Vermont State Income Tax
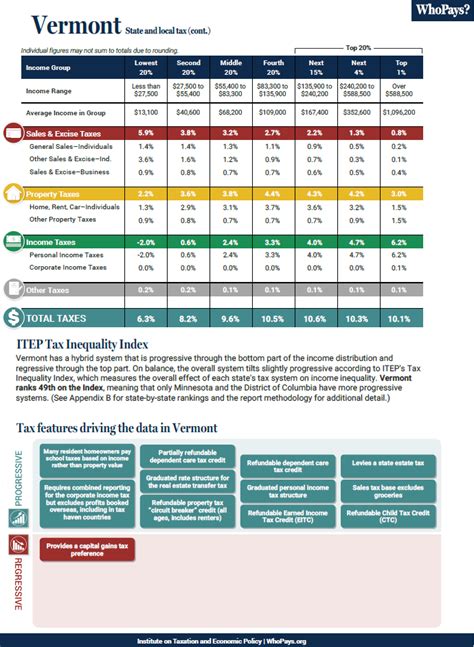
In the beautiful state of Vermont, income taxes play a significant role in shaping the state's fiscal landscape and the lives of its residents. With a unique and progressive tax system, Vermont offers an intriguing study for those interested in understanding the intricacies of state-level taxation. This article aims to delve into the specifics of Vermont's income tax system, exploring its rates, brackets, and the impact it has on the state's economy and its citizens.
Understanding Vermont’s Income Tax Structure

Vermont’s income tax system is designed to be progressive, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. This approach ensures that the tax burden is distributed fairly across different income groups, with those who earn more contributing a larger share. The state’s tax structure is divided into six tax brackets, each with its own rate, which we will explore in detail.
The Vermont Department of Taxes administers and enforces the state's income tax laws, providing resources and guidance to taxpayers. The income tax is a vital source of revenue for the state, funding essential services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and more.
Tax Rates and Brackets
Vermont’s income tax brackets and rates are as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Applicable Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.35% | Up to $10,400 for single filers, $20,800 for joint filers |
| 2 | 6.5% | $10,401 - $25,999 for single filers, $20,801 - $51,999 for joint filers |
| 3 | 7.8% | $26,000 - $159,999 for single filers, $52,000 - $239,999 for joint filers |
| 4 | 8.75% | $160,000 - $214,999 for single filers, $240,000 - $299,999 for joint filers |
| 5 | 9.4% | $215,000 - $324,999 for single filers, $300,000 - $449,999 for joint filers |
| 6 | 9.9% | Over $325,000 for single filers, over $450,000 for joint filers |

These tax rates apply to Vermont residents as well as non-residents with income sourced from within the state. The brackets are designed to ensure that individuals and families with lower incomes pay a lower percentage of their earnings in taxes, while higher-income earners contribute a larger share.
Taxable Income and Deductions
Vermont’s taxable income includes wages, salaries, bonuses, commissions, and other forms of compensation. It also includes income from self-employment, investments, and certain types of retirement income. However, there are several deductions and exemptions available to reduce the taxable income and lower the overall tax liability.
One notable deduction is the Vermont standard deduction, which varies based on filing status. For example, the standard deduction for single filers is $12,600, while it is $25,200 for married couples filing jointly. Additionally, Vermont allows itemized deductions for expenses such as medical costs, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and mortgage interest.
Tax Filing and Due Dates
Vermont residents are required to file their income tax returns annually, typically by April 15th, following the federal tax deadline. However, if the federal deadline is extended, Vermont’s deadline is also extended to match. Taxpayers can file their returns electronically through the Vermont Department of Taxes website or by mailing in a paper return.
For those who owe taxes, the payment is due by the same deadline. Vermont offers various payment options, including electronic funds transfer, credit card, and check or money order by mail. It's important for taxpayers to ensure they meet these deadlines to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Impact on Vermont’s Economy and Residents

