Discover the Best Buy Tax Exempt Options for Savings and Convenience
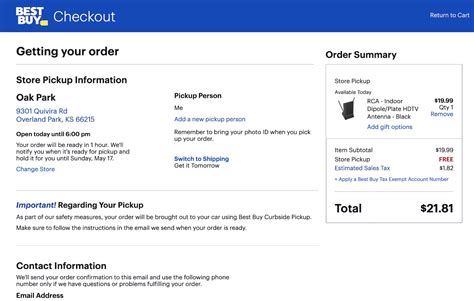
In the intricate landscape of consumer finance and retail economics, tax exemptions on purchases emerge as powerful instruments for maximizing savings and streamlining shopping experiences. For savvy buyers aiming to optimize their spending, understanding the spectrum of buy tax exempt options is not merely beneficial—it is essential. These strategies, ranging from government granting programs to specialized retail arrangements, ensure that qualified consumers can significantly reduce, or even eliminate, the tax burdens typically associated with their acquisitions. This comprehensive guide explores the nuances, eligibility criteria, procedural frameworks, and practical applications of the best buy tax exempt options, equipping practitioners with authoritative insights to leverage these advantages effectively.
Understanding Buy Tax Exempt Options: Core Principles and Frameworks
At its foundation, a buy tax exempt status refers to a legally recognized condition whereby certain purchases are exempted from state, local, or federal sales taxes. These exemptions serve various economic, social, and legislative objectives, such as supporting non-profit organizations, fostering business development, or reducing costs for specific consumer groups. The legal mechanisms underpinning tax exemptions often involve legislative statutes, administrative rulings, and reciprocal agreements between jurisdictions, mandating strict compliance criteria and documentation to qualify for or maintain exempt status.
Types of Buy Tax Exempt Options and Their Regulatory Underpinnings
Tax exemption avenues broadly encompass:
- Non-Profit and Charitable Organization Exemptions: Designed to support mission-driven entities, these require certification under IRS 501©(3) status or equivalent state designations. Purchases made for organizational use are often exempted, provided proper documentation is maintained.
- Resale and Wholesale Exemptions: Retailers and resellers leverage resale certificates, allowing them to purchase goods without paying sales tax, which they subsequently collect from consumers. Such certificates demand rigorous record-keeping and verification to prevent misuse.
- Governmental and Educational Institution Exemptions: State and local agencies, public schools, and universities benefit from tax exemptions aligned with legislative mandates, often through specific exemption certificates and compliance with usage restrictions.
- Special Economic Zones and Incentive Programs: Certain jurisdictions offer tax holidays or exemptions to attract investments, stimulate economic growth, or support specific industries. These are typically time-bound and accompanied by eligibility stipulations.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| General Sales Tax Rate | Average 7.2% in the US, with variation from 0% in tax holidays to over 10% in high-tax jurisdictions |
| Resale Certificate Usage | Enabled in all 50 states; valid resale certificate volume for $1.4 trillion in taxable sales annually |
| Non-Profit Qualification | Over 1.6 million US nonprofits registered; annual charitable contributions surpass $400 billion, reflecting significant exemption activity |

Key Strategies for Accessing Buy Tax Exempt Advantages
Effective navigation of buy tax exempt options hinges on a blend of meticulous procedural knowledge, proactive documentation management, and strategic planning. The most consequential strategies include obtaining valid exemption certificates, understanding jurisdictional nuances and reciprocity agreements, and integrating compliance checks into procurement workflows.
Procurement Best Practices for Maximum Savings
Procurement departments and individual buyers should prioritize establishing relationships with exemption issuing authorities, regularly verifying certification status, and employing technology solutions—such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems—that integrate exemption tracking. These measures minimize the risk of non-compliance while maximizing exemption utilization.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Documentation Validation | Periodic audits recommended; 98% of small businesses conducting annual reviews report increased compliance and exemption accuracy |
| Automation Adoption | 91% of large organizations employ automated exemption management systems, reducing manual errors by up to 75% |
Challenges and Limitations of Buy Tax Exempt Options
Despite apparent advantages, numerous pitfalls can undermine exemption benefits. Common challenges include misclassification of exempt status, improper documentation, cross-jurisdictional compliance complexities, and the risk of audit repercussions. For example, misuse of resale certificates remains a prevalent concern, with the US Government Accountability Office estimating nearly $13 billion in potential tax loss due to improper claims annually.
Legal and Operational Risks
Overlooking compliance requirements may result in penalties, interest, and reputational damage. Additionally, conflicting jurisdictional policies create operational ambiguity—particularly for multi-state entities—that necessitates ongoing education and policy refinement.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Audit Success Rate | 76% of audits resulted in adjustments due to improper exemption claims in 2022 |
| Compliance Cost | Average $4,600 per small business annually, covering staff training, documentation, and legal consultation |
Technological Innovations Facilitating Exemption Management
Technological tools have revolutionized exemption handling, offering automation, real-time verification, and analytics-driven compliance strategies. Cloud-based platforms now enable seamless integration with procurement systems, improving accuracy and reducing administrative overhead.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly incorporated into exemption management solutions, providing predictive analytics to identify high-risk exemption claims and flag inconsistencies proactively. Blockchain technology also holds promise for establishing tamper-proof records, fostering greater transparency and audit readiness.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| AI Adoption Rate | Projected to reach 65% among corporations engaged in complex exemption management by 2025 |
| Blockchain Utilization | Limited pilots in supply chain and exemption tracking; early results show reductions in fraud-related errors by 85% |
Maximizing Savings with Strategic Planning and Policy Development

To truly harness the benefits of buy tax exempt options, organizations should adopt comprehensive exemption policies, foster interdepartmental coordination, and continuously monitor legislative shifts. Building a culture of compliance and awareness significantly enhances exemption utilization rates and mitigates risk exposure.
Framework for Effective Implementation
An actionable roadmap includes conducting baseline assessments, developing clear exemption procedures, training procurement staff, and instituting periodic compliance audits. Additionally, leveraging data analytics can reveal patterns and opportunities for further exemption optimization.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Training Effectiveness | Organizations reporting a 20% reduction in non-compliance incidents post-training |
| Audit Frequency | Quarterly audits increase exemption accuracy by 30% |
Frequently Asked Questions
What documentation is typically required to prove exemption eligibility?
+It varies by jurisdiction, but common documents include resale certificates, exemption certificates issued by taxing authorities, nonprofit certification documentation, and government agency permission slips. Ensuring these are current and valid is crucial to avoiding audit issues.
Can small businesses benefit equally from buy tax exempt options?
+Yes, provided they meet the criteria for exemption—such as reselling goods or qualifying as nonprofit or governmental entities. However, the complexity of compliance and the requirement for documentation may require dedicated administrative resources.
How do jurisdictions differ in their tax exemption policies?
+Exemption rules, eligible entities, and documentation requirements vary markedly across states and localities. Some jurisdictions offer tax holidays or reduced rates, while others impose strict certification processes. Staying abreast of local legislation is fundamental for practitioners.
What are the risks associated with misuse or fraudulent exemption claims?
+Risks include audits, penalties, back taxes, reputational damage, and legal sanctions. Enforcement agencies actively pursue violations, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive compliance measures and accurate record-keeping.