California Corporate Tax
The California Corporate Tax is a vital component of the state's fiscal landscape, impacting businesses of all sizes and industries. As one of the largest economies in the United States, California's tax structure plays a crucial role in shaping its business environment and economic growth. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of California's corporate tax system, exploring its history, key features, rates, and the impact it has on businesses operating within the state. By understanding the nuances of this tax system, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their tax strategies and contribute effectively to the Golden State's thriving economy.
Unraveling the California Corporate Tax Landscape
California, known for its diverse economy and thriving business environment, has a unique tax system that caters to its large and dynamic corporate sector. The state’s corporate tax structure is designed to generate revenue for essential public services while also promoting economic growth and competitiveness. In this section, we will dissect the key elements of California’s corporate tax, shedding light on its rates, base, and the methods employed to calculate and report corporate taxes.
Corporate Tax Rates and Brackets
California’s corporate income tax is a progressive tax, meaning that higher revenues lead to higher tax rates. The state has established tax brackets that correspond to different levels of corporate income. As of 2023, the corporate tax rates in California are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $250,000 | 8.84% |
| $250,001 - $500,000 | 9.12% |
| $500,001 - $1,000,000 | 9.38% |
| $1,000,001 - $2,500,000 | 9.62% |
| Over $2,500,000 | 10.84% |

These rates are applicable to both C-corporations and S-corporations, with some variations in tax calculation based on the entity's legal structure. It's important to note that these rates are subject to change, and businesses should stay updated with any legislative amendments to ensure compliance.
Tax Base and Calculation
The tax base for California’s corporate income tax is determined by the corporation’s net income. Net income is calculated by deducting allowable expenses, such as cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and depreciation, from the corporation’s gross income. The resulting net income is then taxed according to the applicable tax bracket.
California also offers various tax credits and incentives to eligible businesses. These credits can reduce the overall tax liability and provide incentives for specific activities, such as research and development, hiring, or investment in renewable energy. Businesses should explore these opportunities to optimize their tax position and contribute to the state's economic goals.
Reporting and Payment Requirements
Corporate tax returns in California are typically due on the 15th day of the fourth month following the close of the corporation’s fiscal year. For example, if a corporation’s fiscal year ends on December 31st, the tax return would be due by April 15th. However, extensions can be requested, granting an additional six months to file the return. It’s crucial for businesses to adhere to these deadlines to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Payment of corporate taxes is generally due at the time of filing the return. Corporations can remit their taxes through various methods, including electronic funds transfer, credit card, or by mailing a check or money order to the Franchise Tax Board. Late payments may incur penalties and interest, so timely payment is essential for compliance.
The Impact of California’s Corporate Tax on Businesses

California’s corporate tax structure has a significant influence on the business landscape within the state. While it provides essential revenue for public services and infrastructure, it also impacts businesses’ bottom lines and their ability to compete in the global market. Understanding the implications of this tax system is crucial for businesses to make strategic decisions and optimize their operations.
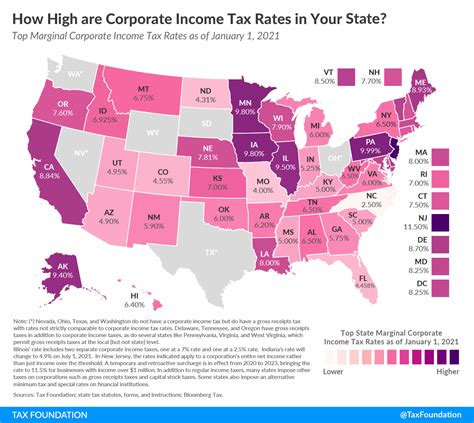
Competitiveness and Tax Burden
California’s corporate tax rates are relatively higher compared to many other states in the U.S. This higher tax burden can make it challenging for businesses, especially those in competitive industries, to maintain profitability and growth. However, it’s important to consider the overall business environment and the benefits that California offers, such as a large consumer market, a skilled workforce, and a robust infrastructure.
