Unemployment Federal Tax Rate

The federal tax rate on unemployment benefits is a crucial aspect of understanding the financial implications for individuals receiving unemployment compensation in the United States. This tax rate directly impacts the take-home income of those who are temporarily out of work and reliant on unemployment benefits to support themselves and their families. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the specifics of the federal tax rate on unemployment, providing an in-depth analysis and practical insights to help individuals navigate this complex topic.
Understanding the Federal Tax Rate on Unemployment
The federal tax rate applicable to unemployment benefits is determined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and is subject to the same income tax rules as regular earned income. It is important to note that unemployment compensation is considered taxable income, and recipients must report and pay taxes on these benefits just like any other form of income.
The federal tax rate for unemployment benefits is not a fixed percentage but rather varies depending on the individual's overall tax liability and the amount of unemployment compensation received. This rate is calculated based on the taxpayer's adjusted gross income, filing status, and other deductions and credits.
Taxation of Unemployment Benefits
Unemployment benefits are generally taxed at the individual’s marginal tax rate, which is the highest rate at which their income is taxed. The marginal tax rate can range from 10% to 37%, depending on various factors, including income level and filing status. For example, an individual with a higher income and filing as single may fall into a higher tax bracket, resulting in a higher tax rate on their unemployment benefits.
It is worth noting that the taxation of unemployment benefits can also be influenced by the presence of other income sources. If an individual has other forms of income, such as wages from a part-time job or investments, these factors can impact the overall tax liability and the effective tax rate applied to unemployment benefits.
Withholding and Payment Options
When receiving unemployment benefits, individuals have the option to choose whether to have federal taxes withheld from their payments. This decision is made by completing a Withholding Election Form provided by the unemployment office. By electing to have taxes withheld, individuals can avoid a large tax bill at the end of the year and spread their tax payments throughout the year.
However, it is important to carefully consider the withholding amount to ensure that it aligns with the individual's expected tax liability. Underwithholding can result in penalties, while overwithholding may lead to a refund, but it could also mean lost interest on that money throughout the year.
Calculating Federal Taxes on Unemployment Benefits

Calculating the exact federal tax rate and liability on unemployment benefits requires a comprehensive understanding of tax laws and individual financial circumstances. Here are some key considerations when determining the federal tax implications of unemployment benefits:
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI)
The individual’s Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is a critical factor in determining the applicable tax rate. AGI is calculated by taking the total income and subtracting certain deductions and adjustments. Higher AGI generally results in a higher tax rate.
Filing Status
The taxpayer’s filing status, such as single, married filing jointly, or head of household, also plays a role in determining the tax rate. Different filing statuses have varying tax brackets and rates, which can significantly impact the overall tax liability.
Tax Deductions and Credits
Tax deductions and credits can reduce the taxable income and, consequently, the tax liability. Common deductions for unemployment recipients include the standard deduction, education expenses, and certain medical costs. Additionally, various tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or Child Tax Credit, may be available to eligible individuals, further reducing their tax burden.
Tax Withholding and Estimated Tax Payments
If an individual opts to have federal taxes withheld from their unemployment benefits, the amount withheld is determined by the information provided on the Withholding Election Form. It is crucial to review this form and ensure that the withholding amount aligns with the expected tax liability to avoid underpayment or overpayment.
For those who choose not to have taxes withheld, they may need to make estimated tax payments throughout the year to cover their tax liability. Failure to make these payments can result in penalties and interest.
| Filing Status | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Single | 10% to 37% |
| Married Filing Jointly | 10% to 35% |
| Head of Household | 10% to 35% |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | 10% to 35% |

