Ad Valorem Tax Meaning

In the realm of taxation, understanding the nuances of different tax types is essential for both individuals and businesses. Among these, the ad valorem tax stands out as a unique and widely implemented form of taxation. Ad valorem taxes, often associated with property taxes, are a cornerstone of many revenue systems worldwide. This article aims to delve into the intricate details of ad valorem taxes, exploring their definition, types, calculation methods, and their significance in the broader context of fiscal policy.
Understanding Ad Valorem Taxes
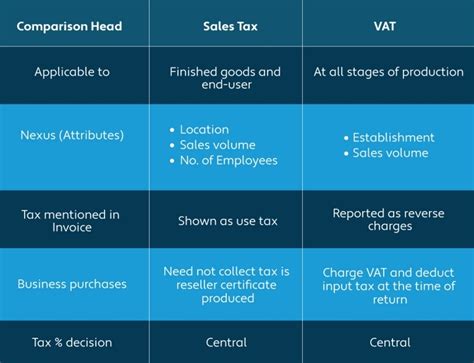
Ad valorem taxes, derived from the Latin phrase meaning “according to value,” are a type of tax imposed on the value of goods, services, or property. This value-based taxation differs from other tax types like specific taxes (based on quantity) or excise taxes (levied on certain products or services). Ad valorem taxes are a percentage of the value of the item or property being taxed, making them a flexible and adaptable form of taxation.
These taxes play a pivotal role in generating revenue for governments, local authorities, and municipalities. They are commonly associated with property taxes, where the tax amount is calculated as a percentage of the assessed value of the property. However, ad valorem taxes extend beyond property and are also applied to a range of goods, commodities, and services, contributing significantly to global tax systems.
Types of Ad Valorem Taxes

Ad valorem taxes encompass a variety of forms, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Property Taxes
One of the most well-known ad valorem taxes is the property tax. This tax is imposed on real estate, including land and buildings, and is a primary source of revenue for local governments. The tax amount is typically calculated as a percentage of the assessed value of the property. For instance, if a property is valued at 500,000 and the tax rate is 1.5%, the annual property tax would be 7,500.
Property taxes are crucial for funding local services such as schools, fire departments, and road maintenance. The assessment process involves regular evaluations to ensure the tax remains fair and proportionate to the property's value.
Customs Duties
Ad valorem taxes are also prevalent in international trade, where they are known as customs duties. These taxes are levied on imported goods based on their value, with rates varying depending on the country of origin and the nature of the product. Customs duties serve multiple purposes, including generating revenue, protecting domestic industries, and regulating trade flows.
For example, consider a country that imposes a 10% ad valorem tax on imported electronics. If a laptop valued at $1,000 is imported, the customs duty would amount to $100. This not only provides revenue but also makes imported goods slightly more expensive, potentially encouraging the purchase of locally produced alternatives.
Sales Taxes
Sales taxes are another common form of ad valorem taxation. These taxes are added to the purchase price of goods or services and are typically calculated as a percentage of the total price. Sales taxes can vary across jurisdictions, with some states or provinces having higher rates than others.
For instance, if a state has a sales tax rate of 8%, a customer purchasing a $500 smartphone would pay an additional $40 in sales tax. Sales taxes are often used to fund specific projects or initiatives and can provide a stable source of revenue for governments.
Calculation Methods
The calculation of ad valorem taxes involves several key steps, each influenced by various factors.
Assessment of Value
Determining the value of the item or property being taxed is the first critical step. For property taxes, this involves an assessment process where professional appraisers evaluate the property’s market value. In the case of goods and services, the value is often based on the transaction price or a standard valuation method.
For instance, when assessing the value of a piece of land for property tax purposes, appraisers consider factors such as location, size, and potential uses. This assessment ensures that the tax burden is distributed fairly among property owners.
Tax Rate Determination
The tax rate is a crucial factor in ad valorem taxation. Tax rates can vary significantly, depending on the jurisdiction and the type of tax. Property taxes, for example, may have rates that differ between residential and commercial properties, with the latter often facing higher rates.
Consider a city with a residential property tax rate of 1.2% and a commercial property tax rate of 1.8%. A homeowner with a property valued at $400,000 would pay $4,800 in taxes, while a business owner with a property valued at the same amount would pay $7,200.
Exemptions and Deductions
Ad valorem taxes often include provisions for exemptions and deductions, which can reduce the taxable value or the overall tax liability. These provisions are designed to provide relief to certain taxpayers or to encourage specific behaviors.
For instance, many jurisdictions offer property tax exemptions for seniors or veterans, reducing the taxable value of their properties. Similarly, businesses may be eligible for deductions based on the type of industry or the level of investment they make in the local economy.
Significance and Impact
Ad valorem taxes have a profound impact on both the economy and society.
Revenue Generation
These taxes are a significant source of revenue for governments at all levels. Property taxes, in particular, provide a stable and predictable income stream for local authorities, enabling them to fund essential services and infrastructure projects.
For example, a large city's property tax revenue can reach billions of dollars annually, allowing for substantial investments in education, public transportation, and urban development.
Equity and Progressivity
Ad valorem taxes can promote equity and progressivity in the tax system. By taxing higher-value properties or goods at a higher rate, these taxes can ensure that those with greater means contribute a larger share of their wealth to the public purse.
This progressive aspect is evident in the graduated tax rates seen in many property tax systems, where higher-value properties face a higher tax rate, resulting in a more equitable distribution of the tax burden.
Economic Impact
Ad valorem taxes can influence economic behavior and decision-making. For instance, higher sales taxes may encourage consumers to seek out alternatives or to make purchases in jurisdictions with lower tax rates. Similarly, customs duties can affect international trade patterns and the competitiveness of domestic industries.
Businesses may respond to ad valorem taxes by adjusting their pricing strategies or by seeking to reduce their tax liability through various means, such as tax planning or relocating their operations.
Conclusion

Ad valorem taxes are a versatile and integral part of modern tax systems. From property taxes to customs duties and sales taxes, these value-based levies play a critical role in funding public services, promoting equity, and shaping economic behavior.
Understanding the intricacies of ad valorem taxes is essential for individuals and businesses alike, as it allows for informed decision-making and a deeper appreciation of the complex world of taxation. As tax systems continue to evolve, ad valorem taxes will remain a key component, shaping the fiscal landscape for years to come.
What is the difference between ad valorem taxes and specific taxes?
+Ad valorem taxes are based on the value of the item or property being taxed, while specific taxes are levied based on the quantity or unit of measurement. For instance, a specific tax might be $10 per gallon of gasoline, regardless of its market value.
How are property tax rates determined?
+Property tax rates are set by local governments and can vary based on factors such as the type of property (residential or commercial), the location, and the budget needs of the jurisdiction. These rates are often approved through public hearings and legislative processes.
Are ad valorem taxes regressive or progressive?
+Ad valorem taxes can be either regressive or progressive, depending on the specific tax system and the design of the tax rates. A regressive tax system would mean that lower-value properties or goods face a higher effective tax rate, while a progressive system would tax higher values at a higher rate.