Virginia State Taxes

Understanding the intricacies of state taxes is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, especially when navigating the diverse tax landscapes across the United States. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of Virginia state taxes, offering an in-depth analysis of the tax system, rates, and regulations that shape the financial obligations of residents and businesses within the Commonwealth of Virginia.
A Comprehensive Guide to Virginia State Taxes
Virginia, nestled along the picturesque Atlantic coastline, boasts a rich history and a thriving economy, making it an attractive destination for both residents and businesses. However, with the benefits come responsibilities, and one of the key responsibilities is understanding and navigating the state's tax system.
Virginia's tax structure is designed to fund a wide range of public services, from education and healthcare to infrastructure development. It's a system that impacts individuals, families, and businesses, influencing financial planning and decision-making. In this guide, we'll explore the nuances of Virginia's tax landscape, offering a detailed breakdown of tax rates, categories, and the unique features that set Virginia's tax system apart.
Virginia's Tax Structure: A Bird's Eye View
Virginia operates on a comprehensive tax system, employing a combination of income taxes, sales taxes, property taxes, and various other taxes and fees to generate revenue for the state. This diverse tax structure ensures that different aspects of economic activity are taxed, creating a balanced approach to revenue generation.
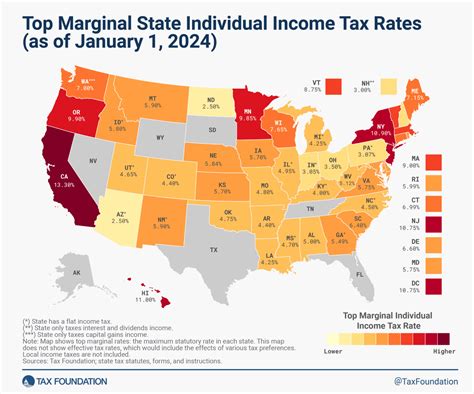
At the core of Virginia's tax system is the income tax, which applies to individuals, trusts, and estates, as well as corporations and partnerships. The state levies taxes on various types of income, including wages, salaries, dividends, and capital gains. The income tax is progressive, meaning higher income brackets face higher tax rates, ensuring a fair distribution of tax burden.
In addition to income taxes, Virginia imposes a sales and use tax on the sale or purchase of tangible personal property within the state. This tax extends to a wide range of goods and services, contributing significantly to the state's revenue. The sales tax rate is uniform across the state, providing a consistent tax environment for businesses and consumers alike.
Property taxes are another crucial component of Virginia's tax landscape. These taxes are levied on real estate and tangible personal property, with rates varying across localities. Property taxes play a vital role in funding local services and infrastructure, making them a critical aspect of the state's tax system.
Income Tax in Virginia: A Detailed Look
Virginia's income tax system is designed to be fair and progressive, ensuring that those with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their earnings to the state's revenue. The state operates on a series of tax brackets, with each bracket carrying a specific tax rate. As income increases, taxpayers move into higher brackets, facing incrementally higher tax rates.
| Tax Bracket (Single Filers) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $3,000 | 2% |
| $3,001 - $5,000 | 3% |
| $5,001 - $17,000 | 5% |
| $17,001 - $50,000 | 5.75% |
| Over $50,000 | 5.75% |
These tax brackets apply to both single and joint filers, with slight variations in the income ranges for married couples filing jointly. The progressive nature of the income tax system ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their income to the state, fostering economic equity.
Sales and Use Tax: Simplifying Consumption
Virginia's sales and use tax is a crucial component of the state's revenue generation strategy, accounting for a significant portion of the state's tax income. The sales tax is imposed on the sale or purchase of tangible personal property, with certain exemptions and exceptions in place.
The standard sales and use tax rate in Virginia is 4.3%, one of the lowest rates in the nation. This rate is applied uniformly across the state, ensuring consistency for businesses and consumers. However, it's important to note that localities have the authority to impose additional sales taxes, known as locality taxes, which can increase the overall sales tax rate.
Virginia's sales tax extends to a wide range of goods and services, including groceries, clothing, electronics, and various other items. However, certain essential items, such as prescription drugs and non-prepared food, are exempt from sales tax, reducing the tax burden on basic necessities.
Property Taxes: Funding Local Services
Property taxes are a critical aspect of Virginia's tax system, providing a significant portion of funding for local services and infrastructure. These taxes are levied on real estate and tangible personal property, with rates determined by local governments.
Virginia's property tax system is ad valorem, meaning the tax is based on the assessed value of the property. The assessed value is determined by local assessors, who take into account factors such as location, size, and improvements made to the property. This valuation process ensures that property taxes are fair and reflective of the property's actual value.
Property tax rates vary significantly across localities in Virginia. While the state sets a maximum rate, individual counties and cities have the authority to set their own rates, leading to a diverse landscape of property tax rates. On average, the effective property tax rate in Virginia is 0.86%, which is slightly lower than the national average.
Other Taxes and Fees: A Diverse Revenue Stream
In addition to income, sales, and property taxes, Virginia employs a range of other taxes and fees to generate revenue. These additional taxes and fees contribute to the state's overall financial stability and fund specific initiatives and services.
- Meals Tax: Virginia imposes a meals tax on food and beverages served in restaurants and other dining establishments. The meals tax rate varies across localities, with some areas adding an additional tax to the standard sales tax rate.
