Illinois Vehicle Sales Tax
The Illinois vehicle sales tax is an essential component of the state's revenue system, playing a crucial role in funding various public services and infrastructure projects. This tax is levied on the purchase or lease of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and even certain types of recreational vehicles. Understanding the intricacies of this tax is vital for both consumers and businesses operating within the state, as it directly impacts their financial obligations and planning.
Understanding the Illinois Vehicle Sales Tax

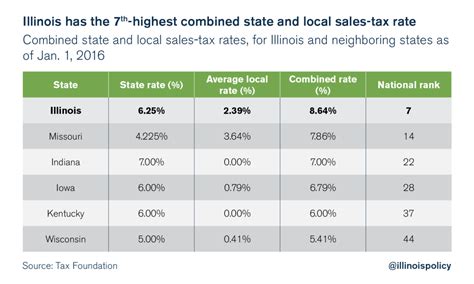
The Illinois vehicle sales tax is a percentage-based tax, meaning the amount owed is calculated as a proportion of the vehicle’s purchase price. This tax is applied to both new and used vehicles, ensuring a consistent revenue stream for the state. The current sales tax rate for vehicles in Illinois stands at 6.25%, which is applicable statewide. However, it’s important to note that local governments have the authority to impose additional taxes, which can vary from one county or municipality to another.
For instance, in the city of Chicago, an additional 2% sales tax is levied on vehicle purchases, bringing the total sales tax rate to 8.25%. This variation in local taxes means that the effective sales tax rate can differ significantly across the state, impacting the overall cost of purchasing a vehicle.
The calculation of the vehicle sales tax is straightforward. The tax is assessed on the total purchase price of the vehicle, including any additional fees or charges. This means that options, accessories, and even delivery fees can contribute to the tax base. To illustrate, if you purchase a new car for $30,000 and the total additional fees amount to $2,000, the sales tax would be calculated on the total sum of $32,000. This calculation ensures that the tax is applied comprehensively, capturing all aspects of the vehicle purchase.
Exemptions and Special Considerations
While the vehicle sales tax is a standard requirement for most vehicle purchases in Illinois, certain transactions or situations may qualify for exemptions or reduced tax rates. These exemptions are designed to cater to specific circumstances and promote particular initiatives within the state.
One notable exemption is for qualifying electric vehicles (EVs). To encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly transportation, Illinois offers a 60% sales tax reduction on the first $50,000 of the purchase price for EVs. This means that for a $50,000 EV, the sales tax would be calculated on $20,000 instead, resulting in significant savings for eco-conscious consumers.
Additionally, there are provisions for military personnel and veterans. Active-duty military members and veterans who have received a Purple Heart are exempt from paying sales tax on vehicle purchases. This exemption is a way for the state to show appreciation for their service and provide financial relief during their vehicle acquisitions.
Another special consideration is for individuals with disabilities. Illinois offers a sales tax exemption for the purchase of vehicles that are modified to accommodate the specific needs of people with disabilities. This exemption ensures that individuals with disabilities can access the transportation they require without the added financial burden of sales tax.
Collection and Remittance Process
The responsibility of collecting and remitting the vehicle sales tax typically falls on the seller or lessor of the vehicle. This means that when you purchase a vehicle from a dealership or a private seller, they are responsible for calculating and collecting the appropriate sales tax. This process ensures that the state receives its due revenue promptly and efficiently.
For private sellers, the process can be a bit more complex. They are required to register with the Illinois Department of Revenue to obtain a seller's permit. This permit allows them to collect and remit sales tax on their vehicle sales. The private seller must then calculate the tax based on the purchase price and remit it to the state within a specified timeframe.
In the case of vehicle leases, the lessor is responsible for collecting and remitting the sales tax. This tax is calculated based on the total lease payments over the lease term. For example, if you lease a vehicle for $300 per month for a period of 36 months, the sales tax would be calculated on the total lease amount of $10,800.
Impact on Vehicle Buyers and Sellers

The Illinois vehicle sales tax has a significant impact on both buyers and sellers of vehicles. For buyers, it represents a substantial financial consideration when planning a vehicle purchase. The tax can add a substantial amount to the overall cost of the vehicle, especially for higher-priced models. This tax is often a factor in decision-making, influencing the type and price range of vehicles that consumers consider.
