Va State Sales Tax
In the United States, sales tax is an essential component of revenue generation for states, playing a crucial role in funding public services and infrastructure. Each state has its own sales tax rates and regulations, making it a complex but fascinating aspect of the American taxation system. This article delves into the intricacies of the Virginia (VA) State Sales Tax, providing an in-depth analysis of its rates, exemptions, and impact on businesses and consumers.
Understanding VA State Sales Tax
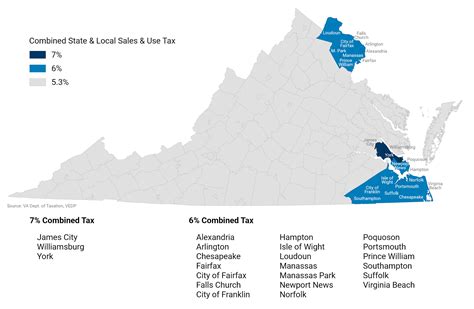
The Commonwealth of Virginia, like many other states, imposes a statewide sales and use tax on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. This tax is a crucial source of revenue for the state, contributing to the funding of vital services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure development. The VA State Sales Tax is administered by the Virginia Department of Taxation, which provides guidelines and regulations for businesses and consumers to navigate this complex taxation system.
As of [CURRENT YEAR], the general state sales tax rate in Virginia stands at 4.3%, which is applied to most retail sales and certain services. However, it's important to note that this general rate is just the base, and local jurisdictions may impose additional sales taxes, creating a range of rates across the state.
Local Sales Tax Rates in Virginia
Virginia allows local jurisdictions, including cities and counties, to levy their own sales taxes, which are added to the state’s base rate. These locality-specific sales taxes can significantly impact the overall sales tax burden on consumers and businesses. For instance, in [CITY/COUNTY], the combined state and local sales tax rate is X.X%, while in [ANOTHER CITY/COUNTY], it is Y.Y%. These variations in sales tax rates across the state can have a notable impact on businesses’ pricing strategies and consumers’ purchasing decisions.
| Locality | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Arlington County | 5.3% |
| City of Alexandria | 6.0% |
| Fairfax County | 5.0% |

The varying sales tax rates across Virginia can be a challenge for businesses operating in multiple localities. It requires them to stay updated with the latest tax rates and ensure compliance with the diverse tax regulations.
Exemptions and Special Considerations

While the VA State Sales Tax applies to a broad range of goods and services, there are several exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of. These exemptions can significantly impact the tax liability and provide relief in certain situations.
Food and Grocery Exemptions
Virginia offers partial exemptions for food and groceries. Prepared foods and meals are generally subject to the full sales tax rate, while unprepared food items, such as raw produce, meats, and dairy products, are exempt from sales tax. This exemption aims to alleviate the tax burden on essential food items, making them more affordable for consumers.
Pharmaceutical Exemptions
Prescription drugs and certain medical devices are exempt from sales tax in Virginia. This exemption is designed to support access to healthcare by reducing the cost of essential medications and medical supplies. However, it’s important to note that over-the-counter medications and certain non-prescription items may still be subject to sales tax.
Services and Intangibles
The sales tax in Virginia also applies to certain services and intangibles, including but not limited to, professional services, admission fees, and digital products. However, there are specific exemptions for services such as healthcare, legal services, and educational services. Understanding these exemptions is crucial for businesses providing services to ensure they are compliant with the state’s regulations.
Compliance and Filing Requirements
For businesses operating in Virginia, compliance with the state’s sales tax regulations is a legal requirement. This involves collecting, remitting, and reporting sales tax to the Virginia Department of Taxation on a regular basis. The frequency of filing and remittance depends on the business’s sales volume and can range from monthly to quarterly filings.
Sales Tax Registration
Any business making taxable sales in Virginia must register for a sales tax permit with the Department of Taxation. This registration process involves providing detailed information about the business, its operations, and the goods and services it offers. The permit allows the business to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state.
