Austin Sales Tax

Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Austin Sales Tax, a critical component of the city's economic landscape. In this in-depth exploration, we delve into the intricacies of sales tax regulations in Austin, Texas, offering a clear understanding of the laws, rates, and their implications for both residents and businesses. Our goal is to provide an expert analysis that informs and empowers, ensuring you have the knowledge to navigate the complex world of sales tax with confidence.
Understanding Austin’s Sales Tax Landscape

Sales tax in Austin, like in many other U.S. cities, is a vital source of revenue for the local government, contributing significantly to the city’s infrastructure, services, and overall economic health. The City of Austin, with its vibrant economy and diverse business landscape, has a unique sales tax structure that warrants a detailed examination.
The Basics of Sales Tax in Austin
Sales tax in Austin is a consumption tax, imposed on the sale of tangible goods and certain services. It is a percentage-based tax, meaning the amount of tax due is calculated as a percentage of the purchase price. This tax is collected by businesses and remitted to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts, the state agency responsible for tax administration.
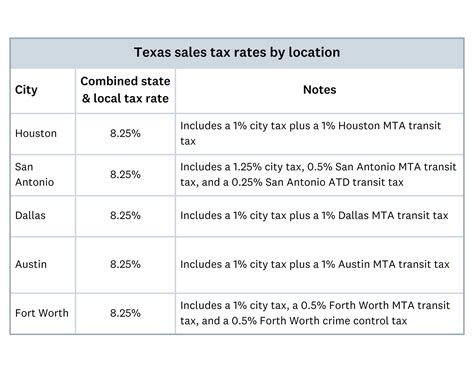
The current sales tax rate in Austin is composed of several layers: the state sales tax rate, the local option sales tax (LOST), and the municipal sales tax. Understanding each of these components is crucial for businesses and consumers alike.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| State Sales Tax | 6.25% |
| Local Option Sales Tax (LOST) | 1.25% |
| Municipal Sales Tax | 1.5% |
The state sales tax of 6.25% is a standard rate across Texas and is applied uniformly to all qualifying transactions. The LOST, often used to fund specific projects or services, is a variable rate that can differ between cities and counties within the state. In Austin's case, the LOST rate is 1.25%, bringing the total state and local option sales tax to 7.5%.
The municipal sales tax of 1.5% is unique to the City of Austin and is used to support city-specific initiatives and operations. Thus, the total sales tax rate in Austin is 8.75%, one of the highest in the state.
Sales Tax Registration and Collection
Businesses operating within Austin city limits are required to register for a sales tax permit with the Texas Comptroller’s Office. This permit authorizes the business to collect sales tax on behalf of the state and local government.
The collection process involves adding the applicable sales tax to the retail price of the goods or services sold. This amount is then remitted to the state on a regular basis, typically monthly or quarterly, depending on the business's sales volume.
For businesses with online sales or those that operate across multiple locations, the sales tax collection process can be more complex, often requiring specialized software and strategies to ensure compliance with varying tax rates and regulations.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The sales tax landscape in Austin has a profound impact on both businesses and consumers. Understanding these implications is key to making informed economic decisions and navigating the city’s business environment effectively.
Effect on Businesses
For businesses, the sales tax rate in Austin can significantly influence pricing strategies and profit margins. A high sales tax rate can reduce the competitiveness of a business’s pricing, particularly when compared to online retailers or businesses located in areas with lower tax rates.
Businesses in Austin must also contend with the administrative burden of sales tax compliance. This includes registering for sales tax permits, calculating and collecting the correct tax amounts, and filing regular sales tax returns. Non-compliance can result in penalties and interest charges, so accurate record-keeping and timely filing are essential.
Moreover, the complex nature of sales tax regulations, with varying rates and exemptions, can pose challenges for businesses, especially those new to the city or those without dedicated accounting or tax compliance staff.
Effect on Consumers
From a consumer perspective, the sales tax rate in Austin can influence purchasing decisions and overall consumer spending. A higher sales tax rate can increase the cost of living, particularly for those on fixed incomes or those with limited financial means.
