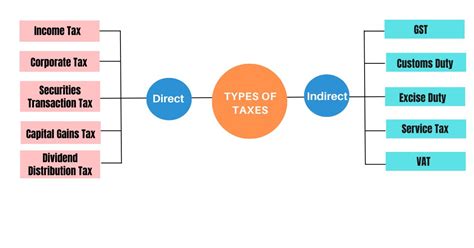
Types Of Taxes
Taxes are an integral part of any economy, serving as a vital source of revenue for governments worldwide. The implementation of various types of taxes allows for the funding of public services, infrastructure development, and the overall well-being of a nation. Understanding the different types of taxes and their implications is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike.
The Landscape of Taxation

Taxation is a complex system designed to allocate the financial burden of a nation’s operations and growth among its citizens and entities. The specific types of taxes vary across jurisdictions, reflecting unique economic, social, and political considerations. In this article, we will delve into the diverse landscape of taxes, exploring their classifications, mechanics, and real-world applications.
Income Taxes: A Cornerstone of Modern Taxation

Income taxes are among the most common and fundamental types of taxes. These taxes are levied on the income earned by individuals and businesses, including wages, salaries, investments, and profits. Income taxes are often progressive, meaning that higher income earners pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes. This approach aims to promote equity and reduce income disparities.
Individual Income Tax
Individuals are subject to personal income taxes based on their taxable income, which is calculated after deducting allowable expenses and credits. The tax rate varies depending on income brackets, with higher rates applied to higher income levels. Many countries offer tax incentives, such as deductions for charitable donations or retirement savings, to encourage certain behaviors and support specific causes.
Corporate Income Tax
Businesses, whether sole proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations, are also subject to income taxes. Corporate income tax rates can vary widely between countries and even within different industries in the same country. Some nations offer tax incentives to attract foreign investment or promote specific sectors, such as renewable energy or research and development.
| Country | Corporate Income Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| United States | 21% |
| Canada | 15% |
| United Kingdom | 19% |

Sales and Consumption Taxes: Levying on Transactions
Sales and consumption taxes are imposed on the sale or purchase of goods and services. These taxes are typically added to the price of the product or service, making them a visible component of the final cost. They are a significant source of revenue for governments, as they capture a broad range of economic activities.
Value-Added Tax (VAT)
Value-Added Tax is a consumption tax levied on the added value at each stage of production and distribution. It is calculated based on the difference between the selling price and the cost of inputs. VAT is often considered a more efficient tax system as it minimizes tax evasion and ensures a broader tax base. It is widely adopted in many countries, especially in Europe.
| Country | VAT Rate |
|---|---|
| European Union | 15-25% |
| Canada | 5% |
| Australia | 10% |
Sales Tax
Sales tax is a consumption tax imposed at the point of sale. It is typically a flat rate applied to the purchase price of goods and services. While similar to VAT, sales tax is generally simpler to administer and understand. However, it can create complexities when goods are sold across state or provincial borders.
Property Taxes: Assessing Real Estate
Property taxes are levied on the ownership or transfer of real estate properties, such as land, buildings, and other improvements. These taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments, helping fund local services like schools, fire departments, and infrastructure.
Real Estate Property Tax
Real estate property taxes are typically based on the assessed value of the property. The assessment is conducted by a government agency, which determines the property’s value based on factors like location, size, and condition. The tax rate is then applied to this assessed value to calculate the annual tax liability.
Transfer Taxes
Transfer taxes are levied on the transfer of property ownership, such as when a property is sold or gifted. These taxes are often calculated as a percentage of the property’s value and are paid by the buyer or the transferor. Transfer taxes can be a significant expense for individuals and businesses involved in real estate transactions.
Excise Taxes: Targeted Levies on Specific Goods

Excise taxes are imposed on specific goods or services, often to discourage their consumption or to raise funds for specific purposes. These taxes are usually included in the price of the product and are often higher for items considered harmful or unnecessary, such as tobacco, alcohol, and luxury goods.
Sin Taxes
Sin taxes are excise taxes imposed on goods considered harmful or addictive, such as tobacco, alcohol, and gambling. These taxes aim to reduce consumption of these goods, improve public health, and generate revenue for social programs. The high tax rates on these items can make them less affordable, leading to reduced demand.
Luxury Taxes
Luxury taxes are levied on high-end, non-essential items like yachts, private jets, and luxury cars. These taxes are designed to generate revenue from those who can afford such indulgences and often carry a social stigma. Luxury taxes can be a significant source of income for governments, particularly in times of economic hardship.
Conclusion: The Complexity of Taxation
Taxation is a multifaceted system, with various types of taxes serving different purposes and addressing diverse economic and social needs. From income taxes to consumption taxes, property taxes, and excise taxes, each type has its own mechanics, implications, and challenges. Understanding these nuances is essential for individuals and businesses to navigate the tax landscape effectively and contribute responsibly to their communities and nations.
How do income taxes affect economic growth and income inequality?
+Income taxes play a crucial role in shaping economic growth and income inequality. Progressive income taxes can help redistribute wealth, reducing income disparities and promoting social mobility. On the other hand, high income taxes can disincentivize work and investment, potentially slowing economic growth. Striking the right balance is a key challenge for policymakers.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a VAT system?
+A Value-Added Tax (VAT) system offers several advantages, including a broader tax base, reduced tax evasion, and simplicity in administration. However, it can also lead to higher prices for consumers and may be complex to implement and manage, especially for small businesses.
How do property taxes impact local communities and homeowners?
+Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments, funding essential services like education and infrastructure. For homeowners, these taxes can be a substantial expense, and their impact can vary based on the assessed value of the property and the local tax rate. Property tax reforms are often debated to ensure fairness and affordability.