Is The Ein And Tax Id The Same
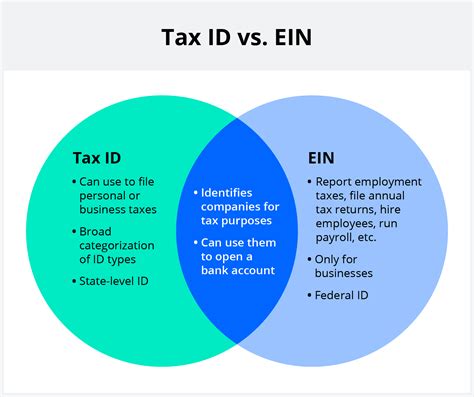
The EIN (Employer Identification Number) and the Tax ID (Tax Identification Number) are often used interchangeably as they serve similar purposes, but there are some subtle differences and nuances to their usage and context. Let's delve into this topic to provide a comprehensive understanding.
Understanding EIN and Tax ID

An EIN, also known as a Federal Employer Identification Number, is a unique nine-digit number assigned to businesses by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. It serves as a crucial identifier for businesses, much like a Social Security Number for individuals. EINs are primarily used for tax purposes, such as filing business tax returns, hiring employees, and opening business bank accounts.
A Tax ID, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses not only the EIN but also other identification numbers used for tax purposes. These include Individual Taxpayer Identification Numbers (ITINs) for individuals who are not eligible for a Social Security Number, and Employer Identification Numbers (EINs) for businesses.
Key Differences and Usage
While the terms EIN and Tax ID are often used synonymously, they differ in their scope and application.
- Scope: EINs are specific to businesses and are used for business-related tax purposes. Tax IDs, however, cover a wider range of tax-related identification numbers, including those for individuals.
- Application: EINs are primarily used for business operations, such as payroll management, business licensing, and reporting business income and expenses. Tax IDs, including ITINs, are used by individuals for tax filing purposes, especially for those without a Social Security Number.
Obtaining an EIN and Tax ID
Obtaining an EIN is a straightforward process for businesses. The IRS provides an online EIN application form, which can be completed and submitted electronically. The process is typically quick, and the EIN is issued immediately upon successful submission.
For individuals requiring a Tax ID, the process varies depending on the specific type of Tax ID needed. ITINs, for instance, are obtained through the IRS using Form W-7. The process involves providing valid identification documents and establishing a valid tax filing purpose. ITINs are particularly useful for foreign nationals, spouses of U.S. citizens, and individuals who are not eligible for a Social Security Number but need to file U.S. tax returns.
Legal and Tax Implications
The distinction between an EIN and a Tax ID is more than just a matter of terminology. It has legal and tax implications, especially when it comes to business operations and tax compliance.
- Business Registration: EINs are essential for registering a business with the IRS and other government agencies. They are used to identify the business for tax purposes and to report business income and expenses accurately.
- Employment Taxes: When a business hires employees, it is required to obtain an EIN. This EIN is used to report and pay employment taxes, including Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) taxes, Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) taxes, and income tax withholdings.
- Business Tax Returns: EINs are necessary for filing business tax returns, such as Form 1120 (for C corporations), Form 1065 (for partnerships), and Form 1040 Schedule C (for sole proprietorships). These returns are used to report business income, expenses, and profits, and to calculate the business's tax liability.
On the other hand, Tax IDs, especially ITINs, are crucial for individuals who are not eligible for a Social Security Number but need to file U.S. tax returns. This includes foreign nationals, non-resident aliens, and individuals with certain types of visas. ITINs allow these individuals to comply with U.S. tax laws and report their income and deductions accurately.
| Type | Scope | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| EIN | Business-specific | Business tax returns, employment taxes, business registration |
| Tax ID | Includes ITINs for individuals | Tax filing for individuals without SSN, business tax purposes |

Conclusion

In conclusion, while the terms EIN and Tax ID are closely related and often used synonymously, they serve distinct purposes. EINs are specific to businesses and are used for various business-related tax functions, while Tax IDs encompass a broader range of identification numbers, including those for individuals. Understanding the differences and the appropriate usage of these terms is essential for businesses and individuals to ensure tax compliance and efficient tax management.
FAQ
Can a business have multiple EINs or Tax IDs?
+
No, a business is typically assigned only one EIN. However, in certain cases, such as for specific tax purposes or when a business undergoes structural changes, additional EINs may be required. Similarly, individuals should only have one Tax ID (ITIN or SSN) for tax purposes.
Are EINs and Tax IDs the same as Social Security Numbers (SSNs)?
+
No, they are not the same. SSNs are unique identification numbers assigned to individuals, while EINs and Tax IDs are used for business and tax purposes. SSNs are primarily used for personal identification and for tracking an individual’s earnings and tax contributions over their lifetime.
How long does it take to obtain an EIN or Tax ID?
+
Obtaining an EIN is typically a quick process, and the number is issued immediately upon successful completion of the online application. For Tax IDs, including ITINs, the process can take several weeks or months, depending on the volume of applications and the completeness of the documentation provided.