Georgia State Tax Payment

In the complex landscape of financial obligations, understanding how to navigate the world of state taxes is paramount. For residents and businesses in the state of Georgia, the process of tax payment is a critical aspect of maintaining compliance with state regulations. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the intricacies of Georgia State Tax Payment, offering an expert analysis of the process, its key considerations, and the potential implications for taxpayers.
Unraveling the Georgia State Tax Payment Process
The Georgia Department of Revenue is the governing body responsible for overseeing tax collection and enforcement within the state. It is essential for taxpayers to understand the various tax types, deadlines, and payment methods to ensure timely and accurate tax submissions.
Types of Taxes in Georgia
Georgia imposes a range of taxes, each serving a specific purpose and catering to different taxpayer groups. Here’s a breakdown of the primary tax types:
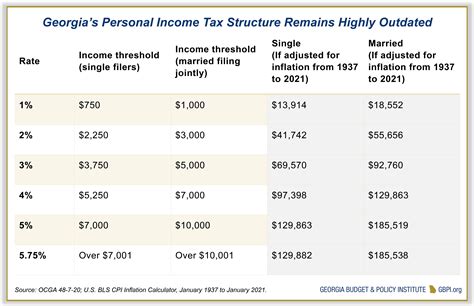
- Income Tax: Individuals and businesses are subject to income tax, which is calculated based on their taxable income. The state offers different tax rates and brackets, depending on the taxpayer's filing status and income level.
- Sales and Use Tax: This tax is levied on the sale of goods and certain services within the state. Businesses are responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax to the state, while individuals may also be subject to use tax on out-of-state purchases.
- Property Tax: Property owners in Georgia are required to pay property taxes, which contribute to local government funding for services such as schools, fire departments, and infrastructure.
- Excise Taxes: These taxes are imposed on specific goods and activities, such as fuel, tobacco, and motor vehicles. Excise taxes are often used to regulate and control certain industries or behaviors.
- Corporate Income Tax: Businesses operating in Georgia, whether incorporated or not, are subject to corporate income tax. This tax is calculated based on the net income generated within the state.
Understanding the applicable tax types is crucial, as it forms the foundation for accurate tax payment and compliance.
Tax Deadlines and Due Dates
Timely tax payment is a critical aspect of financial responsibility. The Georgia Department of Revenue has established specific deadlines for different tax types to ensure efficient revenue collection. Here’s an overview of the key tax deadlines:
| Tax Type | Due Date |
|---|---|
| Income Tax (Individual) | April 15th of each year |
| Income Tax (Corporate) | March 15th for S Corporations April 15th for C Corporations |
| Sales and Use Tax | Varies based on filing frequency (monthly, quarterly, or annually) |
| Property Tax | Typically due in December or January, depending on the county |
| Excise Taxes | Varies based on the specific tax and filing requirements |

Missing these deadlines can result in penalties and interest, underscoring the importance of tax planning and awareness.
Payment Methods and Options
Georgia offers a range of payment methods to cater to different taxpayer preferences and circumstances. These methods include:
- Online Payment: The Georgia Tax Center provides a secure online platform for taxpayers to make payments, view account balances, and manage tax obligations. This method is convenient and allows for real-time transaction processing.
- Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT): Businesses and individuals can set up automatic payments through EFT, ensuring timely tax remittance without manual intervention.
- Credit Card Payment: Taxpayers can use major credit cards to pay their taxes online or over the phone. This method often incurs a convenience fee.
- Check or Money Order: Traditional payment methods are still accepted, with taxpayers able to mail checks or money orders to the designated address.
- Cash Payment: In-person cash payments can be made at authorized payment locations, such as tax offices or designated collection centers.
Choosing the most suitable payment method is essential, as it can impact transaction fees, processing time, and the overall tax payment experience.
Navigating Tax Obligations: Strategies and Considerations

Effective tax management is a multifaceted process that requires strategic planning and a comprehensive understanding of one’s financial obligations. Here, we delve into key strategies and considerations to help taxpayers navigate the complex world of Georgia state taxes.
Tax Planning and Preparation
Tax planning is a proactive approach to managing financial obligations, aiming to minimize tax liabilities and ensure compliance. It involves a thorough analysis of income, expenses, and applicable tax laws to develop a comprehensive tax strategy. Key considerations for tax planning include:
- Understanding Tax Brackets: Taxpayers should be aware of the income tax brackets and rates applicable to their filing status. This knowledge allows for strategic income management to optimize tax efficiency.
- Maximizing Deductions and Credits: Georgia offers various deductions and credits that can reduce taxable income or provide direct tax benefits. Examples include the state income tax deduction, the HOPE scholarship credit, and the homestead exemption for property taxes.
