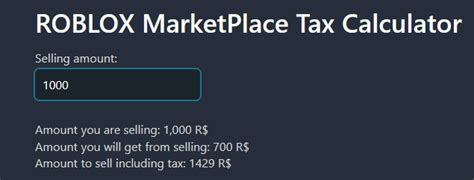
What Is Tax Exempt Interest Income
Understanding the intricacies of the tax system is crucial, especially when it comes to investments and managing personal finances. One concept that often sparks curiosity is tax-exempt interest income. This type of income offers certain advantages and has a significant impact on financial planning. Let's delve into the world of tax-exempt interest income, exploring its definition, how it works, and its implications for investors.
The Nature of Tax-Exempt Interest Income

Tax-exempt interest income refers to the earnings generated from specific investments or bonds that are exempt from federal income taxes in the United States. This exemption is a unique feature of certain types of securities, primarily those issued by state and local governments, also known as municipal bonds or munis.
The primary purpose of offering tax-exempt status to these securities is to encourage investment in local infrastructure projects and essential services. By exempting the interest income from taxation, investors are incentivized to support the growth and development of their communities.
Key Characteristics of Tax-Exempt Interest Income
- Tax Exemption: As the name suggests, the most notable feature is the absence of federal income tax on the interest earned. This can result in a higher after-tax yield compared to taxable investments, making it particularly attractive to investors in higher tax brackets.
- Investor Benefits: Tax-exempt interest income provides investors with a stable source of income, often with lower volatility compared to other investments. It is especially beneficial for those seeking a steady cash flow without the burden of taxes.
- Risk Profile: Municipal bonds are generally considered to be low-risk investments. They are backed by the creditworthiness of the issuing government entity, making them a popular choice for conservative investors.
- Diversification: Including tax-exempt securities in an investment portfolio can enhance diversification. By spreading investments across different asset classes, investors can reduce overall risk while maintaining a balanced approach.
How Tax-Exempt Interest Income Works
When an investor purchases a municipal bond, they essentially lend money to a state or local government entity. In return, the issuer agrees to pay interest at predetermined intervals and repay the principal amount on the bond’s maturity date.
The interest earned on these bonds is what constitutes tax-exempt interest income. The federal government exempts this income from taxation as a way to promote investment in public projects and services. However, it's important to note that state and local taxes may still apply, depending on the investor's residence and the bond's origin.
For instance, let's consider an investor who purchases a municipal bond issued by the state of California. If the bond pays an annual interest rate of 4%, the investor will receive this interest income tax-free at the federal level. However, they may still be subject to state and local taxes in California, as the state's tax laws may differ.
| Municipal Bond Characteristics | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Issuer | State or local government entities |
| Tax Status | Interest income is exempt from federal taxes |
| Risk Profile | Generally low risk, backed by government creditworthiness |
| Maturity | Varies, ranging from short-term to long-term bonds |

The Impact on Investment Strategies
Tax-exempt interest income plays a significant role in shaping investment strategies, particularly for individuals with high tax liabilities. Here’s how it can influence financial planning:
Maximizing After-Tax Returns
For investors in higher tax brackets, tax-exempt securities can be a strategic choice to maximize their after-tax returns. By avoiding federal income taxes on the interest income, they can retain a larger portion of their earnings, effectively boosting their overall returns.
Portfolio Diversification
Incorporating tax-exempt securities into a diversified portfolio can help mitigate risk. By spreading investments across different asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility and potentially increase their overall returns over time.
Planning for Retirement
Tax-exempt interest income can be especially beneficial for retirement planning. By including municipal bonds in a retirement portfolio, individuals can generate a steady stream of tax-free income, reducing their overall tax burden during their golden years.
State and Local Considerations
It’s crucial to consider the tax implications at the state and local levels. Some states may offer additional tax benefits for investing in their own municipal bonds, further enhancing the advantages of tax-exempt interest income. However, it’s essential to research and understand the specific tax laws in your state.
The Future of Tax-Exempt Interest Income
The landscape of tax-exempt interest income is constantly evolving. While it remains a valuable tool for investors, there are several factors to consider when looking ahead:
Potential Tax Reforms
Tax policies are subject to change, and any alterations to the federal tax code could impact the attractiveness of tax-exempt securities. Investors should stay informed about potential reforms and their implications.
Alternative Investment Options
As the financial industry evolves, new investment opportunities arise. While tax-exempt interest income remains a reliable choice, investors should explore a range of options to find the best fit for their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Creditworthiness and Risk
The creditworthiness of issuing government entities is a critical factor. Investors should carefully assess the financial health and stability of the issuer to ensure the safety of their investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any limitations to the tax exemption for municipal bonds?
+Yes, while the interest income is generally exempt from federal taxes, state and local taxes may still apply. Additionally, certain types of municipal bonds, such as private activity bonds, may have specific restrictions and eligibility criteria.
How do I determine the tax-exempt status of a municipal bond?
+The tax-exempt status is typically indicated in the bond’s offering documents. It’s essential to review these documents carefully or consult a financial advisor to ensure the bond meets your tax preferences.
Can tax-exempt interest income be included in a tax-advantaged account like an IRA?
+Yes, tax-exempt interest income can be a valuable addition to tax-advantaged accounts. However, it’s crucial to understand the specific rules and regulations of the account type to ensure compliance.
Are there any risks associated with municipal bonds?
+While municipal bonds are generally considered low risk, they are not without their potential pitfalls. Credit risk, interest rate risk, and market risk are factors to consider. It’s essential to assess these risks and consult a financial professional for guidance.
Can tax-exempt interest income be subject to the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)?
+In certain circumstances, tax-exempt interest income may trigger the Alternative Minimum Tax. It’s advisable to consult a tax professional to understand how the AMT may impact your specific situation.
In conclusion, tax-exempt interest income, primarily generated through municipal bonds, offers a unique opportunity for investors to maximize their returns while supporting local development. By understanding the nuances of this investment type and its tax implications, individuals can make informed decisions to enhance their financial strategies and achieve their long-term goals.