Sales Tax Filing and Remittance
Businesses are required to file sales tax returns and remit the collected tax to the state on a regular basis. The filing deadline is typically the 20th day of the month following the reporting period. For example, for a monthly filing, the return and payment are due on the 20th of the following month. Late filings and non-compliance can result in penalties and interest charges.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The VA State Sales Tax has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers in the state. For businesses, it adds to their operational costs and compliance requirements, especially for those operating in multiple localities with varying tax rates. On the other hand, consumers bear the brunt of the tax, which can influence their purchasing decisions and overall spending habits.
Business Impact
For businesses, managing sales tax compliance is a complex task. They need to stay updated with the latest tax rates, exemptions, and regulations to ensure they are collecting and remitting the correct amount of tax. This involves a significant investment in time and resources, especially for small businesses. Additionally, businesses may need to adjust their pricing strategies to account for the sales tax, which can impact their competitive positioning in the market.
Consumer Impact
Consumers in Virginia are directly affected by the state’s sales tax. The tax adds to the cost of goods and services they purchase, impacting their purchasing power and spending habits. The varying tax rates across localities can also influence where consumers choose to shop, with some seeking out lower tax rates. However, the exemptions for essential items like food and pharmaceuticals can provide some relief, making these items more affordable for consumers.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
As Virginia’s economy and tax landscape continue to evolve, there are several potential changes and implications that could impact the state’s sales tax system. These changes could have significant effects on businesses and consumers, shaping the future of retail and commerce in the state.
Potential Rate Changes
The VA State Sales Tax rate has remained relatively stable in recent years, but there is always the potential for rate changes. The state’s budget needs and economic conditions can influence whether the sales tax rate is increased, decreased, or maintained. A rate change, whether an increase or decrease, would have a direct impact on the cost of goods and services for consumers and the tax liability for businesses.
Online Sales Tax Collection
With the rise of e-commerce, the collection of sales tax on online sales has become a significant issue for states. Virginia, like many other states, has been working to improve its online sales tax collection processes. This includes implementing laws and regulations that require online retailers, even those without a physical presence in the state, to collect and remit sales tax on transactions with Virginia residents. These changes aim to level the playing field for brick-and-mortar retailers and ensure that online retailers contribute to the state’s revenue stream.
Tax Reform and Modernization
As Virginia’s economy and business landscape evolve, there may be calls for tax reform and modernization. This could involve restructuring the sales tax system, introducing new tax categories, or revising the exemptions and special considerations. Tax reform efforts aim to make the tax system more efficient, equitable, and aligned with the state’s economic goals.
Economic Impact and Revenue Generation
The VA State Sales Tax is a significant source of revenue for the state, funding vital public services and infrastructure projects. As the state’s economic needs change, the sales tax revenue may need to be reallocated or adjusted to meet these new demands. Additionally, the economic impact of the sales tax, especially in times of economic downturn or crisis, can be a critical factor in shaping the state’s fiscal policies and strategies.
Conclusion
The VA State Sales Tax is a complex yet crucial aspect of Virginia’s economy and taxation system. It impacts businesses and consumers alike, shaping their operational strategies and purchasing decisions. As Virginia continues to evolve, the sales tax system will likely undergo changes and reforms to adapt to new economic realities and technological advancements. Understanding and navigating this tax landscape is essential for businesses and consumers to ensure compliance and make informed financial decisions.
What is the current sales tax rate in Virginia?
+As of [CURRENT YEAR], the general state sales tax rate in Virginia is 4.3%. However, local jurisdictions may add their own sales taxes, creating a range of rates across the state.
Are there any exemptions to the VA State Sales Tax?
+Yes, there are several exemptions, including partial exemptions for food and groceries, and full exemptions for prescription drugs and certain medical devices.
How often do businesses need to file sales tax returns in Virginia?
+The frequency of filing depends on the business’s sales volume. Businesses with high sales volumes may need to file monthly, while others may file quarterly. The filing deadline is typically the 20th day of the month following the reporting period.
What happens if a business fails to comply with VA State Sales Tax regulations?
+Non-compliance can result in penalties and interest charges. The Virginia Department of Taxation may also take legal action against businesses that consistently fail to meet their sales tax obligations.