However, the revenue generated from sales tax also funds essential city services, such as public transportation, schools, and public safety, which can directly benefit residents. So, while the tax may increase the cost of purchases, it also contributes to the overall well-being and quality of life in the city.
Additionally, consumers can benefit from sales tax holidays that the state and city may occasionally offer, particularly for back-to-school shopping or certain categories of goods. These tax-free periods can provide significant savings for consumers.
Compliance and Exemptions
Navigating the world of sales tax compliance in Austin can be complex, but understanding the regulations and exemptions can help businesses and consumers alike.
Sales Tax Compliance for Businesses
For businesses, compliance with sales tax regulations is a legal obligation. This involves collecting the correct amount of tax, remitting it on time, and maintaining accurate records. Failure to comply can result in penalties and interest charges, as well as potential legal consequences.
To ensure compliance, businesses should consider the following:
- Registration: Ensure your business is properly registered with the Texas Comptroller's Office and has the necessary permits to collect sales tax.
- Training: Provide adequate training to staff members involved in sales and accounting to ensure they understand the sales tax collection process and can identify tax-exempt transactions.
- Software: Invest in reliable sales tax software that can automatically calculate and track sales tax based on the customer's location and the nature of the transaction.
- Regular Filing: Adhere to the scheduled filing deadlines. Late filing can result in penalties and interest charges.
- Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all sales transactions, including the date, amount, and tax collected. This is essential for audit purposes and ensures accurate tax reporting.
Sales Tax Exemptions
While sales tax is applied to most retail transactions, there are certain sales tax exemptions in Austin that businesses and consumers should be aware of. These exemptions can significantly reduce the overall tax burden.
Some common sales tax exemptions in Austin include:
- Food: Many food items, especially unprepared food products, are exempt from sales tax.
- Prescription Drugs: Sales tax is not applied to the purchase of prescription medications.
- Certain Services: Some services, like medical and legal services, are exempt from sales tax.
- Resale: Goods purchased for resale are typically exempt from sales tax, provided the purchaser has a valid sales tax permit and the goods are not consumed or used by the purchaser.
It's important to note that while these are common exemptions, the list is not exhaustive, and specific transactions may have unique considerations. Businesses should consult with tax professionals or refer to the Texas Comptroller's Office guidelines for a comprehensive understanding of sales tax exemptions.
Sales Tax for Online Businesses
In today’s digital age, the sales tax landscape for online businesses in Austin is particularly complex. With the rise of e-commerce, the rules for sales tax collection and remittance have evolved significantly.
Sales Tax for Online Sales
For online businesses, the sales tax collection process is influenced by the Nexus, a legal term referring to a business’s connection or presence in a state. If an online business has a physical presence, or Nexus, in Austin, it is generally required to collect sales tax on all sales delivered to Austin addresses.
The determination of Nexus can be complex and may include factors such as having employees, affiliates, or warehouses within the state. The presence of even a single sales representative in Austin could establish Nexus, triggering the requirement to collect sales tax.
Economic Nexus
In addition to physical presence, Economic Nexus is another critical factor for online businesses. This concept, established by the South Dakota v. Wayfair, Inc. Supreme Court ruling, allows states to require out-of-state sellers to collect and remit sales tax if they meet certain economic thresholds, such as a minimum number of transactions or a minimum amount of sales in the state.
For online businesses, this means that even if they have no physical presence in Austin, they may still be required to collect sales tax if their sales into the city exceed the Economic Nexus threshold set by the state of Texas.
Marketplace Facilitator Laws
Online marketplaces, like Amazon and eBay, have been subject to Marketplace Facilitator Laws in many states, including Texas. These laws require the marketplace itself to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the third-party sellers using their platform.
For businesses selling on these platforms, this means that the marketplace will handle the sales tax collection and remittance process, simplifying the tax compliance aspect of their operations.
Sales Tax for Remote Sellers

For remote sellers, those without a physical presence in Austin, the sales tax landscape can be particularly challenging. The advent of Economic Nexus and Marketplace Facilitator Laws has significantly impacted the way remote sellers operate and their obligations to collect and remit sales tax.
