When Do Property Taxes Come Out

Understanding when property taxes are due is essential for homeowners and property owners alike. Property taxes, also known as real estate taxes, are a significant financial obligation and an important source of revenue for local governments and municipalities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of property taxes, exploring the factors that influence their due dates, the typical timelines, and the potential consequences of late payments.
Property taxes are a crucial component of the tax system, as they contribute to the funding of essential public services and infrastructure. These taxes are imposed on real estate properties, including residential homes, commercial buildings, and even vacant land. The revenue generated from property taxes is utilized to support local government operations, such as maintaining roads, funding public schools, and providing emergency services.
The Determinants of Property Tax Due Dates
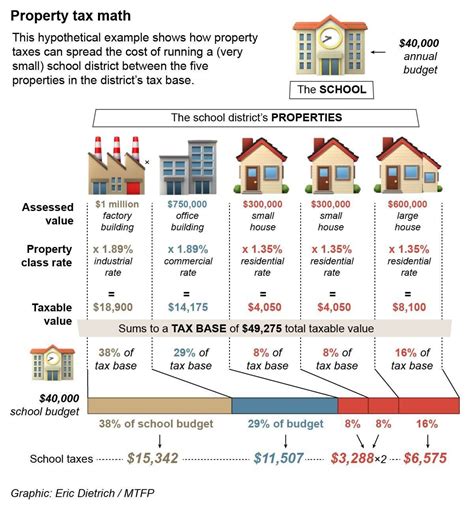
The timing of property tax payments can vary significantly depending on various factors, including the jurisdiction, local laws, and tax assessment processes. While some regions may have a uniform due date for all property owners, others may employ a more complex system with different deadlines based on property types or assessment methods.
One of the primary factors influencing property tax due dates is the tax assessment cycle. Local governments typically conduct periodic assessments to determine the value of properties within their jurisdiction. These assessments are used to calculate the property tax liabilities. The frequency of these assessments can range from annual to once every few years, and they play a crucial role in establishing the tax base.
Another critical determinant is the local government's budget cycle. Property taxes are a vital source of revenue for municipalities, and their due dates are often aligned with the financial year or budget period. This ensures a steady cash flow to support the provision of public services and infrastructure development.
Furthermore, the type of property can also impact the tax due dates. For instance, residential properties may have different payment schedules compared to commercial or industrial properties. Local governments may impose varying tax rates or assessment methods based on the nature of the property, leading to distinct due dates.
Understanding Typical Property Tax Timelines
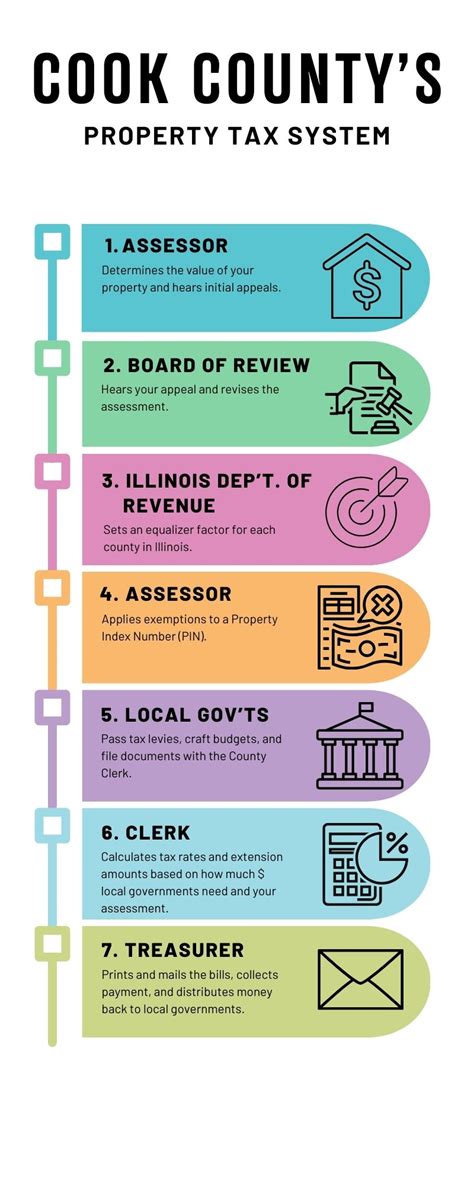
To provide a clearer picture, let's explore some common scenarios and timelines for property tax payments:
Annual Assessments and Due Dates
In many regions, property taxes are assessed annually. This means that property owners receive their tax assessment notices and corresponding due dates once a year. The assessment process involves evaluating the property's value based on factors such as location, size, improvements, and recent sales of comparable properties.