Strategies for Managing Federal Taxes on Unemployment
Understanding the federal tax implications of unemployment benefits is crucial, but it is equally important to explore strategies to effectively manage and minimize the tax burden. Here are some practical tips and insights to help individuals navigate this complex process:
Maximizing Deductions and Credits
Exploring tax deductions and credits can significantly reduce the taxable income and, consequently, the tax liability. It is essential to research and understand the various deductions and credits available to unemployment recipients. For example, individuals with dependent children may qualify for the Child Tax Credit, while those pursuing education or incurring medical expenses may be eligible for specific deductions.
Proper Withholding or Estimated Tax Payments
Ensuring that the appropriate amount of tax is withheld from unemployment benefits or making timely estimated tax payments is crucial. Underwithholding can lead to penalties, while overwithholding may result in a larger refund but could also mean losing out on potential interest earnings. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional or use tax calculators to determine the optimal withholding amount or estimated tax payment schedule.
Consider Taxable and Nontaxable Unemployment Benefits
Not all unemployment benefits are taxed at the same rate. Some states offer taxable and nontaxable unemployment benefits, and understanding the distinction is essential. Nontaxable benefits may have specific requirements or conditions, such as being eligible for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). It is crucial to review the terms and conditions of the unemployment benefits to determine their tax status.
Utilize Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Individuals with access to tax-advantaged accounts, such as Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), can contribute to these accounts to reduce their taxable income. Contributions to these accounts are generally tax-deductible and can provide significant tax benefits, especially for those with unemployment benefits.
Explore Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
During periods of unemployment, individuals may consider investing their savings in tax-efficient strategies. For example, investing in tax-efficient mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) can help minimize the tax impact on investment returns. Additionally, exploring tax-loss harvesting strategies can offset capital gains and reduce the overall tax liability.
The Future of Federal Taxes on Unemployment
The taxation of unemployment benefits is an evolving topic, and it is essential to stay informed about potential changes and developments. Here are some insights into the future implications and potential changes regarding the federal tax rate on unemployment:
Legislative and Policy Changes
The federal tax rate on unemployment benefits is subject to legislative and policy changes. In recent years, there have been discussions and proposals to modify the tax treatment of unemployment compensation. Some policymakers have advocated for making unemployment benefits tax-free, while others have proposed changes to the withholding and reporting requirements. Staying updated on these legislative initiatives is crucial for understanding potential future tax implications.
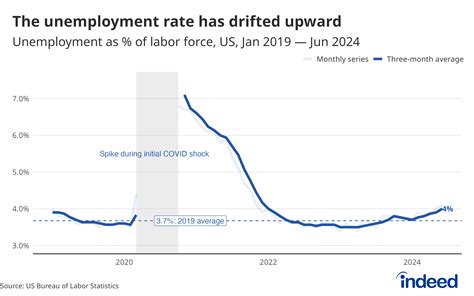
Impact of Economic Conditions
Economic conditions, such as recessions or periods of high unemployment, can influence the taxation of unemployment benefits. During economic downturns, there may be calls for tax relief or temporary measures to ease the financial burden on unemployment recipients. Conversely, in times of economic prosperity, the tax treatment of unemployment benefits may remain unchanged or even face increased scrutiny.
Technological Advancements and Reporting
Advancements in technology and data sharing between government agencies can impact the reporting and taxation of unemployment benefits. Improved data integration and real-time information sharing can enhance the accuracy of tax reporting and reduce instances of underreporting or non-compliance. As technology continues to evolve, the process of reporting and paying taxes on unemployment benefits may become more streamlined and efficient.
Public Perception and Advocacy
Public perception and advocacy efforts can also shape the future of federal taxes on unemployment. Advocacy groups and policymakers may continue to push for tax reforms that benefit unemployment recipients. Additionally, public awareness and education about the tax implications of unemployment benefits can drive policy changes and influence future tax laws.
Conclusion
Understanding the federal tax rate on unemployment benefits is a complex but essential aspect of financial planning for individuals receiving unemployment compensation. By delving into the specifics of taxation, withholding options, and tax management strategies, individuals can navigate this process with confidence and minimize their tax burden. Staying informed about potential legislative changes, economic conditions, and technological advancements is crucial for adapting to future developments in the taxation of unemployment benefits.
Are unemployment benefits always taxable at the federal level?
+Yes, unemployment benefits are generally considered taxable income at the federal level. However, there may be specific circumstances or programs where certain unemployment benefits are exempt from federal taxation. It is important to review the terms and conditions of your unemployment benefits to determine their tax status.
How do I know what tax rate applies to my unemployment benefits?
+The tax rate applicable to your unemployment benefits depends on your overall tax liability and income level. It is calculated based on your adjusted gross income, filing status, and other factors. You can estimate your tax rate by using tax calculators or consulting with a tax professional who can provide personalized guidance.
Can I reduce the federal tax on my unemployment benefits?
+Yes, there are strategies to potentially reduce the federal tax on your unemployment benefits. Maximizing tax deductions and credits, properly withholding or making estimated tax payments, and exploring tax-advantaged accounts are some ways to minimize your tax liability. Consulting with a tax professional can provide tailored advice based on your specific circumstances.
What happens if I don’t pay taxes on my unemployment benefits?
+Failing to pay taxes on your unemployment benefits can result in penalties and interest. The IRS may impose penalties for underpayment or non-payment of taxes, and interest may accrue on any unpaid tax liabilities. It is important to report and pay taxes on your unemployment benefits to avoid these consequences.
Are there any upcoming changes to the federal tax rate on unemployment benefits?
+There may be potential changes to the federal tax rate on unemployment benefits in the future. It is advisable to stay informed about legislative proposals, economic conditions, and technological advancements that could impact the taxation of unemployment benefits. Regularly reviewing tax laws and consulting with tax professionals can help you stay updated on any changes.