What Is Tax Revenue
Tax revenue is a fundamental pillar of modern economies, playing a pivotal role in shaping government policies, infrastructure development, and the overall well-being of a nation. It is a complex yet crucial aspect of fiscal management, encompassing a wide range of taxes levied on individuals, businesses, and various economic activities.
This comprehensive article aims to delve deep into the world of tax revenue, exploring its various facets, the types of taxes that contribute to it, and its profound impact on society. By understanding tax revenue, we can gain insights into the intricate balance between economic growth, social welfare, and governmental responsibilities.
The Significance of Tax Revenue

Tax revenue serves as the primary source of income for governments, enabling them to fund essential services and initiatives that drive a nation’s progress. It is a vital tool for governments to address social inequalities, promote economic development, and maintain a stable financial environment.
The importance of tax revenue can be gauged by its direct influence on critical areas such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, defense, and social security. Governments utilize tax revenue to:
- Build and maintain public infrastructure like roads, bridges, and public transportation systems.
- Fund public services such as education, providing free or subsidized access to quality education for all citizens.
- Offer healthcare services, ensuring affordable and accessible medical care for the population.
- Invest in research and development, fostering innovation and technological advancements.
- Support social welfare programs, assisting vulnerable communities and promoting social equality.
Moreover, tax revenue plays a pivotal role in economic stability. It helps governments manage budget deficits, control inflation, and stimulate economic growth through strategic tax policies. By adjusting tax rates and incentives, governments can influence consumer behavior, investment patterns, and overall economic performance.
Types of Taxes Contributing to Revenue

Tax revenue is a collective outcome of various types of taxes levied by governments. Understanding these tax types is essential to grasp the complexity of tax systems and their impact on different economic sectors.
Income Tax
Income tax is one of the primary sources of tax revenue. It is imposed on the income earned by individuals and businesses. The tax rate often varies based on income brackets, with higher incomes subject to higher tax rates. Income tax plays a crucial role in redistributing wealth and addressing income inequality.
For instance, in the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) collects income taxes, which are used to fund federal programs and services. The tax rates vary from 10% to 37% for individuals, with additional taxes for corporations.
Corporate Tax
Corporate tax is levied on the profits earned by businesses and corporations. It is an essential source of revenue for governments, as it ensures that businesses contribute to the overall economic growth and development of a country.
Consider the case of Ireland, which has a corporate tax rate of 12.5%, attracting numerous multinational corporations and contributing significantly to the country's tax revenue.
Sales and Consumption Tax
Sales tax is imposed on the sale of goods and services. It is a common form of taxation, often levied at the point of purchase. Consumption tax, on the other hand, is a broader category that includes not only sales tax but also excise taxes on specific goods like alcohol, tobacco, and fuel.
In the European Union, Value Added Tax (VAT) is a widely used consumption tax. It is applied at each stage of the supply chain, with businesses collecting the tax on behalf of the government. The VAT rates vary among EU countries, ranging from 17% to 27%.
Property Tax
Property tax is levied on the value of real estate properties, including land, buildings, and other immovable assets. It is a significant source of revenue for local governments, helping fund local services and infrastructure.
The property tax system in the United Kingdom, for example, is based on the value of properties, with rates set by local authorities. The revenue generated from property taxes contributes to funding local services like schools, libraries, and road maintenance.
Excise Taxes
Excise taxes are imposed on specific goods and services, often targeting products that are considered harmful or luxury items. These taxes are usually included in the price of the product and are intended to discourage consumption and generate revenue.
For instance, many countries impose high excise taxes on tobacco products to discourage smoking and fund healthcare initiatives. In the United States, the federal excise tax on cigarettes is $1.01 per pack, with additional state and local taxes varying by jurisdiction.
Impact of Tax Revenue on Society
Tax revenue has a profound impact on society, shaping the distribution of wealth, influencing economic decisions, and determining the overall standard of living. It is a powerful tool that governments use to address social and economic challenges, and its effective management is crucial for a nation’s prosperity.
