Utah Sales Tax Calculator

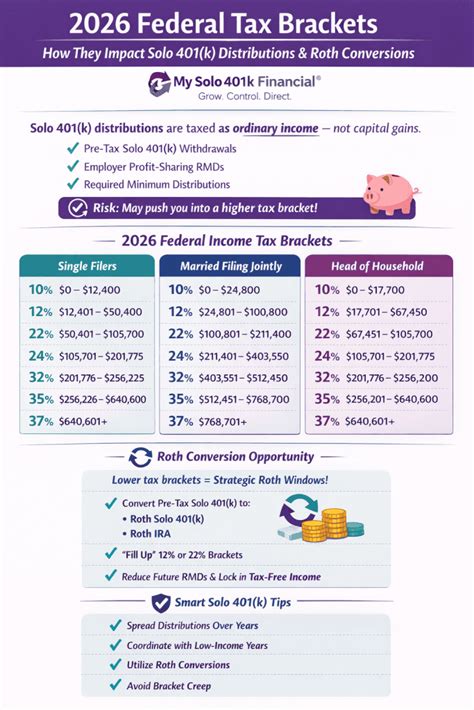
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on understanding and calculating sales tax in the state of Utah. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Utah's sales tax system, providing you with an expert-level understanding of how it works and how to navigate it effectively. Whether you're a business owner, a consumer, or simply curious about the tax landscape, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding Utah’s Sales Tax Structure
Utah, like many other states in the United States, imposes a sales tax on the sale of goods and certain services. This tax is a crucial source of revenue for the state, contributing to its economic development and the provision of public services. The Utah State Tax Commission is responsible for administering and collecting sales taxes, ensuring compliance with the state’s tax laws.
The sales tax rate in Utah is composed of both a state-level tax and a local tax, which varies depending on the jurisdiction where the sale takes place. This unique structure allows for a more localized approach to taxation, with cities and counties having the authority to impose additional sales taxes to fund specific projects or initiatives.
State-Level Sales Tax
The state of Utah applies a uniform sales tax rate of 4.70% across the entire state. This base rate is set by the Utah State Legislature and is applicable to most tangible personal property and certain services. It serves as the foundation for the overall sales tax rate, to which local taxes are added.
| Tax Category | State Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| General Sales Tax | 4.70% |
The state-level sales tax is inclusive of various components, including the Utah Sales and Use Tax, the Special Surcharge, and the Lodging Tax. Each of these components contributes to the overall revenue generated by the state through sales taxes.
Local Sales Taxes
In addition to the state-level sales tax, Utah allows for the imposition of local sales taxes by cities, counties, and special districts. These local taxes can vary significantly across the state, resulting in different sales tax rates depending on the location of the sale.
Local sales taxes are often used to fund specific projects or initiatives, such as infrastructure development, public transportation, or cultural programs. They provide a means for local governments to raise revenue for community-specific needs while ensuring that the burden is distributed among consumers.
The local sales tax rate can range from 0% to 6.05%, depending on the jurisdiction. This variation in tax rates can make it challenging for businesses and consumers to keep track of the applicable sales tax in different areas of the state.
| Jurisdiction | Local Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Salt Lake City | 1.70% |
| Ogden | 1.75% |
| Provo | 1.30% |
| St. George | 1.50% |
| Moab | 2.00% |
Calculating Sales Tax in Utah
Calculating sales tax in Utah involves a straightforward process, but it’s essential to consider both the state-level and local tax rates. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you calculate the sales tax accurately.
Step 1: Determine the State-Level Tax
Start by multiplying the purchase amount by the state-level sales tax rate of 4.70%. This calculation will give you the state tax portion of the total sales tax.
Example: If the purchase amount is $100, the state tax would be calculated as follows:
State Tax = $100 * 0.0470 = $4.70
Step 2: Determine the Local Tax
Next, identify the local tax rate applicable to the jurisdiction where the sale is taking place. Multiply the purchase amount by this local tax rate to find the local tax portion.
Example: If the local tax rate is 1.70% (as in Salt Lake City), the local tax calculation would be:
Local Tax = $100 * 0.0170 = $1.70
Step 3: Combine State and Local Taxes
Add the state tax and the local tax together to find the total sales tax for the purchase.
Total Sales Tax = State Tax + Local Tax
Example: In Salt Lake City, the total sales tax for a $100 purchase would be:
Total Sales Tax = $4.70 + $1.70 = $6.40
Step 4: Add the Sales Tax to the Purchase Price
Finally, add the total sales tax to the original purchase price to determine the final cost of the item or service.
Final Cost = Purchase Price + Total Sales Tax
Example: For the $100 purchase in Salt Lake City, the final cost would be:
Final Cost = $100 + $6.40 = $106.40
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
While most tangible personal property and certain services are subject to sales tax in Utah, there are specific exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of.
Exemptions
Utah provides sales tax exemptions for certain goods and services. These exemptions can vary based on the nature of the item or the purpose for which it is purchased. Some common exemptions include:
- Food and Drugs: Sales tax is generally not applied to unprepared food items, over-the-counter medications, and certain medical supplies.