The due date for annual property taxes is often set a few months after the assessment notices are mailed out. This allows property owners sufficient time to review their assessments, seek any necessary adjustments, and make the necessary financial arrangements. For example, in some jurisdictions, the due date for annual property taxes may fall around June or July, following the assessment period.
Biennial or Triennial Assessments
In certain areas, property assessments are conducted less frequently, such as every two or three years. This approach is known as biennial or triennial assessments. In such cases, property owners may receive assessment notices and tax bills on a less regular basis.
For instance, a jurisdiction with biennial assessments might send out notices and due dates every two years, typically aligning the tax cycle with the local government's budget cycle. This provides property owners with a longer period to prepare for the payment and allows the government to plan its finances accordingly.
Staggered Due Dates for Different Property Types
Some regions employ a more nuanced approach by setting different due dates for various property types. This strategy aims to distribute the tax burden and administrative workload more evenly throughout the year.
For example, a local government might set due dates for residential properties in January, commercial properties in April, and industrial properties in July. This staggered approach ensures that property owners across different sectors have a more manageable payment schedule and reduces the strain on the local tax office during peak periods.
Consequences of Late Property Tax Payments
Failing to pay property taxes on time can have significant consequences for property owners. Local governments have various enforcement mechanisms in place to ensure timely payment and collect outstanding taxes.
One common consequence is the imposition of penalties and interest. Late payment penalties are designed to incentivize property owners to meet their tax obligations promptly. These penalties can accrue over time, adding to the overall tax liability. Additionally, interest may be charged on the outstanding tax amount, further increasing the financial burden.
In more severe cases, property liens may be placed on the property. A lien gives the local government the legal right to claim the property as payment for the outstanding taxes. This can lead to foreclosure proceedings if the taxes remain unpaid. Property owners facing liens may also find it challenging to sell or refinance their properties until the lien is resolved.
Furthermore, late property tax payments can impact credit scores and financial stability. Lenders and financial institutions often consider tax payment history when assessing an individual's creditworthiness. Late or missed payments can reflect negatively on credit reports, potentially affecting future loan approvals and interest rates.
Strategies for Effective Property Tax Management
To avoid the pitfalls of late payments and associated consequences, property owners can employ several strategies to manage their property taxes effectively:
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on the local tax assessment processes, due dates, and any changes to the tax system. Subscribe to official notifications or follow local government websites to receive timely information.
- Review Assessments: Carefully review your property tax assessment notices. Ensure that the assessed value is accurate and reflects the current market conditions. If you believe the assessment is incorrect, seek professional advice and consider appealing the decision within the specified timeframe.
- Budget Planning: Incorporate property tax payments into your annual financial planning. Allocate funds specifically for these obligations to ensure timely payments. Consider setting up automatic payments or reminders to avoid missing deadlines.
- Explore Payment Options: Many local governments offer flexible payment plans or installment options. Explore these alternatives to spread out the tax burden and make payments more manageable. Some jurisdictions may also provide discounts for early payments.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with tax professionals or financial advisors who specialize in property tax matters. They can provide valuable insights, assist with tax planning, and help you optimize your tax obligations while ensuring compliance.
Conclusion
Understanding when property taxes come out is crucial for responsible property ownership. By familiarizing yourself with the local tax assessment processes, due dates, and potential consequences of late payments, you can effectively manage your financial obligations and contribute to the development of your community. Stay informed, plan ahead, and seek professional guidance when needed to navigate the complexities of property taxes with confidence.
FAQs
What happens if I miss the property tax due date?
+Missing the property tax due date can result in penalties, interest charges, and potential legal consequences. It is important to pay attention to the due dates and plan your finances accordingly to avoid any late payment issues.
Can I appeal my property tax assessment if I disagree with the value?
+Yes, you have the right to appeal your property tax assessment if you believe the assessed value is incorrect. The process for appealing varies by jurisdiction, but typically involves submitting an appeal within a specified timeframe and providing supporting evidence to justify your claim.
Are there any payment plans available for property taxes?
+Many local governments offer payment plans or installment options for property taxes. These plans allow you to spread out your tax payments over a period of time, making it more manageable. Contact your local tax office to inquire about the available payment plan options.
How can I stay updated on property tax due dates and changes in my area?
+Stay informed by regularly checking your local government’s website or subscribing to their official notifications. They often provide important updates and announcements regarding property tax due dates, assessment processes, and any changes to the tax system. Additionally, you can follow local news sources or join community forums to stay connected with fellow property owners.