Redistribution of Wealth
Taxation is a key mechanism for governments to redistribute wealth and address income disparities. Progressive tax systems, where higher incomes are taxed at higher rates, aim to reduce the gap between the rich and the poor. This approach ensures that those with higher earning capacities contribute proportionally more to the tax revenue.
For example, the United Kingdom has a progressive income tax system with seven tax brackets, ranging from 0% to 45%. This system ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their income to the tax revenue, supporting social welfare programs and public services.
Economic Growth and Development
Tax revenue plays a vital role in fostering economic growth and development. Governments invest tax revenue in various initiatives that stimulate economic activity, create jobs, and improve overall productivity.
Infrastructure development, for instance, is a significant area where tax revenue is utilized. Governments invest in building roads, bridges, and public transportation systems, which enhance connectivity, facilitate trade, and attract investments. These projects create job opportunities and contribute to long-term economic growth.
Social Welfare and Equality
Tax revenue is a critical tool for governments to promote social welfare and equality. It funds social safety nets, healthcare systems, and education programs, ensuring that all citizens have access to essential services regardless of their financial status.
In many countries, tax revenue is used to provide universal healthcare coverage. For example, in Canada, the single-payer healthcare system is funded primarily through general tax revenue, ensuring that all citizens have access to comprehensive healthcare services without facing financial barriers.
Future Implications and Challenges
As economies evolve and societal needs change, tax revenue systems must adapt to remain effective and fair. The digital age and the rise of the gig economy present new challenges and opportunities for tax authorities.
With the increasing prevalence of online transactions and remote work, tax authorities face the challenge of effectively taxing digital businesses and gig economy workers. The traditional tax system may not capture these new economic activities accurately, leading to potential revenue losses.
Furthermore, the shift towards a greener economy and the focus on sustainability present unique tax considerations. Governments may introduce carbon taxes or environmental levies to discourage harmful practices and incentivize sustainable alternatives. These taxes, however, must be carefully designed to avoid placing an undue burden on lower-income households.
To address these challenges, governments and tax authorities are exploring innovative solutions. These include the development of digital tax systems, the introduction of blockchain technology for tax collection, and the implementation of fair and progressive tax policies that promote economic growth while addressing social inequalities.
Conclusion
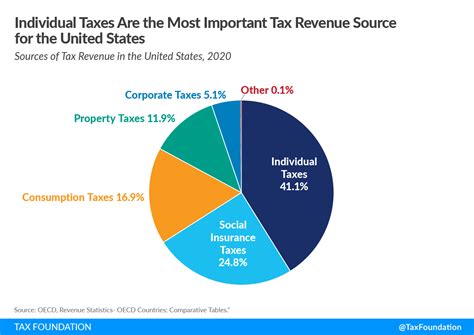
Tax revenue is a complex yet indispensable aspect of modern economies. It serves as the lifeblood of governments, enabling them to fund critical services, drive economic growth, and promote social welfare. By understanding the types of taxes, their impact on society, and the future challenges, we can appreciate the crucial role tax revenue plays in shaping our world.
As we navigate the evolving landscape of taxation, it is essential to strike a balance between economic efficiency and social equity. Effective tax systems must adapt to changing economic realities while ensuring that the benefits of economic growth are shared by all members of society.
What is the primary source of tax revenue for governments?
+Income tax and corporate tax are typically the primary sources of tax revenue for governments. These taxes are imposed on individuals’ and businesses’ income and profits, respectively.
How does tax revenue impact economic growth?
+Tax revenue is crucial for economic growth as it funds infrastructure development, research and development, and other initiatives that stimulate economic activity and create jobs. Additionally, strategic tax policies can influence consumer behavior and investment patterns, further shaping economic growth.
What are some challenges faced by tax authorities in the digital age?
+In the digital age, tax authorities face challenges in effectively taxing digital businesses and gig economy workers. Traditional tax systems may struggle to capture the economic activities of these new economic models, leading to potential revenue losses.