529 Savings Plan Tax Deduction
For those with long-term educational savings goals, the 529 plan stands as a cornerstone strategy, offering not just a pathway to funding future educational expenses but also a mechanism for substantial tax benefits. This article delves into the intricacies of the 529 Savings Plan, exploring its tax advantages, eligibility criteria, contribution limits, and the myriad of investment options it presents. We'll also examine real-world examples to illustrate the plan's effectiveness, providing a comprehensive guide to help you make informed decisions about your financial future.
Unraveling the 529 Savings Plan: A Comprehensive Overview

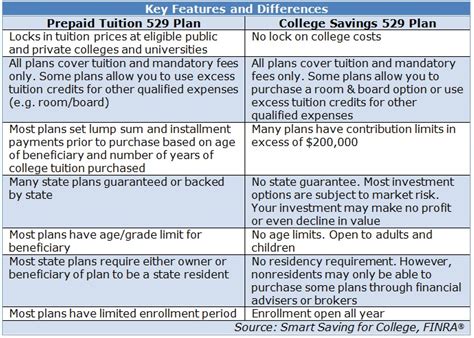
The 529 plan, named after Section 529 of the Internal Revenue Code, is a tax-advantaged savings plan designed to help families and individuals set aside funds for future educational expenses. These plans are sponsored by states, state agencies, or educational institutions and offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive option for long-term educational savings.
Tax Benefits: The Heart of the 529 Plan
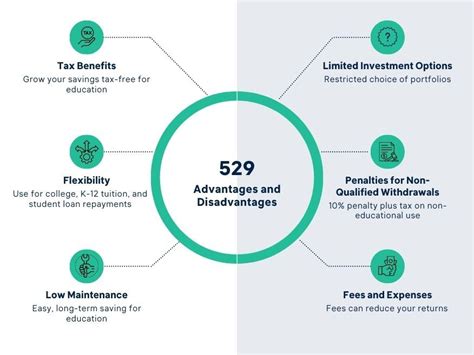
The tax advantages of the 529 plan are its key allure. Earnings within the plan grow tax-free, and qualified distributions are exempt from federal taxes. This means that, unlike traditional savings accounts, the money in a 529 plan is not subject to federal tax when it’s time to withdraw, provided the funds are used for qualified educational expenses. This tax-free growth can significantly boost the plan’s value over time, making it an efficient tool for long-term savings.
Additionally, many states offer state tax benefits for contributions to their 529 plans. This could mean deductions on state tax returns or even tax credits, further enhancing the savings potential of the plan. For instance, in California, contributions to the state's ScholarShare College Savings Plan are tax-deductible up to $4,000 for single filers and $8,000 for joint filers.
Eligibility and Contribution Limits
The 529 plan is open to a wide range of individuals, including parents, grandparents, and even friends of the beneficiary. There are no income limits or age restrictions, making it accessible to most people. However, there are contribution limits, which vary depending on the state and the specific plan.
For example, the Ohio CollegeAdvantage 529 Plan has an annual contribution limit of $2,000 per beneficiary, with a maximum lifetime contribution of $361,000. On the other hand, the Nevada Prepaid Tuition Program allows contributions up to the full cost of attendance at a Nevada public university, which can be a significant amount.
Investment Options: Diversifying for the Future
529 plans offer a variety of investment options to cater to different risk tolerances and investment horizons. These options typically include age-based portfolios, static investment portfolios, and even individual securities. Age-based portfolios automatically adjust their asset allocation as the beneficiary grows older, becoming more conservative as college approaches.
For instance, the Nebraska College Savings Plan offers nine different investment portfolios, ranging from conservative to aggressive. Their age-based option, called the "Nebraska Age-Based Enrollment Portfolio," automatically adjusts the asset allocation based on the beneficiary's age, providing a balanced approach to savings.
| Plan Name | Annual Contribution Limit | Lifetime Contribution Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Ohio CollegeAdvantage 529 Plan | $2,000 | $361,000 |
| Nevada Prepaid Tuition Program | Full cost of attendance | Full cost of attendance |
| Nebraska College Savings Plan | No specific limit | No specific limit |

Real-World Examples: Success Stories
To illustrate the effectiveness of the 529 plan, let’s consider a few real-world scenarios. Mr. and Mrs. Smith, residents of Florida, started a 529 plan for their daughter when she was born. Over 18 years, they contributed a total of 30,000, taking advantage of the state's tax deductions. With the power of compound interest and tax-free growth, their initial investment grew to over 50,000, providing a substantial sum for their daughter’s college education.
In another example, Ms. Johnson, a single parent from New York, opened a 529 plan for her son. She contributed $200 per month, taking advantage of the state's 10% tax credit on contributions. Over 12 years, her contributions, along with the tax credits, grew to over $35,000, a significant achievement given her initial investment.
Maximizing the Benefits: Strategies and Considerations
To make the most of the 529 plan, there are several strategies to consider. First, start early. The power of compound interest works best when there’s a long time horizon. Second, consider the tax benefits of your state’s plan. Some states offer more generous tax benefits than others, so it’s worth researching the options.
Additionally, be mindful of the plan's flexibility. While the primary purpose is for higher education, there are a variety of qualified expenses, including tuition, room and board, books, and even computers. Understanding these qualified expenses can help you maximize the benefits of the plan.
The Future of 529 Plans: Expanding Horizons
The 529 plan is an evolving financial tool, with states and educational institutions constantly improving their offerings. In recent years, some states have expanded the use of 529 plans to include K-12 education expenses, providing even more flexibility for families. Furthermore, there’s a growing trend of plans offering investment options in ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) funds, allowing investors to align their savings with their values.
Looking ahead, the future of 529 plans is bright. With increasing awareness and the growing importance of higher education, these plans are likely to become an even more integral part of financial planning. The continued innovation in investment options and the potential for further tax benefits make the 529 plan a dynamic and exciting financial tool.
Conclusion
The 529 Savings Plan is a powerful tool for long-term educational savings, offering a unique combination of tax advantages, investment options, and flexibility. By understanding the intricacies of these plans and making informed decisions, individuals can effectively prepare for the future educational expenses of their loved ones. With the right strategy and a long-term view, the 529 plan can be a cornerstone of financial planning, providing a secure pathway to achieving educational goals.
Can I use a 529 plan for K-12 education expenses?
+Yes, some 529 plans allow for qualified K-12 education expenses. This includes private school tuition, special needs services, and even homeschooling expenses.
Are there penalties for early withdrawals from a 529 plan?
+Typically, early withdrawals are subject to income taxes and a 10% penalty. However, there are exceptions for certain qualified expenses, such as if the beneficiary receives a scholarship.
Can I use a 529 plan for international educational expenses?
+Yes, 529 plans can be used for international educational expenses as long as the institution is accredited and recognized by the U.S. Department of Education.