Boston Taxes Property

Welcome to a comprehensive guide on property taxes in the city of Boston, Massachusetts. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the property tax system, offering valuable insights and practical information for homeowners, investors, and anyone interested in understanding the fiscal landscape of one of America's most historic and vibrant cities.
The Boston Property Tax Landscape
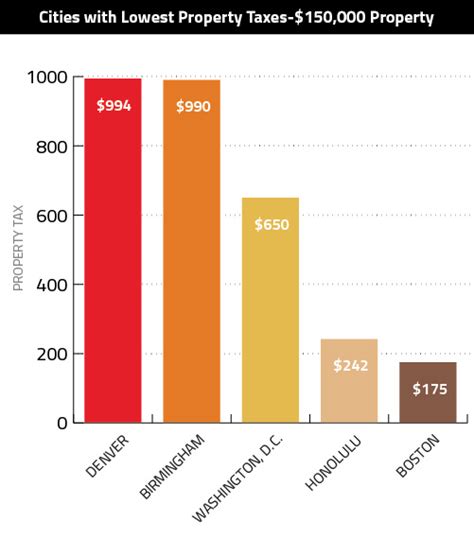
Property taxes are an essential part of the municipal revenue stream for cities across the United States, and Boston is no exception. These taxes contribute significantly to the city’s budget, funding critical services and infrastructure development. Understanding the intricacies of Boston’s property tax system is key to navigating the local real estate market effectively.
Boston's property tax system is structured around a combination of state and local regulations, with the city's fiscal year running from July 1st to June 30th. The city assesses property taxes based on the value of the property, with rates varying depending on the type of property and its location within Boston's unique neighborhoods.
Tax Rates and Assessment Process
Boston’s residential property tax rate for fiscal year 2023 stands at 19.79 per thousand of assessed value, while the commercial tax rate is set at 32.99 per thousand. These rates are subject to change annually, with the city council determining the tax rates based on the city’s budget requirements.
The assessment process involves evaluating the property's value, which is typically done by a professional assessor. The assessed value is then multiplied by the applicable tax rate to determine the property tax liability. Boston's Department of Revenue ensures that this process is fair and transparent, regularly reviewing assessment methods and providing resources for taxpayers to understand their assessments.
To illustrate, consider a single-family home in Boston's Back Bay neighborhood. If this home has an assessed value of $1,000,000, the property tax for the year would be calculated as follows:
| Assessed Value | $1,000,000 |
|---|---|
| Residential Tax Rate | $19.79 per thousand |
| Property Tax | $19,790 |

Tax Exemptions and Discounts
Boston offers a range of tax exemptions and discounts to certain property owners. These incentives are designed to promote specific goals, such as encouraging homeownership, supporting senior citizens, and stimulating economic development in targeted areas.
- Homeowners who occupy their primary residence may be eligible for a residential exemption, which can lower their assessed value by up to $1,000,000.
- Senior citizens who are at least 65 years old and meet income requirements may qualify for a senior citizen exemption, reducing their taxable value.
- Boston also offers tax abatements for certain commercial properties, particularly in designated development areas, to attract businesses and spur economic growth.
Payment Options and Due Dates
Property taxes in Boston are typically due in two installments. The first installment is due on July 1st, and the second installment is due on December 31st. Homeowners have the option to pay their taxes in full by the first due date or make payments in installments. Late payments may incur interest and penalties, so it’s crucial to stay informed about the payment schedule.
The city offers various payment methods, including online payment platforms, direct bank transfers, and traditional mail-in checks. For those who need assistance, the Boston Treasury Collection Division provides resources and support to ensure that taxpayers understand their options and can make timely payments.
Impact on the Real Estate Market

