Vat Tax Id
The Value Added Tax (VAT) Tax Identification Number (TIN) is a crucial element in the world of international taxation and business operations. This unique identifier is assigned to businesses and organizations by their respective governments, serving as a vital tool for tax administration and compliance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of VAT TINs, exploring their purpose, structure, and global variations, while also offering valuable insights for businesses navigating the complex landscape of international taxation.
Understanding the VAT Tax Identification Number

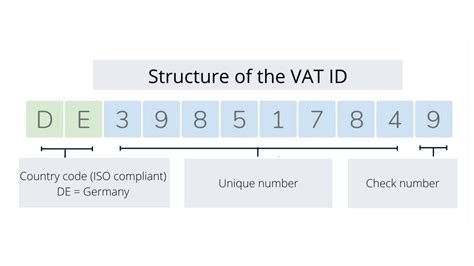
The VAT Tax Identification Number, often simply referred to as a VAT number or VAT ID, is a numerical code assigned by tax authorities to identify and track businesses involved in VAT-related transactions. It serves as a critical tool for tax authorities to monitor and manage the collection of VAT, a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services across various countries.
Key Functions of VAT TINs
- Tax Administration: VAT TINs play a pivotal role in tax administration, enabling tax authorities to efficiently identify and record VAT-registered businesses. This facilitates the accurate collection and allocation of VAT revenue, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
- Cross-Border Transactions: In an increasingly globalized economy, VAT TINs are essential for businesses engaged in international trade. They facilitate cross-border transactions by providing a standardized identification system, allowing for seamless VAT reporting and compliance across borders.
- Tax Refunds and Credits: For businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions, VAT TINs are crucial for claiming tax refunds or credits. By accurately identifying the business and its VAT status, tax authorities can process refunds or credits efficiently, ensuring fair tax treatment for businesses operating across borders.
Global Variations in VAT TIN Structure
VAT Tax Identification Numbers vary in structure and format across different countries and regions. While the underlying purpose remains consistent, the specific format and length of the VAT number can differ significantly.
| Country/Region | VAT Number Format |
|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | XX123456789, where "XX" represents the country code and "123456789" is the unique identifier. |
| United Kingdom (UK) | GB123456789, with "GB" as the country code and "123456789" as the unique identifier. |
| Canada | 123456789RT, a 9-digit number followed by the letters "RT" or "RT0001" for businesses with multiple registrations. |
| United States (US) | No specific VAT system, but businesses may use their Employer Identification Number (EIN) for tax purposes. |
| Australia | 12 345 678 901, a 11-digit number used for both VAT (Goods and Services Tax, GST) and other tax purposes. |

Obtaining and Registering for a VAT TIN
The process of obtaining a VAT Tax Identification Number varies depending on the country or region in which a business operates. Generally, businesses must register with the relevant tax authority and provide essential information such as company details, legal status, and the nature of their business activities.
Registration Requirements
- Business Information: Businesses typically need to provide details such as company name, address, contact information, and the names of directors or owners.
- Business Activities: A clear description of the business’s primary activities and the types of goods or services offered is often required.
- Legal Status: The business’s legal structure, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, or limited company, must be declared.
- VAT Threshold: In some countries, businesses must exceed a certain annual turnover threshold to be eligible for VAT registration.
Registration Procedures
The registration process usually involves completing an application form, either online or in person, and submitting supporting documentation. This may include proof of business registration, financial records, and identification documents for company representatives. Once the application is approved, the tax authority issues the VAT TIN, which the business can then use for VAT-related transactions.
Using a VAT Tax Identification Number
A VAT Tax Identification Number is a powerful tool for businesses operating in the VAT-compliant environment. It allows businesses to:
- Collect and Charge VAT: Businesses can collect VAT from customers and charge it on their sales, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
- Claim VAT Refunds: When businesses incur VAT on purchases related to their business activities, they can use their VAT TIN to claim refunds from the tax authority.
- Facilitate Cross-Border Trade: For international businesses, the VAT TIN is crucial for smooth cross-border transactions, as it provides a standardized identification system accepted by tax authorities worldwide.
- Comply with Reporting Requirements: VAT-registered businesses must submit periodic VAT returns to the tax authority, detailing their VAT liabilities and refunds. The VAT TIN is essential for accurately filing these returns.
Compliance and Penalties
Compliance with VAT regulations is critical, as non-compliance can result in significant penalties and legal consequences. Businesses must ensure they meet their VAT obligations, including timely submission of VAT returns and accurate reporting of VAT liabilities. Failure to do so may lead to fines, interest charges, and, in severe cases, criminal prosecution.
Challenges and Considerations
While VAT Tax Identification Numbers are essential for businesses operating in a VAT-compliant environment, they also present certain challenges and considerations:
- VAT Registration Thresholds: Different countries have varying thresholds for VAT registration, which can impact a business's tax obligations. Understanding these thresholds is crucial for businesses operating across borders.
- VAT Rates and Exemptions: VAT rates and the treatment of specific goods and services vary across countries. Businesses must stay informed about these variations to ensure accurate VAT calculations and compliance.
- Reverse Charge Mechanism: In some cases, the responsibility for paying VAT shifts from the seller to the buyer, known as the reverse charge mechanism. Businesses must be aware of when and how this mechanism applies to their transactions.
- Multi-Country Operations: For businesses operating in multiple countries, managing VAT obligations can be complex. They must navigate different VAT regulations, rates, and reporting requirements, often requiring expert advice and assistance.
Future of VAT Tax Identification Numbers
As the global economy continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of international taxation. VAT Tax Identification Numbers are likely to play an increasingly important role in facilitating cross-border trade and ensuring tax compliance.
Digitalization and VAT
The digitalization of tax systems is a growing trend, with many countries adopting online VAT registration and filing processes. This trend is expected to continue, making VAT TINs even more accessible and efficient for businesses.
Enhanced Data Sharing
With the rise of digital platforms and e-commerce, there is a growing need for enhanced data sharing and collaboration between tax authorities. This could lead to the development of more efficient systems for cross-border VAT compliance, further streamlining the use of VAT TINs.
Potential for Standardization
While VAT Tax Identification Numbers vary in format across countries, there is a possibility of future standardization. This could simplify cross-border transactions and reduce the complexity of managing VAT obligations for businesses operating globally.
Conclusion
The VAT Tax Identification Number is a critical tool for businesses navigating the complex world of international taxation. By understanding the purpose, structure, and variations of VAT TINs, businesses can effectively manage their VAT obligations and leverage the benefits of this unique identifier. As the global economy evolves, staying informed about VAT regulations and utilizing VAT TINs efficiently will be key to successful cross-border business operations.
How do I obtain a VAT Tax Identification Number in my country?
+The process varies by country. Typically, you need to register with the tax authority, provide business details, and meet certain criteria. Check your country’s tax authority website for specific instructions.
Are there any specific requirements for obtaining a VAT TIN in the European Union (EU)?
+Yes, in the EU, businesses must register for VAT if their annual turnover exceeds a certain threshold (varies by country). The VAT number format is standardized across the EU, making it easier for cross-border transactions.
Can a business have multiple VAT Tax Identification Numbers?
+Yes, businesses with operations in multiple countries or jurisdictions may have different VAT TINs for each location. This is common for multinational corporations.
What happens if a business fails to register for VAT when required?
+Non-registration can result in penalties and legal consequences. Businesses should carefully review their turnover and VAT registration thresholds to ensure compliance.
How often must a business submit VAT returns using their VAT TIN?
+The frequency of VAT return submissions varies by country and can be monthly, quarterly, or annually. Businesses should consult their tax authority for specific guidelines.



