How Do You Add Tax To A Price
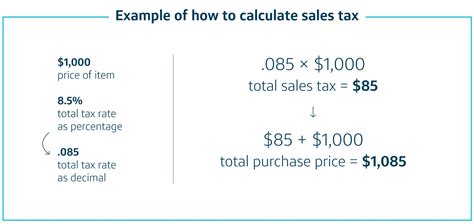
Adding tax to a price is a fundamental concept in commerce, ensuring businesses comply with tax regulations and accurately reflect the total cost to consumers. This process, while seemingly straightforward, can vary based on factors like the type of goods or services, the jurisdiction, and the applicable tax rates. Let's delve into the specifics of adding tax to a price, exploring the various methods and considerations involved.
Understanding Tax Rates and Types

Before we discuss the methods of adding tax, it’s crucial to understand the different types of taxes and their respective rates. Taxes can generally be categorized into two main types: sales tax and value-added tax (VAT). Sales tax is typically calculated as a percentage of the selling price and is often charged on goods and services at the point of sale. On the other hand, VAT is applied at each stage of the supply chain, from production to retail, and is calculated as a percentage of the value added at each stage.
Tax rates can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction. For instance, the European Union has a harmonized VAT system with a standard rate of 15%, but member states can set their own reduced rates for specific goods and services. In contrast, the United States has a more complex system, with sales tax rates varying by state and sometimes even by county or city.
Calculating Sales Tax
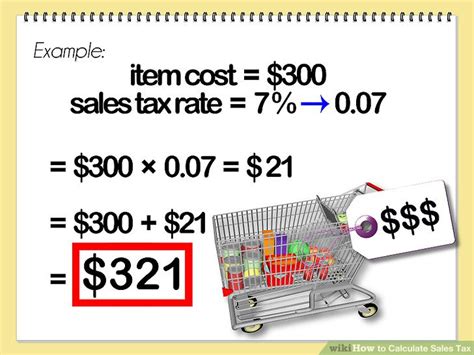
Calculating sales tax is relatively simple. The basic formula is:
Sales Tax = Price x Sales Tax Rate
For example, if a product costs $100 and the sales tax rate is 7%, the sales tax amount would be:
Sales Tax = $100 x 0.07 = $7
So, the total price including tax would be:
Total Price = Price + Sales Tax = $100 + $7 = $107
Calculating VAT
Calculating VAT is a bit more complex, as it involves considering the value added at each stage of the supply chain. The basic formula for calculating VAT is:
VAT = (Selling Price - Purchase Price) x VAT Rate
For instance, if a retailer purchases goods for $80 and sells them for $120, with a VAT rate of 15%, the VAT amount would be:
VAT = ($120 - $80) x 0.15 = $6
Thus, the total price including VAT would be:
Total Price = Selling Price + VAT = $120 + $6 = $126
Methods of Adding Tax

There are several methods businesses can use to add tax to prices, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Inclusive Pricing
In inclusive pricing, the tax is already included in the displayed price. This method is often used for VAT, as it simplifies the pricing process and makes it easier for consumers to understand the total cost. When using inclusive pricing, businesses must ensure that the displayed price includes the tax amount, and the tax rate should be clearly communicated to customers.
Exclusive Pricing
Exclusive pricing, on the other hand, displays the price excluding tax. This method is commonly used for sales tax, as it allows for more flexibility in pricing and can be advantageous for businesses with varying tax rates across different jurisdictions. With exclusive pricing, the tax amount is calculated and added at the point of sale, ensuring compliance with local tax regulations.
Dynamic Tax Calculation
For businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions or selling products with varying tax rates, dynamic tax calculation can be a useful approach. This method involves using software or algorithms to automatically calculate and apply the correct tax rate based on the customer’s location or the product’s tax category. Dynamic tax calculation ensures accuracy and compliance, especially in complex tax scenarios.
Challenges and Considerations
Adding tax to prices can present several challenges, particularly for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions or dealing with complex tax structures. Some key considerations include:
- Tax Rate Changes: Tax rates can fluctuate over time, requiring businesses to stay updated and adjust their pricing strategies accordingly.
- Multiple Tax Jurisdictions: Businesses operating across different states, provinces, or countries must navigate varying tax rates and regulations, making tax compliance a complex task.
- Tax Exemptions: Certain goods or services may be exempt from tax, and businesses must accurately identify and apply these exemptions to avoid overcharging customers.
- Rounding and Precision: When calculating tax, precision is crucial. Businesses must ensure that rounding errors do not significantly impact the final price, especially for high-value transactions.
The Impact of Technology
Advancements in technology have significantly streamlined the process of adding tax to prices. Tax calculation software and e-commerce platforms now offer built-in tax engines that automatically calculate and apply the correct tax rates based on the customer’s location and the product’s attributes. These tools not only enhance accuracy but also reduce the administrative burden on businesses, allowing them to focus on their core operations.
Case Study: Tax Compliance for Online Retailers
Online retailers face unique challenges when it comes to tax compliance. With the rise of e-commerce, many businesses now sell their products across state and country borders, leading to complex tax scenarios. To address this, many online retailers have adopted sophisticated tax compliance solutions. These solutions integrate with e-commerce platforms, automatically calculating and applying the correct tax rates based on the customer’s shipping address and the product’s tax category. By ensuring accurate tax calculations, these solutions not only help businesses stay compliant but also enhance the customer experience by providing transparent pricing information.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Tax
Adding tax to a price is a critical aspect of doing business, requiring careful consideration of tax rates, types, and jurisdictional regulations. Whether it’s sales tax or VAT, businesses must choose the appropriate pricing method and ensure accurate tax calculations to maintain compliance and build trust with their customers. With the right tools and strategies, businesses can navigate the complex world of tax, ensuring their pricing strategies are both compliant and customer-friendly.
How do I determine the correct tax rate for my business?
+The correct tax rate depends on your business location and the nature of your products or services. For instance, in the US, you’ll need to research the sales tax rates for your state, county, and city. Similarly, if you’re dealing with VAT in the EU, you’ll need to understand the standard and reduced rates applicable to your business.
What is the difference between inclusive and exclusive pricing when it comes to tax?
+Inclusive pricing includes the tax in the displayed price, while exclusive pricing displays the price excluding tax. Inclusive pricing is often used for VAT, as it simplifies the pricing process, while exclusive pricing is common for sales tax, allowing for more flexibility in pricing.
How can I stay updated on changing tax rates and regulations?
+Staying informed about tax changes is crucial. You can subscribe to tax newsletters or use tax compliance software that provides regular updates on tax rate changes and new regulations. Additionally, staying in touch with local tax authorities and industry associations can provide valuable insights.
Are there any tax calculation tools or software that can help simplify the process?
+Absolutely! There are various tax calculation software and platforms available that can automate tax calculations based on your business location and product attributes. These tools not only save time but also reduce the risk of errors in tax calculations.