Property taxes play a significant role in shaping Boston’s real estate landscape. They influence investment decisions, property values, and the overall attractiveness of the city’s neighborhoods. Understanding the tax implications is crucial for both buyers and sellers in the Boston market.
Tax Considerations for Buyers
For homebuyers, property taxes are a critical factor in their decision-making process. Prospective buyers often use property tax estimates to evaluate the affordability of a home and to budget for ongoing expenses. They may also consider the potential for tax incentives or exemptions, which can significantly reduce their tax burden.
When evaluating a property, buyers should carefully consider the assessed value and the potential tax liability. This information is readily available through the city's online tax database, which provides detailed information on property assessments and tax histories. Real estate agents and brokers can also provide valuable insights into the tax landscape of specific neighborhoods.
Tax Strategies for Property Owners
Property owners in Boston have several strategies at their disposal to manage their tax liabilities effectively. One common approach is to review their property assessment annually and ensure it accurately reflects the property’s value. If the assessment seems too high, property owners can appeal to the Boston Assessing Department, providing evidence to support their claim.
Another strategy is to take advantage of the available tax exemptions and discounts. For instance, homeowners can apply for the residential exemption, which can significantly reduce their tax bill. Similarly, senior citizens can explore the senior citizen exemption, which can provide much-needed financial relief.
Additionally, property owners can consider investing in energy-efficient upgrades or renovations. Boston offers tax incentives for such improvements, which can not only reduce a property's environmental impact but also lower its tax assessment due to the increased energy efficiency.
Property Tax and Investment Decisions
For real estate investors, property taxes are a key consideration when evaluating potential investment properties. High property taxes can eat into an investor’s profits, making a seemingly lucrative deal less attractive. On the other hand, areas with lower tax rates or tax incentives can provide attractive opportunities for investors.
When assessing an investment property, investors should carefully analyze the tax implications. They should consider not only the current tax rates but also the potential for future rate increases or changes in tax policies. Understanding the local political landscape and the city's fiscal health can provide valuable insights into the stability of the tax environment.
Community Impact and Revenue Allocation
Property taxes are a vital source of revenue for Boston, funding essential services and infrastructure projects that benefit the entire community. The revenue generated from property taxes is allocated to various municipal departments and initiatives, ensuring the city’s continued growth and development.
Services and Infrastructure
Property tax revenue supports a wide range of public services, including education, public safety, transportation, and healthcare. For instance, a portion of the tax revenue goes towards funding Boston’s renowned public school system, ensuring that every child has access to quality education. Property taxes also contribute to the maintenance and improvement of the city’s infrastructure, from roads and bridges to parks and recreational facilities.
In addition, the revenue helps maintain a robust public transportation system, which is crucial for the city's residents and businesses. The Boston Transportation Department uses property tax funds to maintain and expand the city's subway, bus, and bike-sharing systems, promoting sustainable and efficient mobility.
Community Development and Revitalization
Property taxes play a critical role in Boston’s community development initiatives. The city strategically allocates tax revenue to revitalize underserved neighborhoods, improve housing conditions, and stimulate economic growth. This approach not only enhances the quality of life for residents but also attracts new businesses and investment, further strengthening the local economy.
One notable example is the Boston Neighborhood Target Area Program, which uses property tax revenue to fund grants and initiatives aimed at improving housing, business development, and overall quality of life in targeted neighborhoods. This program has been instrumental in revitalizing areas like Roxbury and Dorchester, making them more attractive and vibrant communities.
The Impact on Boston’s Economy
Boston’s robust property tax system has a significant impact on the city’s economy. The revenue generated from property taxes provides a stable and reliable source of funding for the city’s operations, allowing for efficient service delivery and infrastructure development. This, in turn, attracts businesses and creates a conducive environment for economic growth.
The presence of a strong tax base has been a key factor in Boston's reputation as a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship. It has attracted tech giants, startups, and investors, contributing to the city's thriving tech and biotech sectors. Additionally, the stable tax environment encourages businesses to establish long-term operations in Boston, further strengthening the local economy.
Navigating the Tax System: Tips and Resources
Understanding and navigating Boston’s property tax system can be complex, but there are resources available to assist taxpayers. Here are some tips and resources to help you manage your property tax obligations effectively:
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on tax rates, assessment processes, and any changes to the tax system. The Boston Department of Revenue provides regular updates and resources on their website.
- Understand Your Assessment: Review your property assessment annually and ensure it accurately reflects your property's value. If you disagree with the assessment, you can appeal to the Boston Assessing Department.
- Explore Exemptions: Research and apply for any tax exemptions or discounts you may be eligible for. This can significantly reduce your tax liability.
- Payment Options: Take advantage of the various payment methods offered by the city, and consider setting up automatic payments to ensure timely payment and avoid penalties.
- Community Resources: Reach out to community organizations or local real estate professionals for advice and support. They can provide valuable insights into the local tax landscape.
Conclusion
Boston’s property tax system is a critical component of the city’s fiscal health and community development. It provides the necessary revenue to fund essential services, support infrastructure projects, and drive economic growth. By understanding the tax landscape, homeowners, investors, and community members can make informed decisions and actively contribute to the vibrant city of Boston.
Whether you're a first-time homebuyer, a seasoned investor, or a long-time resident, knowing your property tax obligations and the opportunities available can empower you to make the most of your real estate journey in Boston. Stay informed, engage with the community, and take advantage of the resources at your disposal to navigate Boston's tax system with confidence.
How often are property tax rates reviewed and adjusted in Boston?
+Property tax rates in Boston are reviewed and adjusted annually by the city council based on the city’s budget requirements and economic conditions. This ensures that the tax rates remain fair and aligned with the city’s financial needs.
What happens if I miss the property tax payment deadline in Boston?
+Late payments in Boston may incur interest and penalties. It’s important to stay informed about the payment schedule and make timely payments to avoid additional costs. The city offers resources and support to assist taxpayers in managing their payments.
Can I appeal my property assessment in Boston if I believe it is inaccurate?
+Yes, if you believe your property assessment is inaccurate, you have the right to appeal. The Boston Assessing Department provides a formal appeal process, allowing you to present evidence and argue for a reassessment. It’s advisable to seek professional advice to navigate the appeal process effectively.
Are there any tax incentives for green or energy-efficient improvements in Boston properties?
+Absolutely! Boston offers tax incentives for property owners who make energy-efficient improvements. These incentives can reduce the property’s tax assessment, making it more attractive and environmentally friendly. The city encourages such improvements as part of its sustainability initiatives.
How does Boston’s property tax system support community development and revitalization efforts?
+Boston strategically allocates property tax revenue to fund community development initiatives. This includes programs like the Neighborhood Target Area Program, which targets underserved areas for improvement. By investing in these neighborhoods, the city enhances their appeal and attracts new businesses and residents, fostering economic growth and a better quality of life.