- Lodging Tax: A tax is levied on lodging accommodations, such as hotels and motels, to fund tourism and economic development initiatives. Like the meals tax, the lodging tax rate can vary based on the locality.
- Vehicle Registration Tax: Virginia imposes a tax on vehicle registration, with the revenue generated used to maintain and improve the state's transportation infrastructure.
- Estate and Inheritance Taxes: The state also collects taxes on estates and inheritances, ensuring that the transfer of wealth is subject to taxation.
Tax Credits and Incentives: Supporting Businesses and Individuals
Virginia understands the importance of supporting its residents and businesses, and as such, the state offers a range of tax credits and incentives to encourage economic growth and development.
For individuals, Virginia provides tax credits for various expenses, including college tuition, dependent care, and certain medical expenses. These credits help alleviate the tax burden on families and individuals, providing much-needed financial relief.
Businesses, too, benefit from a range of tax incentives. Virginia offers tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investment in certain industries. These incentives are designed to attract businesses and foster economic growth, making Virginia an attractive destination for entrepreneurs and established businesses alike.
Compliance and Enforcement: Navigating the Tax Landscape
Compliance with Virginia's tax laws is a critical aspect of doing business or residing in the state. The Virginia Department of Taxation is responsible for enforcing tax laws and ensuring that taxpayers meet their obligations.
Taxpayers are required to file tax returns and pay taxes on time to avoid penalties and interest. The department offers a range of resources and support to assist taxpayers in understanding their obligations and ensuring compliance. This includes online filing options, tax guides, and assistance from tax professionals.
For businesses, compliance extends beyond tax payments. Businesses must also adhere to various tax regulations, such as registering for tax purposes, obtaining necessary licenses, and maintaining proper records. The Virginia Department of Taxation provides guidance and support to help businesses navigate these requirements.
Tax Incentives for Economic Development
Virginia recognizes the importance of economic development and has implemented various tax incentives to attract businesses and stimulate growth. These incentives are designed to encourage investment, job creation, and innovation within the state.
One notable incentive is the Virginia Enterprise Zone Program, which offers tax credits and other benefits to businesses that locate or expand in designated economically distressed areas. These zones are identified based on factors such as unemployment rates, poverty levels, and population decline.
Additionally, Virginia offers tax incentives for research and development activities. The Research and Development Tax Credit provides a credit against Virginia income tax for eligible research expenses incurred by businesses. This incentive aims to encourage innovation and technological advancement within the state.
Virginia also promotes renewable energy and energy efficiency through tax incentives. The Virginia Solar Energy Tax Credit provides a credit for the installation of solar energy systems, while the Energy Efficiency Tax Credit offers incentives for businesses and individuals who invest in energy-efficient equipment and improvements.
Impact of Virginia's Tax System on the Economy
Virginia's tax system plays a crucial role in shaping the state's economy. The progressive income tax structure ensures a fair distribution of tax burden, while the low sales tax rate promotes consumer spending and economic growth. Property taxes, though varying across localities, contribute significantly to funding local services and infrastructure development.
The state's tax incentives and credits further stimulate economic growth by attracting businesses and encouraging investment. These incentives create a favorable business environment, leading to job creation and economic diversification. Virginia's strategic use of tax policy has contributed to its reputation as a business-friendly state, fostering a thriving economy and attracting a diverse range of industries.
Moreover, the state's commitment to tax fairness and simplicity has resulted in a stable and predictable tax environment. This predictability is attractive to both businesses and individuals, as it allows for effective financial planning and decision-making. Virginia's tax system, with its combination of progressive income taxes, low sales tax, and targeted incentives, has positioned the state as a competitive player in the national economy.
Conclusion: Virginia's Tax Landscape in Focus
Virginia's tax system is a well-designed and comprehensive framework that supports the state's economy and its residents. The progressive income tax structure ensures a fair distribution of tax burden, while the low sales tax rate promotes consumer spending. Property taxes fund local services and infrastructure, and a range of additional taxes and fees contribute to the state's financial stability.
Virginia's commitment to economic development is evident through its tax incentives, which attract businesses and stimulate growth. The state's strategic use of tax policy has positioned it as a competitive destination for businesses, fostering a diverse and thriving economy. The tax system's fairness, simplicity, and predictability make it an attractive choice for individuals and businesses alike.
As Virginia continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic landscapes, its tax system will remain a crucial factor in shaping the state's future. By understanding and navigating Virginia's tax landscape, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions, ensuring compliance and maximizing their financial opportunities within the Commonwealth.
What is the average property tax rate in Virginia?
+
The average effective property tax rate in Virginia is 0.86%, which is slightly lower than the national average.
Are there any tax incentives for renewable energy in Virginia?
+
Yes, Virginia offers tax incentives for renewable energy, including the Virginia Solar Energy Tax Credit and the Energy Efficiency Tax Credit.
What is the Virginia Enterprise Zone Program?
+
The Virginia Enterprise Zone Program offers tax credits and benefits to businesses that locate or expand in designated economically distressed areas.
Are there any tax credits for individuals in Virginia?
+
Yes, Virginia provides tax credits for individuals, including credits for college tuition, dependent care, and certain medical expenses.
How does Virginia’s tax system support economic development?
+
Virginia’s tax system supports economic development through various tax incentives, including the Virginia Enterprise Zone Program and the Research and Development Tax Credit.



