Pa State Tax Form

The Pennsylvania state tax form, known as the PA-40, is an essential document for residents and businesses operating within the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania to fulfill their tax obligations. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the PA-40 form, offering insights into its purpose, structure, and the key considerations for accurate and timely filing. Let's delve into the intricacies of Pennsylvania's tax landscape and explore the essential components of this crucial form.
Understanding the PA-40 Form: A Comprehensive Guide
The PA-40 form is the primary vehicle through which Pennsylvania residents and businesses report their income, deductions, and credits to the Pennsylvania Department of Revenue. It serves as a critical tool for the state to assess and collect taxes, ensuring a fair and efficient revenue collection process. This form encompasses various aspects of an individual’s or business’s financial activities, making it a complex yet essential document for tax compliance.
Form Structure and Key Components
The PA-40 form is meticulously designed to guide taxpayers through the reporting process, with specific sections dedicated to different aspects of taxable income. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
- Personal Information: This section requires taxpayers to provide basic details such as name, address, Social Security Number (SSN), and contact information. Accurate and up-to-date personal information is crucial for proper tax assessment and communication.
- Income Reporting: The heart of the form lies in the income reporting section. Taxpayers must disclose all sources of income, including wages, salaries, tips, business profits, interest, dividends, and any other taxable income. Each income source has its own set of rules and regulations, making this section critical for accurate tax calculations.
- Deductions and Credits: The PA-40 form allows taxpayers to claim deductions and credits, which can reduce their taxable income. Common deductions include mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and certain business expenses. Additionally, Pennsylvania offers various credits, such as the Property Tax/Rent Rebate Program and the School Tax Relief (STAR) program, which can further lower tax liabilities.
- Tax Calculation and Payment: Once all income, deductions, and credits are reported, the form guides taxpayers through the calculation of their total tax liability. This section also includes instructions for making payments, whether through electronic methods or traditional mailing options.
- Signatures and Verification: The final step in the PA-40 form is the signature section. Taxpayers must sign and date the form, verifying the accuracy and completeness of the information provided. This step is crucial as it holds taxpayers accountable for the information submitted.
Key Considerations for Accurate Filing
Filing the PA-40 form accurately is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with Pennsylvania tax laws. Here are some key considerations:
- Keep Accurate Records: Maintain detailed records of income, expenses, and deductions throughout the year. This practice simplifies the filing process and ensures that all relevant information is readily available.
- Understand Tax Laws: Pennsylvania's tax laws can be complex, and staying informed is essential. The Pennsylvania Department of Revenue provides extensive resources, including publications and online guides, to help taxpayers navigate the intricacies of state tax laws.
- Utilize Tax Preparation Software: For those unfamiliar with tax terminology or complex calculations, tax preparation software can be a valuable tool. These programs guide users through the filing process, ensuring accuracy and providing additional support for complex tax situations.
- Seek Professional Help: If your tax situation is complex or if you have questions about specific deductions or credits, consider seeking the advice of a tax professional. Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) and Enrolled Agents (EAs) can provide expert guidance and ensure compliance with Pennsylvania's tax regulations.
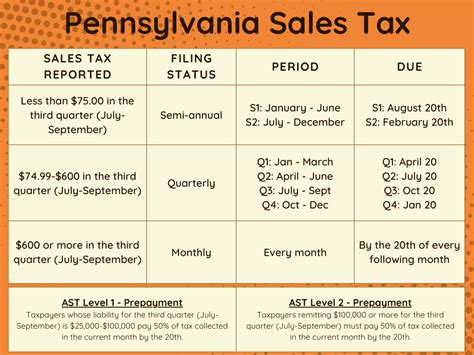
| Pennsylvania Tax Facts | Information |
|---|---|
| State Tax Rate | 3.07% |
| Tax Due Date | April 15th (or the following business day if it falls on a weekend or holiday) |
| Electronic Filing Options | Available through the PA e-file system |

Filing Deadlines and Extensions
The PA-40 form typically has an annual filing deadline of April 15th, coinciding with the federal tax deadline. However, it’s important to note that this deadline may be extended in certain circumstances, such as natural disasters or other emergencies. The Pennsylvania Department of Revenue provides guidance on extensions and late filing procedures, ensuring taxpayers are aware of their options.
Electronic Filing: A Modern Approach
Pennsylvania has embraced modern technology by offering electronic filing options through the PA e-file system. This system provides a secure and efficient way to file tax returns, with real-time status updates and the ability to track refunds. Electronic filing is not only convenient but also reduces the risk of errors, making it an attractive option for many taxpayers.
Future Implications and Tax Planning
Understanding the PA-40 form and Pennsylvania’s tax landscape is not just about compliance; it’s also about strategic tax planning. By comprehending the deductions, credits, and tax rates, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their tax positions. Additionally, staying abreast of changes in tax laws and regulations is crucial for long-term financial planning.
Conclusion: A Step Towards Tax Compliance
The PA-40 form is a vital tool for Pennsylvania residents and businesses to meet their tax obligations. By understanding its structure, key components, and filing requirements, taxpayers can navigate the process with confidence. Accurate and timely filing not only ensures compliance but also contributes to the overall economic health of the Commonwealth. As Pennsylvania continues to evolve its tax policies, staying informed and adapting to changes will be key to successful tax management.
What is the penalty for late filing of the PA-40 form?
+Late filing of the PA-40 form may result in penalties, which can include a failure-to-file penalty and interest on the unpaid tax. The specific penalty amounts and interest rates are determined by the Pennsylvania Department of Revenue and can vary based on the circumstances.
Are there any online resources available to assist with the PA-40 form?
+Yes, the Pennsylvania Department of Revenue offers an extensive online resource library, including publications, forms, and instructional guides. These resources provide step-by-step guidance on completing the PA-40 form and can be accessed through the official website.
Can I file an amended PA-40 form if I discover an error?
+Yes, if you discover an error on your previously filed PA-40 form, you can file an amended return. The process involves completing a new PA-40 form, clearly indicating that it is an amended return, and submitting it along with any supporting documentation.