Wi State Tax
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on the Wisconsin State Tax, an essential aspect of financial management for residents and businesses alike. Understanding the intricacies of state taxes is crucial for ensuring compliance and optimizing financial strategies. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of Wisconsin's tax system, providing you with a detailed overview and valuable insights.
Understanding Wisconsin State Tax: A Comprehensive Overview

The tax system in Wisconsin, like any other state, plays a vital role in funding public services, infrastructure, and social programs. It is a complex yet essential mechanism that ensures the smooth functioning of the state’s economy. Let’s explore the key components and unique features of Wisconsin’s tax landscape.
Income Tax in Wisconsin: Rates and Exemptions
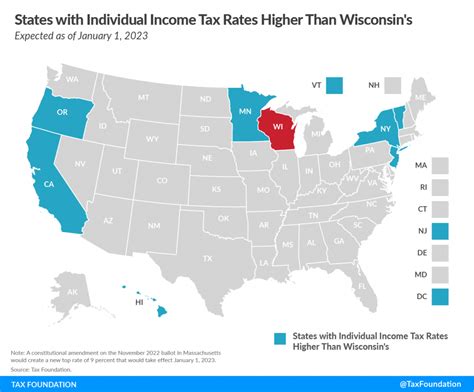
Wisconsin operates on a progressive income tax system, meaning that higher incomes are taxed at a higher rate. As of the current tax year, the state has four tax brackets with corresponding tax rates: 4.8%, 5.84%, 6.27%, and 7.65%. These rates are applicable to various income levels, with the highest rate kicking in for taxable incomes exceeding 232,240 for single filers and 285,300 for joint filers.
It's important to note that Wisconsin offers a variety of deductions and credits to help reduce the tax burden for individuals and families. Some of the notable deductions include those for dependents, education expenses, and retirement contributions. Additionally, the state provides tax credits for various circumstances, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit and the Child and Dependent Care Credit.
Here's a table outlining the income tax rates and brackets in Wisconsin:
| Tax Rate | Taxable Income Range |
|---|---|
| 4.8% | Up to $12,610 (Single) / Up to $15,760 (Joint) |
| 5.84% | $12,610 to $25,220 (Single) / $15,760 to $31,520 (Joint) |
| 6.27% | $25,220 to $176,120 (Single) / $31,520 to $232,240 (Joint) |
| 7.65% | Over $176,120 (Single) / Over $232,240 (Joint) |