For sellers, particularly dealerships and automotive businesses, the sales tax is a critical aspect of their operations. They must ensure accurate calculation and collection of the tax to remain compliant with state regulations. Additionally, dealerships often offer financing options, and the sales tax is a key component of these financial packages, influencing the overall cost of vehicle ownership for their customers.
Moreover, the sales tax revenue generated from vehicle sales is a vital source of income for the state. It funds various public services, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure development. This revenue ensures the state can provide essential services to its residents and maintain its infrastructure, which in turn benefits both businesses and individuals.
Strategies for Managing Sales Tax Costs
Given the significant financial impact of the Illinois vehicle sales tax, both buyers and sellers employ various strategies to manage these costs effectively.
Buyers often engage in meticulous planning and research before making a vehicle purchase. They explore different models, compare prices, and consider the sales tax implications to make an informed decision. Some buyers opt for strategies like purchasing a vehicle at the end of the model year when dealerships may offer better deals, including incentives that can offset the sales tax.
Sellers, especially dealerships, offer a range of financing options and incentives to make vehicle purchases more attractive. These incentives can include reduced interest rates, cash-back offers, or even lease deals that incorporate the sales tax into the overall monthly payment, making the transaction more affordable for buyers.
Additionally, the state's exemptions and reduced tax rates for specific vehicles, like EVs, provide an opportunity for buyers to save significantly on their purchases. These incentives not only benefit the consumer but also align with the state's goals of promoting environmentally friendly transportation and technological advancements.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
The Illinois vehicle sales tax, like many other tax systems, is subject to potential changes and adjustments over time. These changes can be influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, political decisions, and evolving transportation trends.
One potential future implication is the impact of the growing popularity of ride-sharing and car-sharing services. As these services become more prevalent, there may be a need to reassess the tax system to ensure it remains fair and effective. For instance, the state may consider implementing a tax on ride-sharing transactions to generate revenue and maintain a level playing field with traditional vehicle sales.
Another consideration is the ongoing transition to electric and autonomous vehicles. As these technologies become more widespread, the state may need to adjust its tax structure to account for the unique characteristics of these vehicles. This could involve reevaluating tax rates, exploring new tax categories, or even considering incentives to encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly transportation options.
Furthermore, the state may explore alternative tax models to ensure a stable and sustainable revenue stream. One potential model is a vehicle miles traveled (VMT) tax, which would charge drivers based on the number of miles they travel. This approach has been gaining traction in some states as a more equitable way to tax vehicle usage, especially as traditional fuel taxes become less reliable with the rise of electric vehicles.
Conclusion
The Illinois vehicle sales tax is a critical component of the state’s revenue system, impacting both buyers and sellers of vehicles. It plays a significant role in funding essential public services and infrastructure projects. While the current tax rate and structure are well-established, the state’s tax system is dynamic and subject to change, adapting to evolving transportation trends and economic conditions.
Understanding the intricacies of the vehicle sales tax, including exemptions and special considerations, is crucial for both consumers and businesses operating within Illinois. By staying informed about these tax obligations and exploring strategies to manage costs effectively, individuals and businesses can navigate the vehicle sales tax landscape with confidence and make informed financial decisions.
How often does the Illinois vehicle sales tax rate change?
+The Illinois vehicle sales tax rate can change periodically, typically as a result of legislative decisions or budgetary considerations. While the current rate of 6.25% has been stable for some time, it’s important to stay updated with any potential changes, especially during state budget discussions.
Are there any online resources to calculate the sales tax for my vehicle purchase?
+Yes, there are several online calculators available that can help estimate the sales tax for your vehicle purchase. These calculators consider the purchase price, any additional fees, and the applicable tax rate to provide an accurate estimate. Using these tools can be beneficial for budgeting purposes.
What happens if I fail to pay the vehicle sales tax when due?
+Failing to pay the vehicle sales tax when due can result in penalties and interest charges. It’s important to stay compliant with the tax obligations to avoid these additional financial burdens. If you have any concerns or questions about your tax liability, it’s recommended to consult with a tax professional or the Illinois Department of Revenue.
Can I negotiate the sales tax amount with the dealership?
+The sales tax is a mandatory charge set by the state, and dealerships are required to collect and remit this tax. However, you can negotiate the overall price of the vehicle, which indirectly affects the sales tax amount. By negotiating a lower vehicle price, you can potentially reduce the sales tax liability.