- Filing Status and Eligibility: Choosing the appropriate filing status (single, married filing jointly, head of household, etc.) can significantly impact tax liabilities. Taxpayers should understand the eligibility criteria and implications of each status.
- Record-Keeping and Documentation: Proper record-keeping is essential for accurate tax reporting. Taxpayers should maintain organized records of income, expenses, investments, and other relevant financial transactions.
Effective tax planning not only ensures compliance but also provides opportunities to optimize financial outcomes.
Seeking Professional Guidance
The world of taxes can be complex, and navigating it alone may lead to missed opportunities or errors. Engaging the services of tax professionals, such as certified public accountants (CPAs) or enrolled agents, can provide valuable expertise and guidance. Here’s why seeking professional help is beneficial:
- Expertise and Knowledge: Tax professionals stay abreast of the latest tax laws, regulations, and updates. They can provide accurate advice and strategies tailored to the taxpayer's unique circumstances.
- Complex Tax Scenarios: For taxpayers with complex financial situations, such as business ownership, investments, or multiple sources of income, professional guidance is crucial. Tax professionals can navigate these complexities and ensure optimal tax outcomes.
- Audit Representation: In the event of an audit, tax professionals can represent taxpayers before the Georgia Department of Revenue. They possess the knowledge and experience to navigate the audit process effectively.
- Efficient Tax Preparation: Tax professionals can streamline the tax preparation process, saving taxpayers time and effort. They can also identify potential errors and ensure accurate reporting.
While professional services come at a cost, the benefits often outweigh the fees, especially for taxpayers with complex financial situations.
Utilizing Tax Resources and Tools
In today’s digital age, a wealth of tax resources and tools are available to assist taxpayers in managing their obligations. Here are some valuable resources to consider:
- Georgia Department of Revenue Website: The official website provides comprehensive information on tax laws, forms, deadlines, and payment options. It serves as a one-stop resource for taxpayers seeking guidance and support.
- Tax Preparation Software: User-friendly software, such as TurboTax or H&R Block, can simplify the tax preparation process. These tools guide taxpayers through the process, offer calculations, and provide step-by-step instructions.
- Online Tax Calculators: Various online calculators are available to estimate tax liabilities, deductions, and credits. These tools can help taxpayers plan and budget effectively.
- Tax Workshops and Seminars: Local community centers, libraries, or universities may host tax workshops or seminars, providing valuable information and guidance. These events can be particularly beneficial for first-time taxpayers or those seeking a basic understanding of tax obligations.
Utilizing these resources can empower taxpayers to take control of their financial obligations and make informed decisions.
Impact and Implications: A Comprehensive Analysis
The implications of state taxes extend beyond the mere fulfillment of financial obligations. They influence economic growth, business development, and the overall well-being of residents. This section explores the far-reaching impact of Georgia state taxes and offers insights into their implications.
Economic Growth and Development
State taxes play a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape. The revenue generated through taxes is a primary source of funding for essential public services, infrastructure development, and social programs. Here’s how taxes impact economic growth:
- Funding Public Services: Tax revenue supports critical public services such as education, healthcare, public safety, and transportation. These services are essential for a thriving economy and a high quality of life.
- Infrastructure Development: Taxes contribute to the maintenance and expansion of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and public facilities. Well-developed infrastructure attracts businesses and fosters economic growth.
- Business Incentives: The state may offer tax incentives to attract new businesses or encourage existing businesses to expand. These incentives can take the form of tax credits, deductions, or reduced tax rates, stimulating economic activity and job creation.
- Social Programs: Taxes fund social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits, welfare programs, and healthcare initiatives. These programs support vulnerable populations and promote social equality, contributing to a stable and healthy economy.
A well-managed tax system can drive economic growth and development, creating a positive cycle of investment and prosperity.
Business Environment and Competitiveness
The tax landscape can significantly influence the business environment and the competitiveness of a state. Here’s how taxes impact businesses:
- Tax Rates and Competitiveness: Lower tax rates can attract businesses and investors, making the state more competitive. However, a delicate balance must be struck to ensure sufficient revenue for public services.
- Tax Incentives and Credits: Targeted tax incentives can encourage businesses to invest in research and development, create jobs, or locate in specific areas. These incentives can stimulate economic growth and create a favorable business climate.
- Compliance and Administration: A streamlined and efficient tax system reduces administrative burdens on businesses. Clear guidelines, online filing systems, and timely processing of tax returns contribute to a positive business environment.
- Tax Policy Stability: Businesses thrive in an environment with stable and predictable tax policies. Frequent policy changes can create uncertainty and deter investment. A stable tax system encourages long-term planning and business growth.
A well-designed tax system can foster a business-friendly environment, attracting investment and supporting economic development.
