductions, and exemptions to optimize their financial strategies and remain compliant with state tax laws. By understanding the Ma Income Tax Rate, taxpayers can make informed decisions and contribute to the economic vitality of the Commonwealth.
What is the income tax rate for individuals in Massachusetts for the current tax year?
+For the current tax year, the income tax rates for individuals in Massachusetts range from 5.05% to 8.95%. The rates are progressive, with higher income levels taxed at higher rates.
Are there any deductions or exemptions available for individuals filing their taxes in Massachusetts?
+Yes, Massachusetts offers various deductions and exemptions to reduce the tax burden on individuals. These include personal exemptions, standard deductions, and itemized deductions for eligible expenses.
How does the Ma Income Tax Rate impact businesses operating in the state?
+The Ma Income Tax Rate for businesses includes a flat tax rate of 8.8% for corporations. This rate, along with other business-specific deductions and incentives, influences the competitiveness of Massachusetts as a business destination.