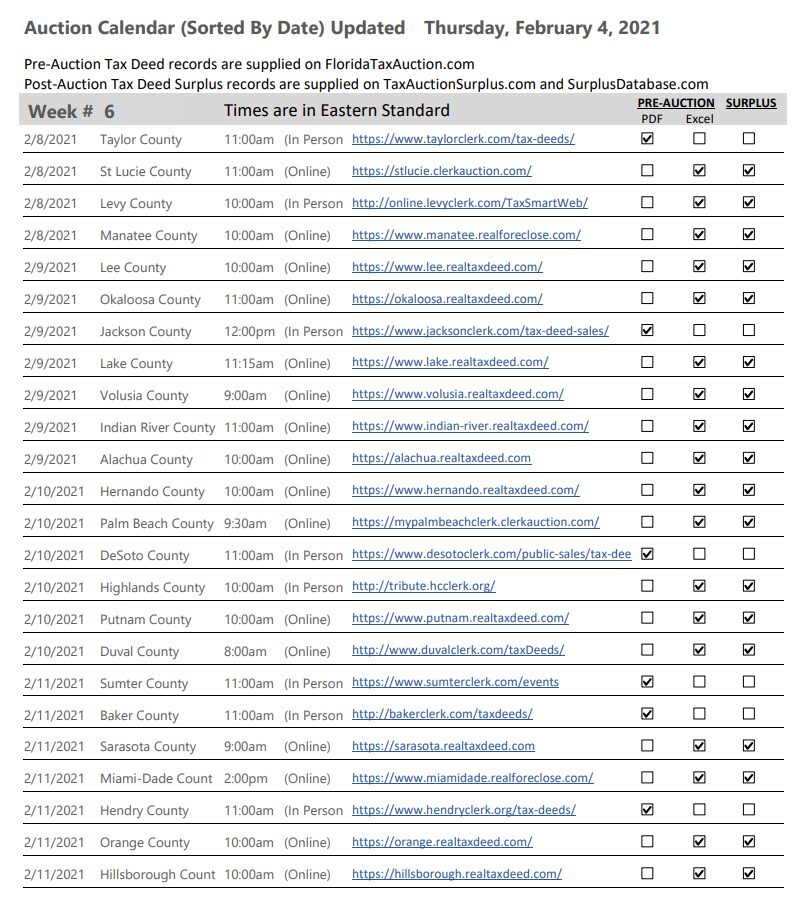
Property Tax Auction

Property tax auctions have become increasingly popular as a means for local governments to collect outstanding property taxes and offer investors and buyers unique opportunities. These auctions offer a unique avenue for property acquisition, often featuring properties with compelling histories and potential for redevelopment. This article delves into the world of property tax auctions, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and potential pitfalls, providing an insightful guide for both investors and the public.
Understanding Property Tax Auctions

Property tax auctions, also known as tax lien or tax deed sales, are public auctions conducted by local government agencies to recover unpaid property taxes. When a property owner fails to pay their property taxes, the government has the legal right to seize the property and sell it at auction to recoup the owed taxes, interest, and penalties.
These auctions are a crucial part of the tax collection process for many municipalities, providing a way to generate revenue and enforce property tax obligations. The properties up for auction can range from residential homes and commercial buildings to vacant land, each with its own unique circumstances and potential for development or investment.
The Auction Process
The process of a property tax auction varies slightly depending on the jurisdiction and type of auction. In a tax lien auction, investors purchase a lien on the property, which gives them the right to collect the debt, including taxes, interest, and penalties, from the property owner. If the debt is not repaid within a certain timeframe, the investor can initiate the process to acquire the property.