Resident Well-being and Quality of Life
State taxes not only impact the economy but also have a direct influence on the well-being and quality of life of residents. Here’s how taxes contribute to a higher standard of living:
- Education and Skills Development: Tax revenue funds public education, ensuring access to quality education for all residents. A well-educated population contributes to a skilled workforce and a vibrant economy.
- Healthcare and Social Services: Taxes support healthcare initiatives, ensuring access to medical care and social services for all residents. This promotes a healthy population and reduces socioeconomic disparities.
- Public Safety and Security: Taxes fund law enforcement, emergency services, and public safety initiatives. A safe and secure environment enhances the overall quality of life and attracts residents and businesses.
- Environmental Initiatives: State taxes can be used to fund environmental protection and sustainability efforts. This contributes to a healthier environment, improved air and water quality, and a more sustainable future.
A responsible and well-managed tax system can lead to a higher quality of life for residents, making the state an attractive place to live and work.
Future Implications and Considerations
As the landscape of taxation evolves, it is essential to consider the future implications and potential changes that may impact taxpayers. Here, we explore some key considerations for the future of Georgia state taxes.
Technological Advances and Tax Administration
The rapid advancement of technology is transforming the way taxes are administered and collected. Here’s how technological innovations may shape the future of tax administration:
- Online Filing and Payment: The trend towards online tax filing and payment is likely to continue, offering convenience and efficiency for taxpayers. Secure online platforms may become the primary method for tax submission and payment.
- Data Analytics and Compliance: Advanced data analytics can enhance tax compliance and enforcement. The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning may enable more accurate tax assessments and identification of potential fraud.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain's decentralized and secure nature may find applications in tax administration, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof record-keeping. This technology could revolutionize tax collection and audit processes.
- Mobile Tax Apps : Mobile applications may become more prevalent, offering taxpayers convenient access to tax information, forms, and payment options. These apps could simplify tax management and provide real-time updates.
Staying abreast of technological advancements is crucial for taxpayers to adapt to changing tax administration processes.
Tax Policy Reforms and Potential Changes
Tax policies are subject to continuous review and potential reforms. Here are some potential changes that may impact Georgia state taxes in the future:
- Income Tax Reform: Discussions around income tax reform, such as adjusting tax brackets or introducing a flat tax rate, may gain momentum. These reforms could impact taxpayers' liabilities and the overall tax system's complexity.
- Sales Tax Expansion: As consumer behavior evolves, the state may consider expanding sales tax to include services or online purchases. This could impact businesses and consumers alike, requiring adjustments in tax collection and remittance.
- Property Tax Reforms: Property tax policies may undergo reforms to address concerns such as fairness, assessment accuracy, and the impact on homeowners. Changes could include reassessment methodologies or adjustments to tax rates.
- Tax Incentive Programs: The state may explore new tax incentive programs to attract specific industries or promote economic development in targeted areas. These programs could offer tax breaks, grants, or other incentives to businesses.
Staying informed about potential tax policy reforms is essential for taxpayers to anticipate and adapt to changing financial obligations.
Economic and Social Factors
Economic and social factors can significantly influence the future of state taxes. Here are some key considerations:
- Economic Growth and Budget Considerations: The state's economic growth and budget priorities will shape tax policies. During economic downturns, tax rates may be adjusted to stimulate the economy, while budget surpluses may lead to tax reforms or rebates.
- Population Trends: Changes in population demographics, such as an aging population or shifts in income distribution, can impact tax policies. These trends may influence tax rates, deductions, and credits to ensure fairness and equity.
- Social Programs and Needs: The demand for social programs, such as healthcare, education, or welfare, can impact tax policies. Increased social needs may lead to adjustments in tax rates or the introduction of new taxes to fund these programs.
- Political Landscape: The political climate and leadership can significantly influence tax policies. Changes in administration or political priorities may lead to tax reforms or initiatives to address specific social or economic concerns.
Understanding the interplay between economic, social, and political factors is crucial for predicting the future trajectory of state taxes.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Approach to Tax Management
In the intricate world of Georgia state taxes, a comprehensive and proactive approach to tax management is essential. By understanding the tax types, deadlines, and payment options, taxpayers can ensure compliance and optimize their financial outcomes. Effective tax planning, seeking professional guidance, and utilizing available resources are key strategies for navigating the complexities of tax obligations.
Moreover, the impact of state taxes extends beyond financial obligations, influencing economic growth, business competitiveness, and resident well-being. A well-managed tax system can drive prosperity and create a thriving environment for all. As the landscape of taxation evolves, staying informed about technological advancements, policy reforms, and economic factors is crucial for taxpayers to adapt and thrive in the future.
In conclusion, a deep understanding of Georgia state tax payment is not just about compliance; it is about empowering taxpayers to make informed decisions, contribute to a vibrant economy, and secure a high quality of life for themselves and their communities



