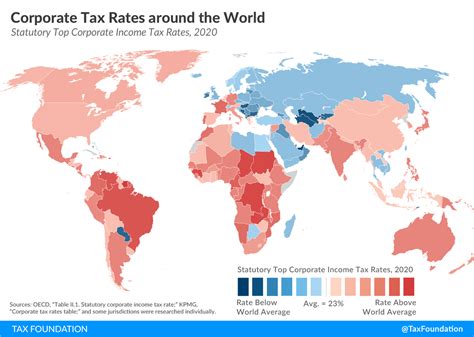
Countries With Zero Income Tax

Income tax, a cornerstone of modern taxation systems, is a levy imposed on an individual's earnings. It is a crucial source of revenue for governments, enabling them to fund public services and infrastructure. However, there are a handful of countries around the world that have adopted a unique approach by implementing a zero income tax policy. In this article, we will explore these nations, their motivations, and the implications of such a strategy.
Understanding Zero Income Tax Countries

While the concept of zero income tax may seem intriguing, it is important to understand the context and the potential trade-offs associated with such a system. Let's delve into the details of these countries and uncover the realities of living in a place with no income tax.
The Bahamas: A Caribbean Tax Haven
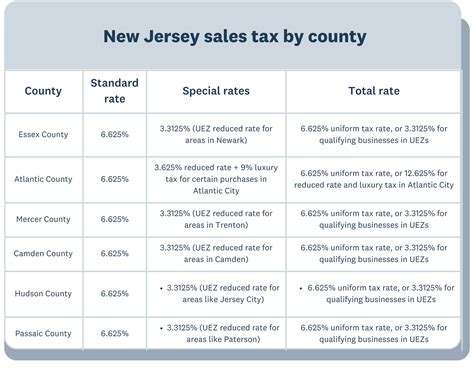
The Bahamas, an archipelago nation in the Caribbean, boasts a zero income tax policy for its residents. This policy has been in place since 2002 and has made the country an attractive destination for high-net-worth individuals and businesses. The Bahamian government generates revenue through other means, such as customs duties, real estate taxes, and a Value Added Tax (VAT) on goods and services.
| Bahamas Revenue Sources | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Customs Duties | 25% |
| Real Estate Taxes | 10% |
| VAT | 15% |
The Bahamas' zero income tax policy has led to a thriving financial services sector, with the country becoming a popular hub for international banking and offshore companies. However, it is important to note that this tax-free status is not extended to all income sources. Certain income, such as that from Bahamian sources or employment within the country, may still be subject to other taxes or levies.
Monako: A Tiny Tax-Free Paradise
Monako, a microstate nestled along the French Riviera, is another country that has adopted a zero income tax policy. With a population of just over 38,000, Monako is known for its luxurious lifestyle and glamorous reputation. The government of Monako generates revenue through other means, including a wealth tax, a value-added tax (VAT), and a range of other indirect taxes.
| Monako Revenue Sources | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Wealth Tax | 20% |
| VAT | 18% |
| Other Indirect Taxes | 25% |
The zero income tax policy in Monako has contributed to its reputation as a tax haven, attracting individuals and businesses seeking tax-efficient solutions. However, it is crucial to understand that this policy is not universally applicable. Residents of Monako are still subject to other forms of taxation, and certain income sources may be taxed differently.
United Arab Emirates: A Middle Eastern Tax-Free Zone
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), a federation of seven emirates, has implemented a zero income tax policy for its residents. This policy has been in place since the country's formation in 1971 and has played a significant role in attracting expatriates and businesses to the region. The UAE generates revenue through a range of other taxes, including a corporate tax, a value-added tax (VAT), and excise duties.
| UAE Revenue Sources | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Corporate Tax | 15% |
| VAT | 5% |
| Excise Duties | 10% |
The UAE's zero income tax policy has been a key factor in its economic growth and diversification. The country has become a hub for international trade, finance, and tourism. However, it is essential to note that this policy is not extended to all income sources. Certain income, such as that from UAE-based businesses or investments, may be subject to other taxes.
Other Countries With Limited Income Taxation
While the aforementioned countries have implemented a complete zero income tax policy, there are other nations that have adopted limited income taxation or have significantly reduced tax rates. These countries include:
- Qatar: A flat income tax rate of 10% is applied to the income of expatriates working in the country.
- Saudi Arabia: Income tax is levied on non-residents, with rates ranging from 2.5% to 20% depending on the source of income.
- Oman: Oman has a progressive income tax system, but the highest tax rate is only 15%, making it one of the lowest in the region.
