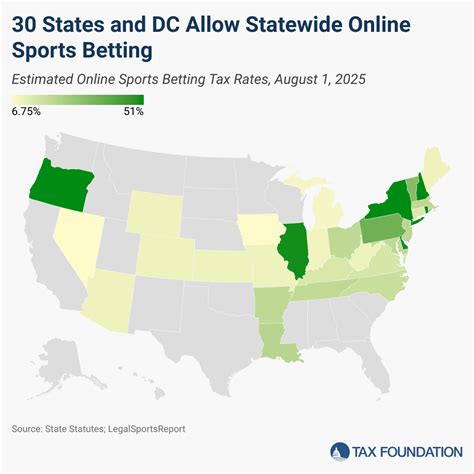
Grumman F6f Hellcat: Fastest Carrier Fighter Of Wwii
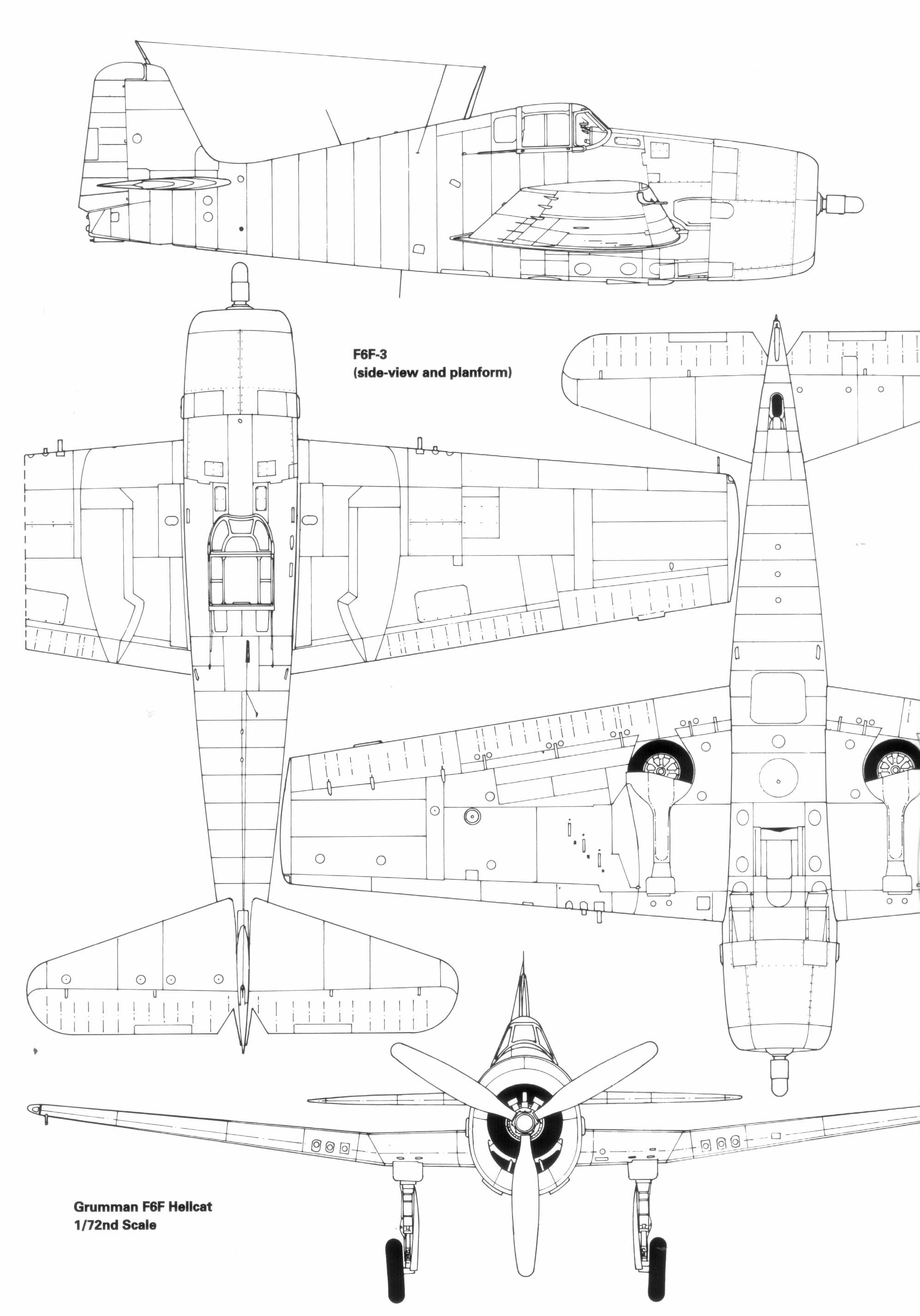
The Grumman F6f Hellcat was built to win air superiority from the decks of American aircraft carriers during World War II. Recognized for reliability, ruggedness, and firepower, the Grumman F6f Hellcat quickly earned a reputation for turning every carrier into a formidable fighting platform. In this article, we explore how the Grumman F6f Hellcat secured its place as one of the fastest carrier fighters of WWII and reshaped naval air combat.
From its design philosophy to its operational history, the Grumman F6f Hellcat set a benchmark for durability and mission readiness. The aircraft was engineered to be easy to maintain on crowded carriers, even under demanding conditions, which translated into higher sortie rates and survivability in combat.
Key Points
- Reliability on harsh carrier decks and quick turnaround times boosted mission availability.
- Powerful, smooth engine and aerodynamic refinements improved climb and sustained speed.
- Armament setup favored air superiority with effective guns and cannons for short-range dogfighting.
- Easy maintenance and robust landing gear enhanced carrier operations and survivability in combat.
- Successful deployment influenced post-war naval aviation design and doctrine.
Design features and engineering choices

