Iowa State Tax
Iowa's tax system plays a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of the state, impacting both residents and businesses. With a focus on fairness and economic growth, Iowa has implemented various tax policies that contribute to its fiscal health. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of Iowa's state tax system, shedding light on its structure, key components, and the implications it has for individuals and businesses alike.
Understanding Iowa’s State Tax Structure
Iowa’s tax system is designed to generate revenue for state operations while maintaining a competitive business environment. The state collects taxes through a variety of sources, including income taxes, sales taxes, property taxes, and various excise taxes. Each of these tax categories serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall fiscal health of the state.
Income Tax: A Progressive Approach
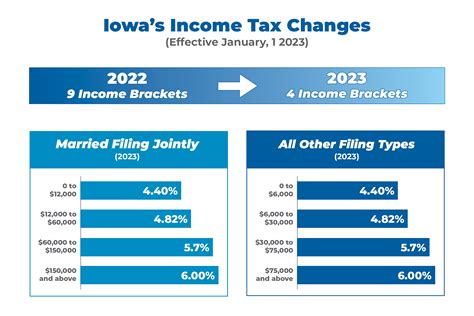
Iowa’s income tax system follows a progressive structure, meaning that higher income earners pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes. This approach aims to ensure that the tax burden is distributed fairly across different income levels. The state’s income tax rates are divided into tax brackets, with the current rates ranging from 0.36% to 8.98% for individuals and 0.36% to 12% for corporations.
For instance, let's consider a hypothetical case of two individuals with different annual incomes. Person A earns $30,000, while Person B earns $100,000. Person A would fall into the lowest tax bracket, paying an effective tax rate of approximately 3.6%, resulting in an income tax liability of $1,080. On the other hand, Person B, with a higher income, would be subject to a higher tax rate, let's say 6.9%, resulting in an income tax liability of $6,900.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $2,075 | 0.36% |
| $2,076 - $3,625 | 0.96% |
| $3,626 - $6,550 | 3.6% |
| $6,551 - $11,450 | 4.56% |
| $11,451 and above | 8.98% |

This progressive income tax structure ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger share, promoting economic fairness and providing resources for essential state services.
Sales and Use Tax: A Broad-Based Revenue Source
Iowa’s sales and use tax is another significant revenue generator for the state. The sales tax is applied to the retail sale of most goods and some services within the state, with a standard rate of 6%. However, certain categories, such as food and drugs, are exempt from sales tax, providing some relief to consumers.
In addition to the standard rate, Iowa also imposes a 1% sales tax for local purposes, known as the Local Option Sales Tax (LOST). This additional tax is utilized by counties and cities to fund specific projects or services, providing a flexible revenue stream for local governments.
For example, a consumer purchasing a new laptop in Iowa would pay a sales tax of 6% on the purchase price. If the laptop costs $1,000, the sales tax would amount to $60, making the total cost $1,060. This revenue contributes to the state's overall tax income and supports various state initiatives.
Property Tax: Assessing Real Estate and Personal Property
Property tax is a significant source of revenue for local governments in Iowa, funding essential services such as schools, roads, and public safety. The property tax system assesses taxes on both real estate and personal property, with rates varying across counties and municipalities.
The assessment process involves evaluating the fair market value of properties, which is then multiplied by the applicable tax rate. These rates are set by local authorities and can differ significantly between regions. The resulting tax liability is then distributed among property owners based on the assessed value of their properties.
To illustrate, consider a homeowner in Iowa with a property valued at $200,000. If the applicable tax rate is 2%, the annual property tax liability would amount to $4,000. This tax revenue is then utilized by the local government to fund various community services and infrastructure projects.
Tax Incentives and Credits: Promoting Economic Development

Iowa offers a range of tax incentives and credits aimed at attracting businesses and stimulating economic growth. These incentives provide relief to businesses, making Iowa an attractive location for investment and job creation.
High-Quality Jobs Program
The High-Quality Jobs Program is a tax credit initiative designed to encourage businesses to create high-paying jobs in Iowa. Businesses that meet the program’s criteria, such as creating a specified number of new jobs with an average annual wage above a certain threshold, can qualify for tax credits.
For instance, a manufacturing company that establishes a new facility in Iowa and creates 50 new jobs with an average annual wage of $60,000 may be eligible for tax credits. These credits can significantly reduce the company's tax liability, providing an incentive for job creation and investment.
Research Activities Credit
Iowa’s Research Activities Credit aims to foster innovation and research within the state. Businesses engaged in qualified research activities can claim a tax credit equal to a percentage of their qualified research expenses. This credit encourages businesses to invest in research and development, contributing to Iowa’s knowledge-based economy.
A software development company based in Iowa, for example, may qualify for the Research Activities Credit if it conducts significant research and development activities. By claiming this credit, the company can reduce its tax liability, making Iowa an attractive hub for technology and innovation.
Iowa’s Tax Climate and Economic Impact
Iowa’s tax system has a profound impact on the state’s economic climate and business environment. The state’s approach to taxation aims to strike a balance between generating revenue and maintaining a competitive business landscape.
Attracting Businesses and Creating Jobs
Iowa’s tax incentives and competitive tax rates have proven successful in attracting businesses and creating jobs. The state’s focus on economic development and support for businesses has led to a thriving business climate, with companies choosing Iowa as a hub for their operations.
For instance, a multinational corporation considering expansion may be drawn to Iowa due to its attractive tax incentives and a supportive business environment. The state's tax structure, coupled with its skilled workforce and strategic location, can make Iowa an ideal choice for businesses seeking growth and long-term success.
Funding Essential Services and Infrastructure
The revenue generated through Iowa’s tax system is vital for funding essential services and infrastructure projects. From education and healthcare to transportation and public safety, the tax income supports the state’s commitment to providing high-quality services to its residents.
For example, the sales tax revenue collected from local businesses contributes to the funding of schools, ensuring that Iowa's youth have access to quality education. Similarly, property tax revenue supports the maintenance and development of critical infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, benefiting both residents and businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Iowa’s tax system compare to other states in terms of competitiveness?
+
Iowa’s tax system is generally considered competitive when compared to other states. Its progressive income tax structure, combined with targeted tax incentives, creates a favorable environment for businesses and individuals. However, the competitiveness can vary based on specific industries and the unique needs of businesses.
Are there any tax breaks or exemptions for senior citizens in Iowa?
+
Yes, Iowa offers various tax breaks and exemptions for senior citizens. These include property tax credits, income tax deductions, and sales tax exemptions for certain purchases. These provisions aim to provide financial relief to older adults and ensure their economic well-being.
How does Iowa’s sales tax rate compare to other states?
+
Iowa’s standard sales tax rate of 6% is on the lower end of the spectrum when compared to other states. Some states have higher sales tax rates, while others have lower rates or additional local taxes. Iowa’s sales tax structure aims to balance revenue generation with competitiveness.
What are the requirements for businesses to qualify for Iowa’s tax incentives?
+
The requirements for businesses to qualify for Iowa’s tax incentives vary depending on the specific program. Generally, businesses must meet criteria related to job creation, investment, or research activities. These criteria are designed to encourage economic growth and innovation.