Arkansas State Tax Rate
Arkansas, the Natural State, is renowned for its diverse landscapes, vibrant cities, and rich cultural heritage. Nestled in the heart of the South, it offers a unique blend of natural beauty and economic opportunities. As with any state, understanding its tax landscape is crucial for both residents and businesses. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Arkansas' state tax rates, providing a detailed analysis of the various taxes levied and their implications.
Unraveling the Arkansas State Tax Landscape

Arkansas maintains a balanced approach to taxation, aiming to support its economy while fulfilling its fiscal responsibilities. The state’s tax system is designed to be progressive, ensuring that higher-income earners contribute a larger proportion of their income to state revenues. This progressive nature is evident in the income tax structure, which forms a significant part of Arkansas’ overall tax revenue.
Income Tax: A Progressive Approach
Arkansas levies individual income taxes based on a progressive tax rate schedule. This means that as income increases, so does the tax rate applied to that income bracket. Currently, the state operates with six income tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets and their corresponding tax rates are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to 2,300</td><td>1.9%</td></tr> <tr><td>2,301 - 4,000</td><td>2.5%</td></tr> <tr><td>4,001 - 6,500</td><td>3.0%</td></tr> <tr><td>6,501 - 11,000</td><td>4.0%</td></tr> <tr><td>11,001 - 25,000</td><td>5.0%</td></tr> <tr><td>Over 25,000 | 6.0% |
It’s important to note that these rates are for single filers. Married couples filing jointly may have slightly different tax brackets and rates.
Sales and Use Tax: A Key Revenue Generator
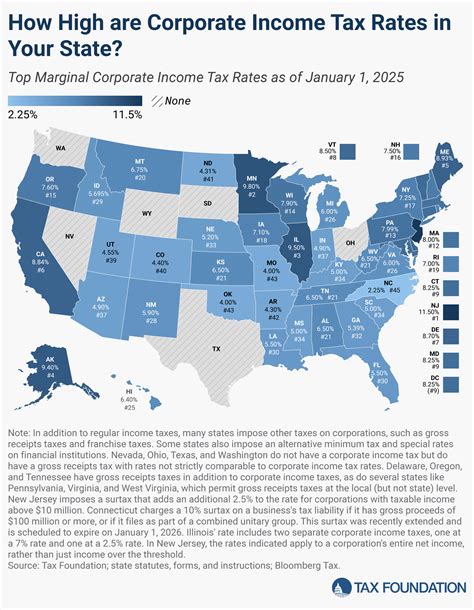
Sales and use tax is another significant component of Arkansas’ tax revenue. The state imposes a general sales and use tax rate of 6.5%. This rate is applicable to most retail sales of tangible personal property and certain services. However, it’s worth noting that some localities in Arkansas also impose their own additional sales tax, which can bring the total sales tax rate to as high as 11.5% in certain areas.
The state's sales and use tax is collected by retailers at the point of sale and then remitted to the Arkansas Department of Finance and Administration (DFA). The DFA is responsible for administering and enforcing the state's tax laws, ensuring compliance, and providing guidance to taxpayers.
Property Tax: Assessing Real Estate
Property tax is a vital source of revenue for local governments in Arkansas, including counties, cities, and school districts. Unlike the state’s income and sales tax rates, which are uniform across the state, property tax rates can vary significantly depending on the location of the property. These rates are set by local taxing authorities and are used to fund a wide range of public services, such as schools, roads, and emergency services.
Arkansas' property tax system operates on an ad valorem basis, meaning the tax is calculated based on the assessed value of the property. The assessed value is typically a percentage of the property's fair market value. The specific assessment rate can vary by jurisdiction and property type. For instance, residential properties may have a lower assessment rate compared to commercial or industrial properties.
Once the assessed value is determined, the property tax rate, often referred to as the millage rate, is applied. One mill is equal to one-tenth of one cent, or $0.001. So, a millage rate of 50 mills would equate to a tax rate of 5%. The millage rate is set by the local taxing authority and can change from year to year based on budgetary needs and voter-approved initiatives.
Other Arkansas State Taxes
In addition to the taxes mentioned above, Arkansas imposes various other taxes to generate revenue and fund specific programs and initiatives.
- Motor Fuel Tax: Arkansas levies a tax on the sale of motor fuels, such as gasoline and diesel. This tax is used to fund road construction and maintenance.
- Franchise Tax: Corporations doing business in Arkansas are subject to a franchise tax, which is based on the company's capital and surplus.
- Severance Tax: Arkansas imposes a tax on the extraction of natural resources, such as oil and gas, to support the state's infrastructure and environmental programs.
- Excise Taxes: The state also levies excise taxes on various goods and services, including tobacco products, alcoholic beverages, and certain recreational activities.
Implications and Considerations

Arkansas’ state tax system, with its progressive income tax, sales and use tax, and localized property tax, offers a balanced approach to revenue generation. While the state’s tax rates are competitive compared to many other states, it’s important for individuals and businesses to understand the full scope of Arkansas’ tax landscape to make informed financial decisions.
For businesses, particularly those considering expansion or relocation, understanding the state's tax incentives and programs can be crucial. Arkansas offers a range of incentives, such as tax credits and abatements, to attract and support businesses. These incentives can significantly reduce a company's tax liability, making Arkansas an attractive business destination.
On the individual level, Arkansas's progressive income tax structure ensures that the tax burden is shared equitably across different income levels. This approach fosters a sense of fairness and supports the state's social and economic goals. However, it's essential for individuals to stay informed about tax laws and potential changes, especially during tax season, to ensure compliance and take advantage of any applicable deductions or credits.
Staying Informed and Up-to-Date
The tax landscape in Arkansas, as in any state, is subject to change. New legislation, economic trends, and budgetary considerations can all impact tax rates and structures. It’s crucial for taxpayers, whether individuals or businesses, to stay informed about these changes to ensure compliance and optimize their tax strategies.
The Arkansas Department of Finance and Administration provides a wealth of resources and information on its website, including tax forms, publications, and guidance documents. Additionally, taxpayers can stay updated on tax law changes, deadlines, and new initiatives through various communication channels, such as the DFA's social media platforms and email newsletters.
For those seeking personalized tax advice or assistance, it's advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional who can provide tailored guidance based on individual or business circumstances. These professionals can help navigate the complexities of Arkansas' tax system, ensuring compliance and maximizing tax benefits.
How often are Arkansas state tax rates reviewed and potentially changed?
+Arkansas state tax rates, particularly the income tax rates, are typically reviewed and adjusted during the legislative session, which occurs annually. However, changes can also be made outside of the legislative session if deemed necessary by the state's leadership or in response to economic conditions or budgetary needs.
Are there any tax incentives or programs available for businesses in Arkansas?
+Absolutely! Arkansas offers a range of tax incentives and programs to attract and support businesses. These include tax credits for job creation, investment incentives, and abatements for certain types of businesses or industries. The Arkansas Economic Development Commission provides detailed information on these incentives.
How does Arkansas's state tax system compare to other states in the region or nationwide?
+Arkansas's state tax system is generally considered competitive compared to many other states, especially in the South. Its income tax rates are relatively low, and the sales tax rate, while not the lowest in the region, is still competitive. However, it's important to note that each state has its own unique tax structure, and a comprehensive analysis would be needed to fully compare Arkansas to other states.
Understanding Arkansas’ state tax rates is a crucial step in navigating the state’s economic landscape. By staying informed and up-to-date on tax laws and changes, individuals and businesses can make strategic decisions that align with their financial goals and obligations. Whether it’s filing taxes, planning investments, or making business decisions, a clear understanding of Arkansas’ tax system is essential.