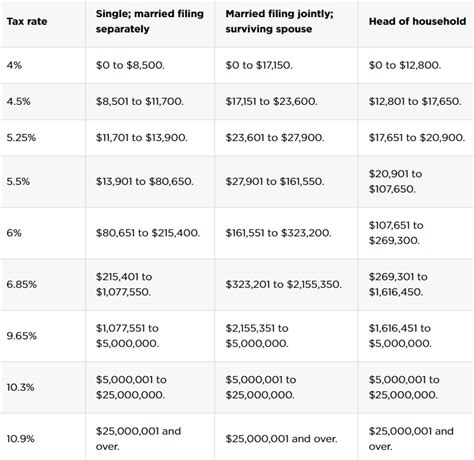
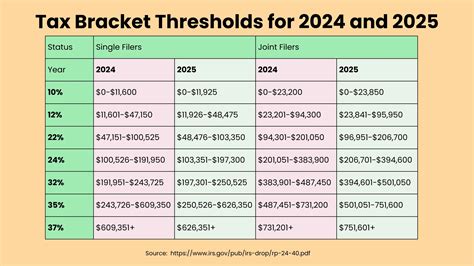
Avoid As One's Taxes Nyt

Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the topic "Avoiding Taxes: Unraveling the Strategies and Their Implications."
Taxes are an integral part of any economy, providing the necessary revenue for governments to function and support various public services. However, the concept of tax avoidance, often confused with tax evasion, has gained attention for its controversial nature and impact on global economies. This article aims to delve into the strategies employed by individuals and corporations to minimize their tax liabilities, the ethical considerations surrounding these practices, and the potential consequences for society as a whole.
The Evolution of Tax Avoidance Strategies

Tax avoidance is not a new phenomenon; it has evolved alongside tax systems themselves. Over the years, individuals and businesses have devised creative ways to reduce their tax burdens, often leveraging loopholes and legal complexities within tax laws. These strategies have become increasingly sophisticated, particularly with the advent of globalization and the rise of international tax planning.
Historical Context
The history of tax avoidance can be traced back to ancient civilizations. For instance, in ancient Egypt, farmers would underreport their crop yields to reduce their tax obligations. Fast forward to the 21st century, and we see a much more complex landscape, with multinational corporations utilizing intricate structures to minimize their global tax bills.
Modern Strategies
In today's globalized world, tax avoidance strategies have become an art form. Here are some common techniques employed by those seeking to minimize their tax liabilities:
- Transfer Pricing: Multinational corporations often engage in complex transactions between their subsidiaries, allowing them to shift profits to jurisdictions with lower tax rates. This strategy, known as transfer pricing manipulation, can significantly reduce tax liabilities.
- Offshore Accounts: Setting up offshore bank accounts or shell companies in tax havens is a well-known tactic to avoid taxes. These jurisdictions offer minimal taxation and often provide anonymity, making it difficult for tax authorities to track financial activities.
- Tax Shelters: Tax shelters are investment strategies designed to reduce tax liabilities. They often involve complex financial instruments and may be marketed as legitimate tax-saving opportunities, but they can sometimes blur the line between avoidance and evasion.
- Double Taxation Agreements: Countries often sign double taxation agreements to avoid taxing income twice. However, these agreements can be exploited to reduce tax obligations by strategically routing income through multiple jurisdictions.
- Intra-Group Loans: Corporations may use intra-group loans, where one subsidiary lends money to another at a favorable interest rate, effectively shifting profits and reducing tax liabilities in high-tax jurisdictions.
The Ethical Dilemma: Avoidance vs. Evasion