The Grumman F6f Hellcat was designed around a strong, forgiving airframe that could absorb battle damage and keep flying. Its large radial engine provided steady power, while simplified systems reduced maintenance demands. Pilots could concentrate on tactics rather than wrestling with mechanical issues, a critical factor in its combat success. The combination of rugged construction and good handling made the Grumman F6f Hellcat popular with crews who needed reliability as a daily asset on carrier operations.
Operational history and impact

In combat, the Grumman F6f Hellcat repeatedly outperformed adversaries in terms of sortie rate and effectiveness. Its development aligned with carrier air group strategies that emphasized control of the air and protection of strike aircraft. The Hellcat's success contributed to the decline of enemy air operations in the Pacific and helped secure significant victories for Allied forces.
Legacy and lessons for later fighters

As a bridge between early WWII fighters and post-war jet interceptors, the Grumman F6f Hellcat demonstrated how reliability, ease of maintenance, and operator-friendly handling could define a fighter's success. The aircraft's design influenced subsequent naval fighters and remains a benchmark for survivability under carrier conditions.
What made the Grumman F6f Hellcat so effective in combat?

+
The Grumman F6f Hellcat earned its effectiveness through a blend of exceptional reliability, sturdy construction, and a powerplant that delivered consistent performance on demanding carrier operations. Its forgiving handling allowed pilots to focus on engagement tactics, while its durability minimized downtime on crowded decks.
How did the Grumman F6f Hellcat compare to other carrier fighters of its era?

+
Compared with contemporaries, the Hellcat offered higher mission readiness and better survivability under fire. While some rivals emphasized speed or maneuverability, the Hellcat balanced endurance, ease of maintenance, and effective armament, enabling more consistent combat performance.
Which design choices contributed most to its reliability?

+
Key design choices included a robust airframe, simplified hydraulic and electrical systems, an engine with good fuel efficiency and cooling, and a gear system optimized for routine carrier deck operations. These factors reduced maintenance needs and increased aircraft availability during campaigns.
How many Grumman F6f Hellcat aircraft were produced, and how long did they serve?

+
Thousands of Grumman F6f Hellcat fighters were produced across multiple variants, serving on U.S. Navy carriers well into the late 1940s and supporting post-war operations before retirement or conversion to other roles. The aircraft’s longevity reflects its robust design and ongoing effectiveness in air-to-air combat.