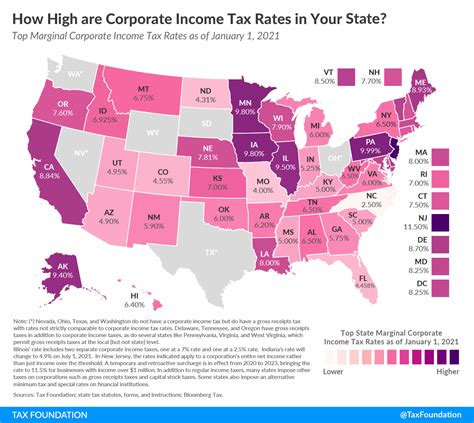
How Do You Figure Sales Tax
Sales tax is an essential component of the revenue generation process for many governments around the world. It is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services, contributing significantly to public funds. Understanding how sales tax is calculated and applied is crucial for businesses and consumers alike. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process, providing a detailed breakdown of the steps involved in figuring sales tax.
The Fundamentals of Sales Tax Calculation

Sales tax calculation is a straightforward process, but it varies depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the transaction. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you understand how it works.
Step 1: Determining the Taxable Amount
The first step in calculating sales tax is identifying the taxable amount. This is typically the total cost of the goods or services being purchased, excluding any applicable discounts or exemptions. For instance, if you buy a laptop for 1,200 and there's a 10% discount applied, the taxable amount would be calculated based on the discounted price of 1,080.
Step 2: Understanding the Sales Tax Rate
Sales tax rates can vary significantly depending on the region. These rates are typically set by local or state governments and can be a fixed percentage or a combination of different rates for different goods or services. For example, in the United States, sales tax rates can range from 0% to over 10%, with some states having varying rates for specific items like groceries or clothing.
Step 3: Calculating the Sales Tax
Once you have the taxable amount and the applicable sales tax rate, calculating the sales tax is a simple multiplication. Let’s continue with the laptop example. If the sales tax rate in your area is 8%, the calculation would be: 1,080 (taxable amount) x 0.08 (sales tax rate) = 86.40. So, the sales tax for this purchase would be $86.40.
Step 4: Adding the Sales Tax to the Total
After calculating the sales tax, the next step is to add it to the original cost of the goods or services. This gives you the final, tax-inclusive price. In our laptop example, the total cost would be 1,080 (taxable amount) + 86.40 (sales tax) = $1,166.40. This is the amount the consumer would pay at the point of sale.
| Step | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Taxable Amount | $1,200 (original price) - $120 (discount) = $1,080 | $1,080 |
| Sales Tax | $1,080 x 0.08 (sales tax rate) = $86.40 | $86.40 |
| Total Cost | $1,080 (taxable amount) + $86.40 (sales tax) | $1,166.40 |

Complexities and Variations in Sales Tax Calculation
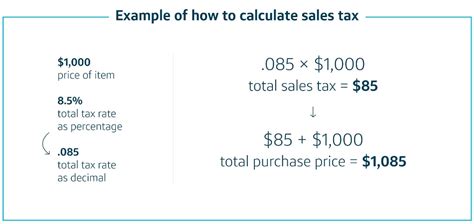
While the basic calculation of sales tax is straightforward, there are several complexities and variations that can make it more challenging. These include:
- Multiple Tax Rates: Some jurisdictions apply different sales tax rates to different categories of goods or services. For example, food items might have a lower sales tax rate than electronics.
- Exemptions and Discounts: Certain goods or services may be exempt from sales tax, such as prescription medications or educational materials. Additionally, discounts or promotions can reduce the taxable amount, affecting the final sales tax calculation.
- Rounding Rules: Sales tax calculations often involve rounding, which can impact the final total. Some jurisdictions round up to the nearest cent or dollar, while others use more complex rounding rules.
- Tax Holidays: In certain periods, often during peak shopping seasons, governments may implement "tax holidays" where sales tax is temporarily waived or reduced for specific goods.
- Online Sales Tax: With the rise of e-commerce, calculating sales tax for online purchases can be more complex, especially when considering the buyer's location and the seller's shipping practices.
Real-World Applications and Impact
Understanding how sales tax is calculated is crucial for both businesses and consumers. For businesses, accurate sales tax calculations ensure compliance with tax laws and help maintain a positive relationship with customers. Missteps in sales tax calculations can lead to legal consequences and reputational damage.
For consumers, being aware of how sales tax is calculated helps in budgeting and understanding the true cost of goods and services. It also empowers consumers to question and verify sales tax calculations, especially in situations where the tax is not clearly displayed.
Sales Tax in Different Industries
Sales tax impacts various industries differently. For instance, in the hospitality industry, sales tax is often applied to room rates and food and beverage purchases. In contrast, the healthcare industry may have specific rules regarding sales tax on medical equipment or services.
| Industry | Sales Tax Impact |
|---|---|
| Retail | Sales tax is a significant factor, applied to most goods sold. |
| Hospitality | Sales tax is applied to room rates, food, and beverages. |
| Healthcare | Sales tax rules vary for medical equipment and services. |
| E-commerce | Online sales tax calculations can be complex due to varying state laws. |
The Future of Sales Tax Calculation
As technology advances, the process of calculating sales tax is becoming increasingly automated. Tax software and online tools can now handle complex calculations, including variations in tax rates and exemptions. This not only reduces the risk of errors but also streamlines the tax calculation process, making it more efficient for businesses.
Furthermore, the rise of digital commerce has led to a more complex sales tax landscape, with businesses often needing to navigate a web of varying state and local tax laws. This has prompted some calls for a more uniform sales tax system, which could simplify calculations and compliance for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions.
FAQs
How often do sales tax rates change?
+
Sales tax rates can change annually or even more frequently, depending on the jurisdiction. It’s essential to stay updated with the latest rates to ensure accurate calculations.
Are there tools available to calculate sales tax automatically?
+
Yes, there are numerous online calculators and software tools designed to simplify sales tax calculations. These tools can be especially useful for businesses handling multiple transactions daily.
What happens if I overpay or underpay sales tax?
+
Overpayment or underpayment of sales tax can have different consequences. In some cases, an overpayment may be refunded, while underpayment could lead to penalties and interest charges. It’s always best to consult with a tax professional for guidance.