Economic Nexus and Remote Sellers
The Economic Nexus rules, as mentioned earlier, have broadened the reach of sales tax collection requirements. Remote sellers who meet the state’s Economic Nexus threshold are now required to collect and remit sales tax, even if they have no physical presence in Austin.
This threshold is typically based on the number of transactions or the total sales volume into the state. For example, a remote seller might be required to collect sales tax if they make over 200 transactions or have $100,000 in sales in Texas within a calendar year.
Use Tax and Remote Sellers
In addition to sales tax, remote sellers should be aware of Use Tax, a tax that is imposed on the use, storage, or consumption of goods or services purchased from an out-of-state seller. While the seller may not collect sales tax, the buyer is responsible for paying the equivalent amount in Use Tax.
The Use Tax rate in Austin is the same as the sales tax rate, 8.75%. This tax is typically self-reported by the buyer on their state tax return, ensuring that purchases from out-of-state sellers are not tax-free.
Marketplace Facilitator Laws and Remote Sellers
For remote sellers operating on online marketplaces, the Marketplace Facilitator Laws can provide a level of simplicity and security. These laws require the marketplace to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the sellers, ensuring compliance and removing the administrative burden from the sellers themselves.
However, it's important for remote sellers to understand that while the marketplace handles the tax collection, they are still responsible for the accuracy of the tax amounts and may be liable for any discrepancies or non-compliance.
Future Trends and Developments
The sales tax landscape in Austin, like in many cities across the U.S., is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and evolving legal frameworks.
Impact of E-commerce and Digital Sales
The rise of e-commerce and digital sales has had a significant impact on the sales tax landscape in Austin. With more transactions taking place online, the traditional physical presence-based tax collection system has become increasingly outdated and difficult to enforce.
The Economic Nexus rules, as discussed earlier, are a response to this shift, ensuring that even remote sellers who have significant economic connections to the state are required to collect and remit sales tax.
Potential Changes in Sales Tax Rates
Sales tax rates in Austin, like in other cities, can be subject to change based on various factors, including economic conditions, budgetary needs, and public policy decisions. While the current rate of 8.75% has been stable for some time, there is always the potential for adjustments in the future.
Any changes in the sales tax rate would have significant implications for both businesses and consumers. A rate increase could make Austin less competitive in terms of pricing, while a rate decrease could stimulate economic growth and consumer spending.
Potential Sales Tax Holidays
Sales tax holidays, temporary periods when sales tax is not collected on certain types of purchases, have become a popular tool used by states and cities to stimulate the economy and provide relief to consumers.
While Austin has not historically observed many sales tax holidays, there is potential for future implementation, particularly if neighboring cities or states adopt similar measures. Sales tax holidays can provide significant savings for consumers and boost retail sales, especially for big-ticket items like electronics or school supplies.
The Role of Technology in Sales Tax Compliance
Advancements in technology, particularly in the realm of sales tax software, are transforming the way businesses approach sales tax compliance. These tools can automate the sales tax calculation process, ensuring accuracy and compliance with varying tax rates and regulations.
Moreover, with the increasing complexity of sales tax laws, especially for online and remote sellers, these technologies can provide valuable support in staying compliant and avoiding costly penalties.
Conclusion
The sales tax landscape in Austin is a complex but critical aspect of the city’s economy, impacting both businesses and consumers in significant ways. Understanding the rates, regulations, and exemptions is key to navigating this landscape successfully.
For businesses, compliance with sales tax regulations is essential for legal and financial reasons. The high sales tax rate in Austin can influence pricing strategies and competitiveness, while also contributing to the funding of essential city services.
Consumers, on the other hand, face increased costs due to the sales tax, but they also benefit from the services and infrastructure that the tax revenue supports. Sales tax holidays can provide occasional relief and savings.
As the sales tax landscape continues to evolve, particularly with the rise of e-commerce and digital sales, staying informed and adapting to changes is crucial for both businesses and consumers alike. With the right understanding and tools, navigating the world of Austin sales tax can be a smoother and more manageable process.
What is the current sales tax rate in Austin, Texas?
+The current sales tax rate in Austin, Texas is 8.75%, which includes the state sales tax rate of 6.25%, a local option sales tax (LOST) of 1.25%, and a municipal sales tax of 1.5%.