To mitigate the impact of the tax burden, businesses can explore various strategies. These may include optimizing their tax structure, utilizing tax credits and incentives, or considering alternative tax jurisdictions for specific operations. A thorough understanding of California's tax laws and a proactive tax planning approach can help businesses navigate these challenges effectively.
Economic Growth and Investment
Despite the higher tax rates, California’s corporate tax system has played a pivotal role in driving economic growth and investment within the state. The revenue generated from corporate taxes contributes significantly to public services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and social welfare programs. These investments create a conducive environment for businesses, fostering innovation, talent attraction, and overall economic prosperity.
Additionally, California's tax structure often includes incentives and tax breaks for specific industries or activities, encouraging investment in sectors deemed strategic for the state's economic development. These targeted incentives can offset the higher tax rates and make California an attractive destination for businesses seeking to expand or establish their operations.
Compliance and Tax Planning
California’s corporate tax system requires businesses to navigate a complex set of rules and regulations. Compliance with these tax laws is essential to avoid penalties and legal issues. Businesses must accurately report their income, deduct allowable expenses, and calculate their tax liability according to the applicable tax rates.
To ensure compliance, businesses often engage the services of tax professionals or utilize tax software that is tailored to California's specific tax laws. These tools and expertise help businesses stay updated with any changes in tax regulations and make informed decisions regarding tax planning and strategy.
Future Outlook and Implications
California’s corporate tax landscape is subject to ongoing changes and reforms, influenced by economic trends, political dynamics, and the state’s revenue needs. As the state continues to evolve, businesses must stay vigilant and adapt their tax strategies to align with these changes.
Potential Tax Reforms
There have been ongoing discussions and proposals for tax reforms in California, aimed at simplifying the tax system, reducing tax rates, and promoting economic growth. These reforms could have significant implications for businesses, impacting their tax liability and overall competitiveness. Staying informed about these potential changes is crucial for businesses to plan and adapt their tax strategies accordingly.
Economic Trends and Business Opportunities
California’s dynamic economy offers a plethora of business opportunities, and understanding the tax landscape is essential for capitalizing on these prospects. As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, businesses can leverage tax incentives and credits to drive innovation and stay ahead of the curve. Staying abreast of industry trends and tax developments can provide a competitive edge and open doors to new growth opportunities.
International Business Considerations
For businesses with international operations or aspirations, California’s corporate tax system can present unique considerations. Cross-border tax planning and compliance become crucial aspects to navigate. Businesses must understand the interplay between California’s tax laws and international tax regulations to optimize their global tax position and avoid double taxation.
What are the key differences between California's corporate tax and federal corporate tax in the U.S.?
+California's corporate tax system operates independently from the federal corporate tax system. While both systems share some similarities, such as progressive tax rates, there are significant differences. California's tax rates are generally higher than the federal rates, and the state offers its own set of tax credits and incentives. Additionally, California has specific rules and regulations regarding tax filing, payment, and compliance that differ from federal requirements.
How can businesses optimize their tax position in California?
+Businesses can optimize their tax position in California by staying updated with tax laws and regulations, utilizing tax credits and incentives, and engaging in proactive tax planning. This may involve restructuring their tax strategies, exploring alternative tax jurisdictions for specific operations, and leveraging the expertise of tax professionals or specialized software.
What are some common challenges businesses face when navigating California's corporate tax system?
+Businesses often face challenges related to compliance, such as understanding the complex tax laws and regulations, accurately calculating tax liability, and staying updated with any changes. Additionally, the higher tax rates in California can impact businesses' competitiveness and profitability, requiring strategic tax planning to mitigate these challenges.
How do California's tax incentives and credits benefit businesses?
+California's tax incentives and credits provide businesses with opportunities to reduce their tax liability and promote specific activities or investments. These incentives can offset the higher tax rates and make California an attractive destination for businesses, particularly in sectors that align with the state's economic development goals.
In conclusion, California’s corporate tax system is a critical component of the state’s fiscal framework, impacting businesses and shaping the economic landscape. By understanding the nuances of this tax structure, businesses can navigate its complexities, optimize their tax strategies, and contribute to California’s thriving economy. As the state continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be key for businesses to thrive within this dynamic tax environment.