Day Trading Taxes

In the world of day trading, where decisions are made swiftly and trades are executed with precision, understanding the tax implications is crucial. This article aims to delve into the intricate world of day trading taxes, providing a comprehensive guide for traders to navigate the financial and legal aspects of their trading activities. With the right knowledge, traders can optimize their tax strategies and ensure compliance with the law, thereby maximizing their returns and minimizing potential pitfalls.
Unraveling the Complexity of Day Trading Taxes

Day trading taxes are a unique aspect of the financial landscape, often misunderstood and overlooked by novice traders. This section aims to demystify the process, offering a step-by-step guide to understanding and managing these taxes effectively. From the moment a trader initiates their first trade, they are subject to specific tax regulations, and it is essential to be aware of these rules to avoid any legal or financial repercussions.
Determining Taxable Income from Day Trading
The first step in managing day trading taxes is understanding what constitutes taxable income. In this context, taxable income refers to the profits made from day trading activities. This income is subject to various tax rates and regulations, depending on the trader’s status and the specific rules in their jurisdiction.
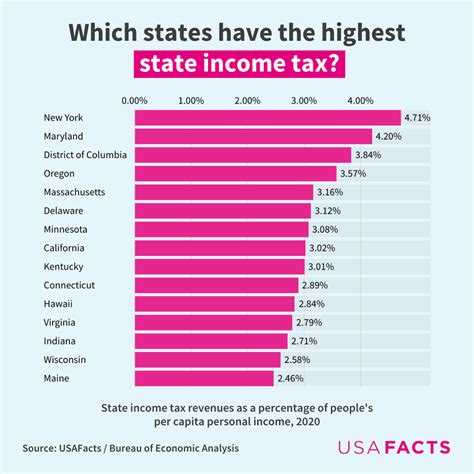
For instance, in the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats day trading profits as ordinary income. This means that these profits are taxed at the trader's marginal tax rate, which can vary based on the individual's overall income level. Other countries may have different tax classifications for day trading profits, which traders must be aware of to ensure compliance.
| Jurisdiction | Tax Classification |
|---|---|
| United States | Ordinary Income |
| United Kingdom | Capital Gains Tax |
| Australia | Capital Gains Tax |
| Canada | Capital Gains Tax |

