Hawaii State Tax
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Hawaii State Tax system. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Hawaii's tax structure, providing you with a detailed understanding of how taxes work in this unique state. Hawaii's tax landscape is shaped by its distinct geography, vibrant economy, and diverse population, making it an intriguing subject for exploration.
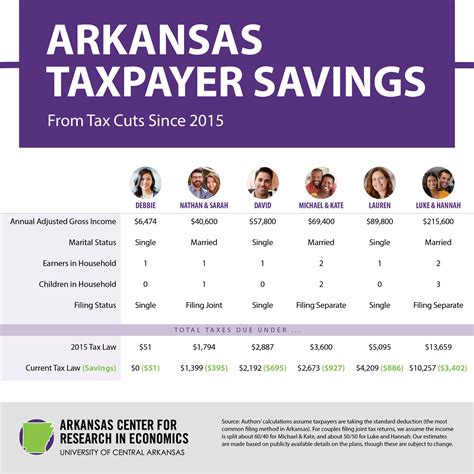
Income above 20,000 in Hawaii is taxed at a rate of 6.4%.">What is the tax rate for income over 20,000 in Hawaii? +
Income above 20,000 in Hawaii is taxed at a rate of 6.4%.
Understanding Hawaii’s Tax System

Hawaii, known for its breathtaking natural beauty and vibrant culture, has a tax system that reflects its position as a leading tourist destination and a thriving business hub. The state’s tax structure is designed to support its economy while also providing essential services to its residents.
State Income Tax
One of the key components of Hawaii’s tax system is its state income tax. Hawaii operates on a progressive tax rate structure, meaning that as your income increases, so does the tax rate applied to your earnings. This progressive system ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger portion of their income to the state’s revenue.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $4,999 | 1.4% |
| $5,000 - $9,999 | 3.2% |
| $10,000 - $19,999 | 4.4% |
| Above $20,000 | 6.4% |

Hawaii's income tax system offers various deductions and credits to reduce the tax burden for individuals and families. These include deductions for dependents, education expenses, and certain business-related costs. Additionally, the state provides tax credits for low-income earners and those with qualifying disabilities.
General Excise Tax
Another significant tax in Hawaii is the General Excise Tax (GET). This tax is applied to most transactions, including the sale of goods and services, and is often passed on to the consumer as part of the total cost. The GET is a 4% tax that is collected by businesses and remitted to the state.
However, Hawaii also has a Use Tax, which is similar to the GET but applies to goods purchased outside the state and brought into Hawaii for use. This ensures that all transactions are taxed fairly, regardless of where they occur.
Property Tax
Property owners in Hawaii are subject to property taxes, which are based on the assessed value of their real estate. The county government handles property tax assessments and collections, with rates varying across the state’s different counties.
The property tax rate in Hawaii is typically lower compared to other states, reflecting the state's commitment to attracting and retaining residents and businesses. However, the unique geography of Hawaii, with its limited land area, can lead to higher property values and subsequently higher tax liabilities for homeowners.
Tax Benefits and Incentives
Hawaii’s tax system also includes various tax incentives aimed at promoting economic development and supporting specific industries. These incentives are designed to encourage investment, job creation, and innovation within the state.
Enterprise Zones
The state has designated certain Enterprise Zones where businesses can benefit from reduced tax rates and other incentives. These zones are typically located in economically disadvantaged areas, aiming to stimulate growth and create opportunities for local communities.
Businesses operating within these zones may be eligible for reduced income tax rates, property tax abatements, and accelerated depreciation on qualifying assets. These incentives can significantly reduce the tax burden for businesses operating in these designated areas.
Research and Development Tax Credits
Hawaii encourages research and development activities by offering tax credits to businesses engaged in qualified research. These credits can offset a portion of the income tax liability, providing an incentive for companies to invest in innovation and technological advancements.
Film and Digital Media Tax Credits
Recognizing the importance of the film and digital media industry, Hawaii provides tax incentives to production companies. These incentives include refundable tax credits based on the amount spent on qualified production expenses within the state. This initiative aims to attract film and media projects, creating economic opportunities and showcasing Hawaii’s stunning locations.
Tax Administration and Compliance
Hawaii’s Department of Taxation is responsible for administering and enforcing the state’s tax laws. The department provides resources and guidance to taxpayers, ensuring compliance with the complex tax system.
Taxpayers in Hawaii are required to file tax returns annually, with deadlines typically falling in April. Late filings and non-compliance can result in penalties and interest charges. It is essential for individuals and businesses to stay informed about their tax obligations and seek professional advice when needed.
Online Tax Filing and Payment
Hawaii offers a convenient online platform for taxpayers to file their returns and make payments. This digital system streamlines the process, providing a user-friendly interface for residents and businesses to fulfill their tax obligations efficiently.
Tax Refunds and Appeals
Taxpayers who overpay their taxes may be eligible for tax refunds. The Department of Taxation processes these refunds promptly, ensuring that taxpayers receive their money back in a timely manner. In cases of disputes or errors, taxpayers have the right to appeal tax assessments through a formal process outlined by the department.
Future Implications and Challenges
As Hawaii’s economy continues to evolve, the state’s tax system must adapt to meet changing needs. One of the key challenges is balancing revenue generation with the cost of living, which is relatively high in Hawaii due to its isolated location.
The state's reliance on tourism and certain industries makes it vulnerable to economic downturns. Therefore, Hawaii must explore diversification strategies and consider long-term sustainable revenue sources to ensure financial stability. This may involve revisiting tax policies and exploring innovative approaches to taxation.
Sustainable Tourism and Tax Policy
Hawaii’s unique environment and natural resources are integral to its tourism industry. As such, the state must carefully consider the impact of tourism-related taxes on both visitors and local businesses. Striking a balance between generating revenue and preserving the islands’ natural beauty is crucial for Hawaii’s long-term sustainability.
Taxation and Economic Equality
Hawaii’s tax system plays a vital role in addressing economic disparities. The state’s progressive income tax structure and targeted tax credits aim to provide support to lower-income earners and promote economic equality. However, ongoing evaluation and adjustments are necessary to ensure that the tax system remains effective in achieving these goals.
Conclusion

Hawaii’s tax system is a dynamic and intricate network of policies and incentives designed to support the state’s economy and provide essential services to its residents. From progressive income taxes to targeted incentives, Hawaii’s approach to taxation reflects its unique position as a thriving island paradise.
As Hawaii continues to evolve, its tax policies will play a crucial role in shaping the state's future. By staying informed and actively engaging with the tax system, individuals and businesses can contribute to Hawaii's economic prosperity while enjoying the benefits of living in this remarkable state.
What is the tax rate for income over 20,000 in Hawaii?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Income above 20,000 in Hawaii is taxed at a rate of 6.4%.
Are there any tax incentives for renewable energy projects in Hawaii?
+
Yes, Hawaii offers tax incentives for renewable energy projects, including tax credits and exemptions. These incentives aim to promote the adoption of clean energy technologies.
How does Hawaii’s property tax system work for second homes or vacation properties?
+
Property taxes for second homes or vacation properties in Hawaii are based on the assessed value, just like primary residences. However, there may be additional considerations, such as transient accommodation taxes, for properties used for short-term rentals.