- Bermuda: Bermuda has a zero income tax policy for its residents, but non-residents are subject to a 10% tax on their local income.
Implications and Trade-offs
Implementing a zero income tax policy comes with both advantages and challenges. Let's explore some of the key implications:
Attracting Investment and Talent
One of the primary benefits of a zero income tax policy is its ability to attract foreign investment and highly skilled professionals. Countries with such policies become desirable destinations for businesses and individuals seeking tax-efficient environments. This influx of investment can drive economic growth, create jobs, and boost the overall prosperity of the nation.
Diversifying Revenue Streams
To compensate for the absence of income tax revenue, governments must diversify their income sources. This often leads to the implementation of other forms of taxation, such as consumption taxes (VAT), property taxes, or specific levies on certain industries. Diversifying revenue streams can provide a more stable financial foundation for the country.
Inequality and Social Welfare
A zero income tax policy can have implications for income inequality and social welfare. Without progressive income taxes, the gap between the rich and the poor may widen. Additionally, governments may need to find alternative funding sources for social programs and public services, which could impact the overall welfare of the population.
Impact on Public Services
Funding public services and infrastructure becomes a challenge in countries with zero income tax. Governments may need to prioritize certain areas of public spending and allocate resources efficiently. This could lead to a different approach to service delivery and potentially impact the quality and accessibility of public services.
International Relations and Compliance
Countries with zero income tax policies may face scrutiny from international organizations and other nations. They may be perceived as tax havens and subject to pressure to comply with global tax standards and transparency initiatives. Maintaining good international relations and adhering to global tax norms become crucial for these countries.
Future Outlook and Considerations
As the world continues to evolve, the concept of zero income tax remains a topic of interest and debate. Here are some key considerations and potential future developments:
Sustainable Revenue Models
Countries with zero income tax policies must continually evaluate and adapt their revenue models to ensure long-term sustainability. This may involve exploring new sources of revenue, such as digital taxes or innovative tax structures, to keep pace with changing economic landscapes.
International Tax Cooperation
With the increasing focus on global tax cooperation and transparency, countries with zero income tax policies may need to enhance their international tax frameworks. This could involve participating in international tax agreements and sharing information to prevent tax evasion and maintain good relations with other nations.
Social Welfare and Equality
Governments in countries with zero income tax policies will need to carefully consider the distribution of wealth and the provision of social safety nets. Finding a balance between economic growth and social welfare will be crucial to ensure the long-term well-being of their citizens.
Tax Policy Reform
The landscape of taxation is ever-changing. Countries may consider revisiting their tax policies to adapt to emerging economic trends and technological advancements. Tax reforms could include introducing new taxes, adjusting existing rates, or exploring alternative tax systems to address evolving needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
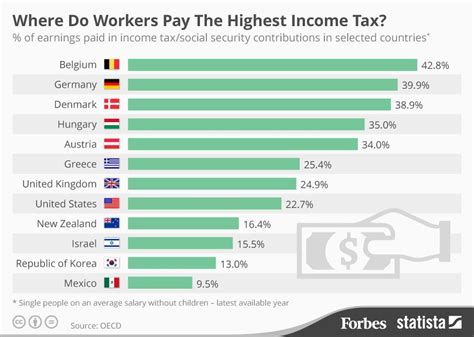
What are the main advantages of living in a country with zero income tax?
+Living in a country with zero income tax can offer several advantages, including increased disposable income, potential tax savings, and a more competitive business environment. It can attract investment, create job opportunities, and foster economic growth.
How do countries with zero income tax generate revenue?
+Countries with zero income tax generate revenue through alternative means such as consumption taxes (VAT), property taxes, corporate taxes, and specific levies on certain industries. They may also rely on natural resource revenues or tourism-related income.
Are there any potential drawbacks to a zero income tax policy?
+Yes, a zero income tax policy may lead to increased income inequality, reduced funding for social programs, and challenges in providing quality public services. It can also attract scrutiny from international organizations and potentially impact a country’s reputation.
Can a zero income tax policy be sustainable in the long term?
+The sustainability of a zero income tax policy depends on a country’s ability to diversify its revenue streams and adapt to changing economic conditions. It requires careful planning and the exploration of innovative revenue models to ensure long-term financial stability.
What is the impact of zero income tax on a country’s economic growth?
+A zero income tax policy can have a positive impact on a country’s economic growth by attracting investment, fostering business development, and creating a competitive business environment. It can stimulate economic activity and contribute to job creation.