Keeping Accurate Records for Tax Purposes
Maintaining meticulous records is a vital aspect of day trading, not just for trade analysis but also for tax purposes. Accurate record-keeping ensures that traders can substantiate their income and expenses to the tax authorities, which is crucial for audit purposes.
Traders should maintain a detailed log of all their trades, including the date, time, security, quantity, purchase price, and sale price. Additionally, they should keep records of any fees, commissions, or other expenses related to their trading activities. These records should be organized and easily accessible, as they may be required during tax season or in the event of an audit.
Filing Taxes for Day Trading Profits
When it comes to filing taxes for day trading profits, the process can vary depending on the trader’s jurisdiction and their tax status. In general, traders should report their day trading income on their annual tax return, using the appropriate tax forms.
For example, in the United States, day traders typically report their profits on Schedule C or Schedule D, depending on their trading activity and tax strategy. Traders should consult with tax professionals to determine the best approach for their specific situation.
| Jurisdiction | Tax Form |
|---|---|
| United States | Schedule C or Schedule D |
| United Kingdom | Self-Assessment Tax Return |
| Australia | Capital Gains Tax Schedule |
| Canada | T3 Tax Form |
Strategies to Minimize Tax Burden
While it is essential to comply with tax regulations, traders can also explore strategies to minimize their tax burden legally. One effective strategy is tax loss harvesting, which involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income.
Another strategy is to utilize tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans in the United States. These accounts offer tax benefits, such as tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals, which can significantly reduce the overall tax liability for day traders.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Day Trading Tax Strategies
To illustrate the practical application of day trading tax strategies, let’s examine a few case studies of successful traders and their approaches to managing taxes.
Case Study 1: John’s Tax-Efficient Trading Strategy
John, a seasoned day trader based in the United States, has developed a tax-efficient trading strategy that maximizes his returns while minimizing his tax liability. He achieves this by employing a combination of tax loss harvesting and utilizing tax-advantaged accounts.
Each year, John reviews his portfolio and identifies securities that have underperformed. He then strategically sells these securities at a loss, offsetting his capital gains and reducing his taxable income. This strategy, known as tax loss harvesting, allows him to minimize his tax burden without affecting his overall portfolio performance.
Additionally, John contributes a significant portion of his trading profits to his Individual Retirement Account (IRA). By doing so, he takes advantage of the tax-deferred growth within the IRA, which means his investments can grow tax-free until he withdraws them in retirement. This strategy not only reduces his current tax liability but also provides a substantial tax benefit in the long term.
Case Study 2: Sarah’s International Tax Considerations
Sarah, a day trader based in the United Kingdom, faces unique tax challenges due to her international trading activities. She trades on various global exchanges, which means she must navigate the tax regulations of multiple jurisdictions.
To manage her tax obligations effectively, Sarah works closely with a tax advisor who specializes in international finance. Together, they ensure that Sarah complies with the tax regulations in each country where she trades. This involves understanding the specific tax rates and reporting requirements for each jurisdiction, as well as staying updated on any changes in tax laws.
Furthermore, Sarah strategically plans her trading activities to minimize her tax burden. For instance, she may choose to trade more actively in jurisdictions with lower tax rates or consider establishing a trading entity in a tax-friendly jurisdiction to benefit from more favorable tax treatments.
Future Outlook: Emerging Trends in Day Trading Taxes
As the day trading landscape continues to evolve, so do the tax regulations and strategies. Traders must stay informed about emerging trends and changes in tax laws to ensure they remain compliant and can take advantage of new opportunities.
The Rise of Crypto Day Trading and Its Tax Implications
With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrency trading, day traders are now faced with the unique challenge of managing taxes for digital assets. Crypto day trading brings a new set of tax considerations, including the classification of cryptocurrencies as property or currency, and the specific tax rates and reporting requirements for crypto transactions.
Traders who engage in crypto day trading must stay updated on the evolving tax regulations in their jurisdiction. For instance, in the United States, the IRS has issued specific guidelines for reporting cryptocurrency transactions, and traders must ensure they comply with these rules to avoid penalties.
Global Tax Reforms and Their Impact on Day Traders
In recent years, there has been a global push for tax reforms, particularly in the realm of financial transactions. These reforms aim to address issues such as tax evasion, money laundering, and the fair distribution of tax burdens. Day traders should be aware of these reforms, as they may significantly impact their tax obligations.
One notable example is the OECD's Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project, which aims to prevent multinational companies from avoiding taxes by shifting profits to low-tax jurisdictions. While this project primarily targets large corporations, it may also have implications for day traders who engage in international trading activities. As such, traders should stay informed about global tax reforms and their potential impact on their trading strategies.
The Role of Technology in Simplifying Day Trading Taxes
Advancements in technology are playing a significant role in simplifying the process of managing day trading taxes. Various software and applications are now available to help traders track their trades, calculate gains and losses, and generate tax reports. These tools can significantly reduce the time and effort required to manage taxes, allowing traders to focus more on their trading activities.
Additionally, technology is facilitating better collaboration between traders and tax professionals. With secure online platforms, traders can easily share their trading data with tax advisors, who can then provide real-time tax advice and guidance. This integration of technology into the tax process is enhancing efficiency and accuracy, making tax management a less daunting task for day traders.
What are the key differences between day trading taxes and traditional investment taxes?
+
Day trading taxes differ from traditional investment taxes in several ways. Day traders typically face higher tax rates due to the classification of their profits as ordinary income, while long-term investors often benefit from lower capital gains tax rates. Additionally, day traders must carefully track and report each trade, whereas traditional investors may only need to report transactions annually.
Are there any tax advantages for day traders in specific jurisdictions?
+
Yes, certain jurisdictions offer tax advantages for day traders. For instance, some countries have lower tax rates for capital gains or provide tax incentives for certain types of trading activities. Traders should research the tax regulations in their jurisdiction and consider establishing trading entities in tax-friendly locations.
How can day traders stay updated on tax regulations and changes?
+
Day traders should regularly consult tax professionals who specialize in financial markets. Additionally, staying informed through industry publications, online forums, and tax authority websites can help traders stay updated on any changes in tax laws and regulations.
What are some common mistakes day traders make when it comes to taxes?
+
Common mistakes include failing to keep accurate records, not understanding the tax implications of different trading strategies, and neglecting to report day trading income. Traders should educate themselves on tax regulations and consult professionals to avoid costly errors.
Are there any tax strategies that day traders should avoid?
+
Yes, day traders should avoid tax strategies that border on illegal or unethical practices, such as tax evasion or manipulation of records. It is crucial to maintain transparency and compliance with tax regulations to avoid legal repercussions.