These tax rates are subject to change annually, so it's advisable to refer to the official Wisconsin Department of Revenue website for the most up-to-date information.
Sales and Use Tax: A Look at Wisconsin’s Consumption Tax
In addition to income tax, Wisconsin imposes a sales and use tax on the sale or lease of tangible personal property and certain services. The base rate for sales tax in Wisconsin is 5%, which is applied to most retail transactions. However, certain jurisdictions within the state may levy additional taxes, known as local sales taxes, resulting in a higher overall sales tax rate.
It's important to understand that certain items are exempt from sales tax in Wisconsin. These exemptions include prescription drugs, most food items, and certain agricultural products. Additionally, Wisconsin offers a use tax, which is applicable to purchases made outside the state but used within Wisconsin. This ensures that all consumers contribute to the state's revenue, regardless of where they make their purchases.
For businesses operating in Wisconsin, it's crucial to be aware of the sales tax collection and remittance requirements. The state provides resources and guidance to help businesses comply with sales tax regulations, including registration processes and filing deadlines.
Property Tax: Assessing Wisconsin’s Real Estate Landscape
Property tax is a significant revenue source for local governments in Wisconsin, used to fund schools, fire departments, and other essential services. The property tax system in Wisconsin is decentralized, with individual counties and municipalities setting their own tax rates and assessment practices.
The property tax in Wisconsin is calculated based on the assessed value of the property and the applicable tax rate. The assessed value is determined through a process of appraisal and assessment, which varies across counties. This decentralization means that property tax rates can differ significantly between different areas within the state.
Homeowners in Wisconsin benefit from various property tax exemptions and credits, such as the Homestead Credit, which provides a tax credit to eligible homeowners. Additionally, the state offers a Property Tax Limit program, which caps the annual increase in property taxes for qualifying properties.
It's important for property owners to stay informed about their local tax assessments and rates, as these can have a significant impact on their financial planning. Regularly reviewing property tax bills and understanding the assessment process can help homeowners identify any discrepancies or potential challenges.
Business Taxes: Navigating the Landscape for Entrepreneurs
Wisconsin offers a business-friendly environment with a range of tax incentives and programs to support entrepreneurship and economic growth. The state’s business tax landscape includes various taxes and fees, such as the Corporate Franchise Tax, Unincorporated Business Tax, and Wisconsin Sales and Use Tax, among others.
For businesses, understanding the tax obligations and available incentives is crucial for financial planning and growth. Wisconsin provides resources and guidance to help businesses navigate the tax landscape, including tax registration processes, filing requirements, and tax incentive programs.
One notable incentive in Wisconsin is the Wisconsin Economic Development Corporation (WEDC) program, which offers a range of tax credits and grants to support business growth and job creation. This program aims to attract and retain businesses, making Wisconsin an attractive destination for entrepreneurs.
Wisconsin’s Tax Credits and Incentives: A Boost for Residents and Businesses
Wisconsin recognizes the importance of tax incentives in promoting economic development and supporting its residents. The state offers a variety of tax credits and incentives designed to benefit individuals, families, and businesses alike. These incentives aim to encourage investment, stimulate job growth, and provide financial relief to those in need.
For individuals, Wisconsin provides tax credits such as the Earned Income Tax Credit and the Homestead Credit, which help reduce the tax burden for low- and moderate-income households. Additionally, the state offers tax deductions for various expenses, including medical costs, dependent care, and education-related expenses.
Businesses, too, benefit from a range of tax incentives in Wisconsin. The state provides tax credits for job creation, research and development, and investment in certain industries. These incentives aim to attract and retain businesses, fostering economic growth and job opportunities.
One notable tax incentive program in Wisconsin is the Enterprise Zone Program, which offers tax benefits to businesses that locate or expand within designated Enterprise Zones. These zones are typically in economically distressed areas, and the program aims to stimulate economic development and create jobs.
Filing and Payment Options: Simplifying the Process for Taxpayers
Wisconsin offers a range of filing and payment options to cater to the diverse needs of its taxpayers. Whether you’re an individual filing your annual return or a business managing complex tax obligations, the state provides user-friendly platforms and resources to ensure a smooth and efficient process.
For individual taxpayers, Wisconsin offers the e-file option, allowing residents to file their tax returns electronically. This method is not only convenient but also secure, ensuring that your personal information remains protected. Additionally, the state provides the option to pay your taxes online through various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and electronic checks.
Businesses in Wisconsin have access to dedicated tax filing platforms and resources, such as the Wisconsin Online Filing System. This system enables businesses to file their tax returns, pay taxes, and manage their tax obligations efficiently. The platform offers a user-friendly interface, making it easier for businesses to stay compliant with state tax regulations.
Furthermore, Wisconsin provides resources and guidance to assist taxpayers in understanding their filing requirements and obligations. The state's website offers comprehensive information on tax forms, due dates, and payment options, ensuring that taxpayers have the necessary tools to navigate the tax filing process successfully.
Conclusion: Navigating Wisconsin’s Tax Landscape

Understanding Wisconsin’s tax system is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within the state. From income tax brackets to sales and use tax rates, property tax assessments, and a range of tax incentives, the state’s tax landscape is multifaceted. By staying informed and utilizing the resources provided by the Wisconsin Department of Revenue, taxpayers can navigate this landscape with confidence and ensure compliance with state tax regulations.
What is the income tax rate in Wisconsin for the current year?
+
As of the current tax year, Wisconsin has four income tax brackets with rates ranging from 4.8% to 7.65%. The specific rates and taxable income ranges can be found on the Wisconsin Department of Revenue website.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Wisconsin?
+
Yes, Wisconsin offers sales tax exemptions for certain items, including prescription drugs, most food items, and agricultural products. These exemptions aim to reduce the tax burden on essential goods.
How does Wisconsin’s property tax system work?
+
Wisconsin’s property tax system is decentralized, with individual counties and municipalities setting their own tax rates and assessment practices. The property tax is calculated based on the assessed value of the property and the applicable tax rate.
What tax incentives are available for businesses in Wisconsin?
+
Wisconsin offers a range of tax incentives for businesses, including tax credits for job creation, research and development, and investment in specific industries. These incentives aim to attract and retain businesses, fostering economic growth.
How can I file my Wisconsin state tax return online?
+
To file your Wisconsin state tax return online, you can use the e-file option provided by the Wisconsin Department of Revenue. This secure platform allows you to electronically file your return and provides various payment options for tax payment.