Vermont’s income tax system has a significant impact on both the state’s economy and the financial well-being of its residents. The progressive tax structure ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger portion of their income, which helps fund essential public services and infrastructure projects.
Economic Development and Infrastructure
The revenue generated from income taxes plays a crucial role in Vermont’s economic development. It funds initiatives such as road and bridge construction, public transportation improvements, and the maintenance of vital infrastructure. These investments attract businesses and create job opportunities, contributing to the state’s overall economic growth.
Furthermore, the income tax revenue supports critical industries like healthcare and education. It funds healthcare initiatives, ensuring access to quality medical services for all Vermonters. In the education sector, the tax revenue is used to enhance public schools, provide scholarships, and support higher education institutions, fostering a skilled workforce and a knowledgeable population.
Social Safety Net and Equity
Vermont’s income tax system also contributes to the state’s social safety net, providing support for vulnerable populations. The revenue is used to fund programs such as Medicaid, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), and housing assistance. These programs ensure that low-income individuals and families have access to essential services and resources, promoting social equity and reducing poverty.
Tax Relief and Stimulus Measures
In response to economic challenges, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, Vermont has implemented tax relief measures to support its residents and businesses. These measures include tax deferrals, expanded tax credits, and economic stimulus packages. For example, during the pandemic, Vermont offered tax relief to businesses affected by closures and reduced revenues.
Additionally, Vermont has a Homestead Tax Credit, which provides property tax relief to eligible homeowners. This credit helps reduce the tax burden on homeowners, particularly those with lower incomes, promoting homeownership and financial stability.
Comparison with Other States
Vermont’s income tax system differs significantly from that of many other states. While some states have flat tax rates or no income tax at all, Vermont’s progressive approach ensures a more equitable distribution of the tax burden. This can make Vermont’s tax system more attractive to individuals and businesses seeking a fair and balanced taxation system.
Compared to neighboring states, Vermont's income tax rates are generally competitive. For instance, New Hampshire has no income tax, while Massachusetts has a flat tax rate of 5.05%. Vermont's progressive brackets allow it to maintain a competitive edge while still generating sufficient revenue to support its public services.
Business Climate and Incentives
Vermont’s tax system also includes provisions for businesses, offering incentives to attract and retain companies. For example, the state provides tax credits for research and development activities, job creation, and investment in renewable energy projects. These incentives encourage businesses to establish and expand in Vermont, contributing to the state’s economic growth and job market.
Furthermore, Vermont offers tax exemptions for certain types of businesses, such as manufacturers and agricultural enterprises. These exemptions can help reduce the tax burden on specific industries, making Vermont an attractive location for businesses in these sectors.
Future Implications and Considerations
As Vermont continues to evolve and face new economic challenges, its income tax system will play a crucial role in shaping the state’s future. Here are some key considerations and potential implications:
Economic Growth and Revenue
Vermont’s income tax revenue is closely tied to the state’s economic growth. As the economy expands, more individuals and businesses will contribute to the tax base, generating additional revenue. This revenue can be used to fund essential services, invest in infrastructure, and support economic development initiatives.
However, economic downturns can impact tax revenue, potentially leading to budget constraints and the need for tax increases or cuts to public services. Balancing the need for revenue with the impact on taxpayers is a delicate task for policymakers.
Tax Reform and Simplification
There have been ongoing discussions about tax reform in Vermont, with some advocating for a simpler tax system. While the current system is progressive and equitable, it can be complex for taxpayers, particularly those with diverse income sources or unique financial situations. Simplifying the tax code and reducing the number of brackets could make filing taxes more accessible and reduce compliance costs.
Remote Work and Digital Economy
The rise of remote work and the digital economy has brought about new challenges for state tax systems. Vermont, like many other states, is considering how to tax income earned remotely by non-residents who work for Vermont-based companies. Finding a balanced approach that doesn’t deter remote workers or companies from doing business in the state will be crucial.
Sustainable Funding for Public Services
Vermont’s income tax revenue is essential for funding public services, including education, healthcare, and social safety net programs. As the state’s population ages and healthcare costs rise, ensuring sustainable funding for these services becomes increasingly important. The income tax system will need to adapt to meet these evolving needs while maintaining its progressive and equitable nature.
Conclusion
Vermont’s income tax system is a vital component of the state’s fiscal framework, shaping its economy and the lives of its residents. With a progressive approach, Vermont ensures that its tax system is fair and contributes to the well-being of its citizens. As Vermont navigates economic challenges and opportunities, its income tax system will continue to play a central role in shaping the state’s future.
What is the current Vermont income tax rate for 2023?
+The current income tax rates for Vermont in 2023 range from 3.35% to 9.9%, depending on the tax bracket an individual or joint filer falls into. These rates are subject to change annually, so it’s essential to check with the Vermont Department of Taxes for the most up-to-date information.
Are there any tax credits or deductions available in Vermont?
+Yes, Vermont offers various tax credits and deductions to reduce taxable income. These include the Vermont standard deduction, itemized deductions for expenses like medical costs and charitable contributions, and specific tax credits such as the Homestead Tax Credit for eligible homeowners.
How does Vermont’s income tax system compare to other states?
+Vermont’s income tax system is unique compared to many other states. While some states have flat tax rates or no income tax, Vermont’s progressive approach ensures a more equitable distribution of the tax burden. Its rates are generally competitive with neighboring states, offering a balanced approach to taxation.
What are the tax filing deadlines in Vermont?
+Vermont’s income tax returns are typically due by April 15th, in line with the federal tax deadline. However, if the federal deadline is extended, Vermont’s deadline is also extended to match. It’s important to stay updated on any changes to the tax filing deadlines.
How does Vermont support businesses through its tax system?
+Vermont offers various tax incentives and exemptions to attract and retain businesses. These include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investment in renewable energy. Additionally, certain industries, like manufacturing and agriculture, may be eligible for tax exemptions.