In contrast, a tax deed auction involves the direct sale of the property to the highest bidder. Here, the winning bidder immediately gains ownership of the property, often with a clear title, but may also assume responsibility for any outstanding taxes, liens, or other encumbrances.
| Auction Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Tax Lien Auction | Investors purchase liens, allowing potential property acquisition if debt is not repaid. |
| Tax Deed Auction | Direct property sale to highest bidder, with immediate ownership but potential encumbrances. |
Benefits and Opportunities
Property tax auctions offer a range of benefits and opportunities for both investors and the community:
Investment Opportunities
Investors can find attractive deals at property tax auctions, often purchasing properties at a fraction of their market value. These properties may require renovations or have unique challenges, but they also present the potential for significant returns through redevelopment, rental income, or resale.
For instance, an investor might purchase a tax lien on a property with a beautiful lakefront view but in need of extensive repairs. By acquiring the lien and subsequently the property, they can transform it into a desirable rental property or a luxurious home, reaping the benefits of the location and their investment.
Community Revitalization
Property tax auctions contribute to community revitalization efforts. By selling properties that have been neglected or abandoned due to non-payment of taxes, these auctions can lead to the redevelopment of neighborhoods, improving property values and the overall quality of life for residents.
In a case study, a city conducted a tax deed auction for a run-down commercial building in a struggling downtown area. The winning bidder transformed the building into a vibrant mixed-use development, bringing new businesses, residents, and a renewed sense of community to the area.
Tax Revenue Generation
Property tax auctions provide a crucial source of revenue for local governments. By selling properties with delinquent taxes, governments can recoup lost revenue, which can be reinvested into community services, infrastructure, and public works projects.
Consider a county facing a budget shortfall due to decreased property tax income. By holding a successful tax deed auction, they can generate significant revenue, allowing them to maintain vital services and plan for future community improvements.
Challenges and Considerations
While property tax auctions present attractive opportunities, they also come with their share of challenges and considerations:
Due Diligence
Conducting thorough due diligence is crucial when considering properties at auction. Investors should research the property’s history, including any outstanding liens, encumbrances, or legal issues. They should also assess the property’s physical condition, potential for redevelopment, and market demand.
A failure to perform adequate due diligence could result in unforeseen expenses or legal complications, undermining the potential benefits of the investment.
Risk of Ownership
Acquiring a property through a tax auction comes with the responsibility of ownership, including all associated costs and potential liabilities. Investors must be prepared to manage the property, including maintenance, repairs, and compliance with local regulations.
For example, an investor might purchase a property with the intent to flip it quickly for a profit. However, if they underestimate the extent of necessary repairs or face unexpected legal challenges, they could find themselves in a situation where the costs outweigh the potential gains.
Competitive Bidding
Property tax auctions often attract competitive bidding, especially for desirable properties. Investors must carefully consider their bidding strategy, taking into account their budget, potential returns, and the competitive landscape.
In a tax lien auction, for instance, investors must decide whether to bid aggressively to secure the lien or take a more conservative approach, allowing others to drive up the price and potentially increasing their chances of acquiring the property later.
Conclusion
Property tax auctions offer a unique intersection of investment opportunity and community impact. By understanding the process, benefits, and challenges, investors can navigate these auctions successfully, finding attractive properties with the potential for significant returns. Simultaneously, these auctions contribute to community revitalization and provide essential revenue for local governments.
Whether you're an experienced investor or a curious member of the public, exploring the world of property tax auctions can offer valuable insights into the complex interplay between real estate, finance, and community development.
What are the typical steps involved in a property tax auction?
+The process varies, but generally, it includes an announcement period, a registration and due diligence phase, the auction itself, and post-auction procedures for finalizing the sale and transferring ownership.
How can I find out about upcoming property tax auctions in my area?
+Check with your local government’s tax department or treasurer’s office. They often publish auction notices and provide information on the auction process and available properties.
Are there any risks associated with investing in properties through tax auctions?
+Yes, risks include unknown property conditions, legal issues, and potential competition from experienced bidders. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research and due diligence to mitigate these risks.
What happens if the winning bidder fails to complete the purchase after winning the auction?
+In most cases, the bidder forfeits their deposit, and the property may be resold at a later date. The specific consequences can vary depending on the jurisdiction and auction terms.



