Texas Gas Tax
The Texas Gas Tax, officially known as the State Motor Fuel Tax, is a crucial component of Texas's transportation funding system. It plays a significant role in the maintenance and development of the state's vast road network, contributing to the overall economic growth and quality of life for Texans.
This article delves into the intricacies of the Texas Gas Tax, exploring its history, purpose, and impact on the state's infrastructure and economy. We will examine the tax rate, its distribution, and the benefits it brings to Texas residents and businesses. By understanding the Texas Gas Tax, we can appreciate its vital role in shaping the state's transportation landscape.
Understanding the Texas Gas Tax

The Texas Gas Tax is a per-gallon excise tax levied on motor fuels, including gasoline and diesel. It is a key revenue source for the State Highway Fund, which finances various transportation projects and initiatives across the state. The tax is an essential mechanism for maintaining and expanding Texas’s extensive road network, ensuring safe and efficient travel for all users.
Historical Context
The origins of the Texas Gas Tax can be traced back to the early 20th century when the state first introduced a motor fuel tax to fund road construction and maintenance. Over the years, the tax rate has undergone several adjustments to meet the evolving needs of the state’s infrastructure. The current tax structure reflects a careful balance between generating sufficient revenue and ensuring affordability for Texas drivers.
Tax Rate and Distribution
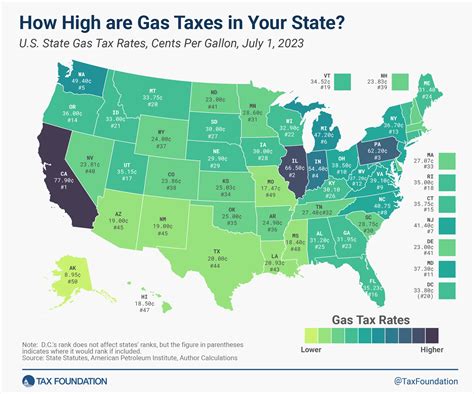
As of [insert current date], the Texas Gas Tax stands at 0.20 per gallon</strong> for gasoline and <strong>0.25 per gallon for diesel fuel. This rate is consistent across the state, ensuring uniformity and simplicity for taxpayers. The tax is collected at the wholesale level, with distributors and retailers passing on the cost to consumers at the pump.
| Fuel Type | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Gasoline | $0.20 per gallon |
| Diesel | $0.25 per gallon |
The revenue generated from the Texas Gas Tax is distributed through a complex system, with a significant portion dedicated to the State Highway Fund. This fund supports a wide range of transportation projects, including highway construction, maintenance, and improvement, as well as public transportation initiatives.
Benefits of the Texas Gas Tax

The Texas Gas Tax offers several advantages to the state and its residents. By providing a dedicated funding source for transportation infrastructure, the tax ensures the continuous development and upkeep of roads, bridges, and highways. This, in turn, enhances safety, reduces travel time, and supports economic growth by facilitating the efficient movement of goods and people.
Economic Impact
The Texas Gas Tax plays a vital role in the state’s economy. It directly supports the transportation sector, which is a significant employer and contributor to Texas’s GDP. Additionally, the tax revenue funds critical infrastructure projects, attracting businesses and investors to the state. The well-maintained road network improves access to markets, resources, and employment opportunities, benefiting both businesses and residents alike.
Environmental Considerations
While the primary focus of the Texas Gas Tax is on funding transportation infrastructure, it also indirectly contributes to environmental sustainability. By maintaining and improving roads, the tax helps reduce traffic congestion and vehicle emissions. Efficient road networks encourage the use of public transportation and promote the adoption of cleaner energy alternatives, aligning with Texas’s commitment to environmental stewardship.
Future Outlook and Challenges
As Texas continues to experience population growth and economic expansion, the demand for reliable transportation infrastructure will only increase. The Texas Gas Tax will play a crucial role in meeting these challenges, providing the necessary funds for road expansion and modernization. However, the state must also address the evolving nature of transportation, including the rise of electric vehicles and alternative fuels, to ensure the tax remains relevant and effective.
One key challenge is the potential decline in gas tax revenue as more drivers adopt electric vehicles. To address this, Texas may need to explore alternative funding mechanisms, such as road user charges or vehicle miles traveled taxes. These strategies could ensure a sustainable funding source for transportation infrastructure, regardless of the fuel type used.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is the Texas Gas Tax calculated and collected?
+The Texas Gas Tax is calculated based on the wholesale price of motor fuels and is collected from distributors and retailers. The tax rate is applied per gallon, and the revenue is remitted to the state.
What projects does the Texas Gas Tax fund?
+The tax primarily funds road construction, maintenance, and improvement projects. It also supports public transportation initiatives, ensuring a comprehensive approach to transportation infrastructure development.
How does the Texas Gas Tax compare to other states?
+Texas’s gas tax rate is relatively low compared to many other states. However, the state’s vast size and diverse transportation needs make it challenging to directly compare tax rates and infrastructure funding.
Are there any exemptions or discounts for the Texas Gas Tax?
+Yes, certain entities, such as government agencies and public transportation authorities, may be eligible for tax exemptions or discounts. These provisions are designed to support specific transportation-related activities and services.
How can I stay updated on changes to the Texas Gas Tax?
+You can monitor official state websites and news outlets for any updates or proposed changes to the Texas Gas Tax. Additionally, transportation advocacy groups and industry associations often provide valuable insights and information on transportation funding and policy developments.