Tax avoidance and tax evasion are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts with different legal and ethical implications.
Tax Avoidance
Tax avoidance is the legal utilization of tax laws to minimize one's tax burden. It involves finding creative ways to structure transactions or take advantage of legal loopholes, all within the boundaries of the law. While tax avoidance is legal, it raises ethical questions about fairness and the role of taxation in society.
Tax Evasion
Tax evasion, on the other hand, is the illegal act of concealing income or assets to avoid paying taxes. This can involve providing false information to tax authorities, failing to report income, or using fraudulent means to reduce tax liabilities. Tax evasion is a criminal offense and can result in severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
The Gray Area
The distinction between avoidance and evasion is not always clear-cut. Some tax avoidance strategies, while technically legal, may push the boundaries of ethical behavior. For instance, aggressively interpreting tax laws to one's advantage may be legal but could be seen as morally questionable.
The Impact on Society and the Economy
Tax avoidance, especially on a large scale, can have significant implications for societies and economies. Here are some key considerations:
Revenue Loss for Governments
When individuals or corporations successfully avoid taxes, governments lose out on potential revenue. This revenue is crucial for funding public services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social welfare programs. A substantial loss in tax revenue can lead to budget deficits and a strain on public finances.
Inequality and Social Justice
Tax avoidance, particularly by high-net-worth individuals and multinational corporations, can exacerbate income inequality. While some individuals and businesses find ways to minimize their tax obligations, others, especially those with lower incomes, may have limited access to such strategies. This can create a sense of injustice and contribute to social disparities.
Global Tax Competition
The rise of tax avoidance strategies has led to a global tax competition among countries. Jurisdictions compete to attract businesses and investors by offering lower tax rates or more favorable tax regimes. While this competition can stimulate economic growth, it can also lead to a "race to the bottom," where countries continuously lower tax rates to remain competitive, potentially harming their ability to fund public services.
Complexity and Compliance
The increasing complexity of tax avoidance strategies has made tax compliance more challenging for both individuals and businesses. Staying compliant with tax laws requires a deep understanding of often intricate and ever-changing regulations. This complexity can lead to higher costs for compliance and increased burdens on taxpayers.
Future Implications and Potential Solutions
Addressing the challenges posed by tax avoidance requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some potential strategies and their implications:
International Cooperation
Enhancing international cooperation is crucial to combating tax avoidance. Initiatives like the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project, led by the OECD, aim to standardize tax rules and prevent multinational corporations from exploiting loopholes. Increased information sharing among tax authorities can also help identify and address tax avoidance strategies.
Simplification of Tax Laws
Simplifying tax laws and regulations can make it more difficult for individuals and corporations to find loopholes. Clear and straightforward tax rules can reduce the incentive for aggressive tax planning and make compliance more accessible.
Tax Havens and Transparency
Addressing the issue of tax havens is essential. Encouraging transparency and information exchange between jurisdictions can help identify and close down tax havens, reducing the incentives for tax avoidance. This may involve international agreements and sanctions against countries that facilitate tax avoidance.
Public Awareness and Education
Promoting public awareness and education about tax issues can foster a sense of responsibility and understanding. When individuals and businesses are aware of the implications of tax avoidance, they may be less likely to engage in such practices.
Ethical Tax Planning
Encouraging ethical tax planning practices can help shift the focus from aggressive tax avoidance to responsible tax management. Tax professionals and advisors can play a crucial role in promoting transparency and ensuring that tax strategies align with ethical standards.
Conclusion

Tax avoidance is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a nuanced understanding. While it is essential to acknowledge the legal right of individuals and businesses to minimize their tax liabilities, the potential consequences for society and the economy cannot be ignored. By fostering international cooperation, simplifying tax laws, and promoting ethical tax practices, we can strive for a more equitable and sustainable tax system.
What is the difference between tax avoidance and tax evasion?
+Tax avoidance is a legal practice where individuals or businesses use strategies within the boundaries of the law to minimize their tax liabilities. Tax evasion, on the other hand, is an illegal act involving the concealment of income or assets to avoid paying taxes.
How does tax avoidance impact the economy and society?
+Tax avoidance can lead to revenue loss for governments, affecting their ability to fund public services. It can also exacerbate income inequality and create a sense of injustice. Additionally, it contributes to global tax competition, which may harm a country’s ability to maintain adequate tax rates for public services.
What are some common tax avoidance strategies used by corporations?
+Common strategies include transfer pricing manipulation, setting up offshore accounts in tax havens, using tax shelters, and exploiting double taxation agreements. These tactics aim to shift profits to lower-tax jurisdictions, reducing overall tax liabilities.