- Educational Materials: Textbooks, school supplies, and certain educational resources are exempt from sales tax.
- Clothing and Footwear: Clothing and footwear items below a certain price threshold are exempt from sales tax.
- Agricultural Equipment: Sales tax is not applied to agricultural machinery and equipment used in farming operations.
- Certain Services: Services such as legal, medical, and financial services are often exempt from sales tax.
Special Considerations
Utah also has specific tax considerations for certain industries and transactions. These include:
- Construction and Remodeling: Sales tax is applied to the sale of building materials and services related to construction and remodeling projects.
- Vehicle Sales: Vehicle sales are subject to a separate registration fee and a sales tax based on the vehicle's value. The sales tax rate for vehicles is different from the general sales tax rate.
- Online Sales: Out-of-state sellers are required to collect and remit sales tax on online sales to Utah residents, provided certain conditions are met.
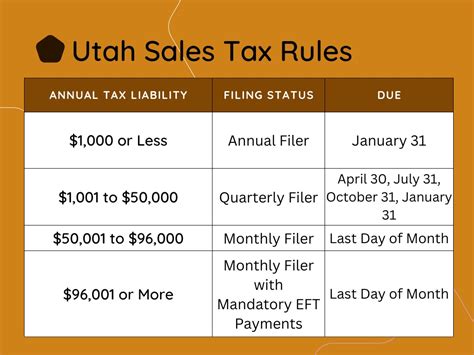
Compliance and Reporting
Businesses operating in Utah have a responsibility to comply with the state’s sales tax laws and regulations. This includes accurately calculating and collecting sales tax from customers, as well as properly reporting and remitting the collected taxes to the Utah State Tax Commission.
Businesses should maintain accurate records of sales transactions, including the breakdown of state and local taxes collected. These records are essential for audit purposes and ensuring compliance with tax laws.
The Utah State Tax Commission provides resources and guidance to help businesses understand their sales tax obligations. They offer registration processes, tax rate databases, and reporting forms to facilitate compliance.
Future Implications and Trends
The sales tax landscape in Utah is subject to change as the state’s economy evolves and legislative priorities shift. Here are some potential future implications and trends to consider:
Economic Development Initiatives
Utah’s sales tax structure provides an opportunity for local governments to fund specific economic development projects. As the state continues to attract businesses and promote economic growth, local sales taxes may be adjusted to support these initiatives.
Online Sales Tax Collection
With the growth of e-commerce, the collection of sales tax on online sales has become a significant focus for states. Utah may continue to refine its laws and regulations to ensure fair tax collection from out-of-state sellers, especially as more consumers turn to online shopping.
Tax Simplification Efforts
The variation in local sales tax rates across Utah can create complexities for businesses and consumers. There may be future efforts to streamline and simplify the tax structure, potentially through the adoption of uniform tax rates or simplified tax collection methods.
Environmental Initiatives
Some states have explored the idea of using sales tax revenue to fund environmental initiatives and sustainability projects. Utah may consider allocating a portion of its sales tax revenue towards such causes, especially as environmental concerns gain prominence.
Conclusion
Understanding and navigating Utah’s sales tax system is essential for both businesses and consumers. By comprehending the state’s unique sales tax structure, including the state-level and local tax rates, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and ensure compliance with tax laws.
This guide has provided an in-depth look at Utah's sales tax, from its structure and calculation to exemptions and future implications. As the state continues to evolve, staying informed about sales tax changes will be crucial for effective tax management and compliance.
How often do sales tax rates change in Utah?
+Sales tax rates in Utah can change periodically, usually as a result of legislative actions or local government decisions. While the state-level tax rate is relatively stable, local tax rates can be subject to more frequent adjustments. It’s essential for businesses and consumers to stay updated on any changes to ensure accurate tax calculations.
Are there any tools available to calculate sales tax in Utah?
+Yes, there are online tools and calculators available that can assist with sales tax calculations in Utah. These tools often allow you to input the purchase amount and the applicable tax rates to determine the total sales tax. They can be particularly useful for businesses with multiple locations or for consumers making significant purchases.
How can businesses stay updated on sales tax changes in Utah?
+Businesses can stay informed about sales tax changes by regularly checking the Utah State Tax Commission’s website, which provides updates and announcements regarding tax law modifications. Additionally, businesses can subscribe to tax newsletters or alerts to receive timely notifications of any changes.
Are there any penalties for underreporting or non-compliance with sales tax in Utah?
+Yes, Utah imposes penalties for underreporting or non-compliance with sales tax laws. Penalties can include fines, interest charges, and even criminal prosecution in severe cases. It’s crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records and comply with tax obligations to avoid these penalties.
Can individuals file for a sales tax refund in Utah?
+Individuals who believe they have overpaid sales tax in Utah can file for a refund. The process involves completing a sales tax refund application and providing supporting documentation. It’s important to review the refund guidelines and eligibility criteria before initiating the refund process.