Taxes And Transfers
Taxes and transfers are fundamental components of any economy, shaping the financial landscape and influencing the lives of individuals and businesses alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of taxes and transfers, exploring their impact, mechanisms, and implications. By examining real-world examples and industry data, we aim to provide an in-depth analysis that sheds light on this essential aspect of economic systems.
The Role of Taxes in Economic Systems

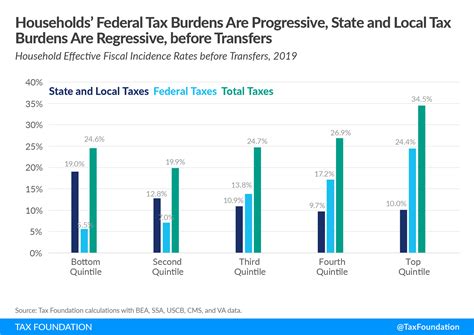
Taxes are a vital tool for governments to raise revenue, fund public services, and influence economic behavior. They are a fundamental component of any nation’s fiscal policy, with the primary goal of sustaining the government’s operations and providing for the well-being of its citizens. The tax system in most countries is designed to be progressive, meaning that those with higher incomes pay a larger proportion of their earnings in taxes.
The progressive tax system aims to promote fairness and reduce income inequality. For instance, in the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) collects federal income taxes based on different tax brackets, with higher income earners paying a larger percentage of their income. This ensures that the tax burden is distributed more equitably across the population.
Types of Taxes and Their Impact
Taxes can be categorized into various types, each serving a specific purpose and affecting different aspects of the economy. Here are some key types of taxes and their roles:
- Income Tax: As mentioned earlier, income tax is a progressive tax that is levied on an individual’s or entity’s earnings. It is a significant source of revenue for governments, allowing them to fund essential services like education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Sales Tax: Sales tax is imposed on the sale of goods and services. It is typically added to the purchase price, making it a regressive tax as it affects lower-income individuals relatively more. However, some jurisdictions offer exemptions or reduced rates for essential items.
- Property Tax: Property taxes are levied on real estate and are usually based on the assessed value of the property. They are a vital source of revenue for local governments, funding schools, emergency services, and local infrastructure.
- Corporate Tax: Corporations are subject to corporate tax on their profits. This tax is often complex, with varying rates and provisions, and can significantly impact a company’s financial health and investment decisions.
- Excise Tax: Excise taxes are imposed on specific goods or services, such as tobacco, alcohol, or fuel. They are often used to discourage consumption of certain products or to raise revenue for specific purposes, like funding healthcare initiatives.
| Tax Type | Revenue Source | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Income Tax | Personal & Corporate Earnings | Funding Public Services, Reducing Income Inequality |
| Sales Tax | Retail Sales | Revenue for State/Local Governments, Potential Impact on Consumer Spending |
| Property Tax | Real Estate Value | Funding Local Services, Influencing Property Values |
| Corporate Tax | Business Profits | Impact on Corporate Financial Decisions, Attracting Investments |
| Excise Tax | Specific Goods/Services | Discouraging Consumption, Funding Specific Initiatives |
Transfers: Redressing Economic Inequality

Transfers, also known as social benefits or welfare programs, are a crucial mechanism for governments to redistribute wealth and reduce economic disparities. They provide financial assistance to individuals and families who are facing economic hardship, ensuring a basic level of support and promoting social equity.
Common Transfer Programs
Transfer programs vary widely across countries, but some common examples include:
- Unemployment Benefits: These are payments made to individuals who have lost their jobs through no fault of their own. They provide temporary financial support until the individual can find new employment.
- Social Security: Social security programs provide financial assistance to elderly individuals, ensuring they have a stable income during their retirement years.
- Medicaid and Medicare: These programs provide healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and the elderly, respectively. They ensure access to essential medical services for those who cannot afford private insurance.
- Child Benefits: Many countries offer financial support to families with children, helping to offset the costs of raising a family and encouraging higher birth rates.
- Housing Assistance: Rental subsidies and other housing benefits are often provided to low-income households to ensure they have access to safe and affordable housing.
The Impact of Transfers on Society
Transfers have a profound impact on society, improving the well-being of vulnerable individuals and families. They reduce poverty, improve access to healthcare and education, and promote social mobility. For instance, a study by the OECD found that social transfers in member countries reduced the poverty rate by an average of 37% in 2020.
Moreover, transfers can have positive economic effects. By providing a basic level of support, they can stimulate consumer spending, which in turn boosts economic growth. For example, the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities estimates that every dollar spent on unemployment benefits generates $1.61 in economic activity.
The Interaction of Taxes and Transfers
Taxes and transfers are closely interconnected and often work together to achieve economic and social goals. While taxes provide the revenue for transfer programs, transfers can influence the design and effectiveness of the tax system.
Tax-Transfer Policies
Governments can use tax-transfer policies to achieve specific objectives. For instance, they can reduce taxes on low-income earners while increasing transfers to provide a more equitable distribution of resources. This approach, known as a negative income tax, can be more efficient than traditional welfare programs as it simplifies the administration process and reduces the stigma often associated with welfare.
The Role of Behavioral Economics
Understanding the behavior of individuals and businesses in response to taxes and transfers is crucial. Behavioral economics studies how psychological, social, and emotional factors influence economic decisions. By incorporating behavioral insights, policymakers can design more effective tax and transfer systems.
For example, studies have shown that people are more likely to respond to a reduction in taxes than an increase in transfers of the same amount. This is known as the framing effect, and it suggests that how a policy is presented can significantly impact its effectiveness.
Future Implications and Challenges
The world of taxes and transfers is constantly evolving, influenced by changing economic landscapes, technological advancements, and societal needs. Here are some key implications and challenges for the future:
Automation and the Future of Work
As automation and artificial intelligence continue to advance, the nature of work is changing. This could lead to significant shifts in the tax base, with potential reductions in income tax revenues as more jobs become automated. Governments will need to adapt their tax systems to ensure a stable revenue stream.
Digital Economy and Taxation
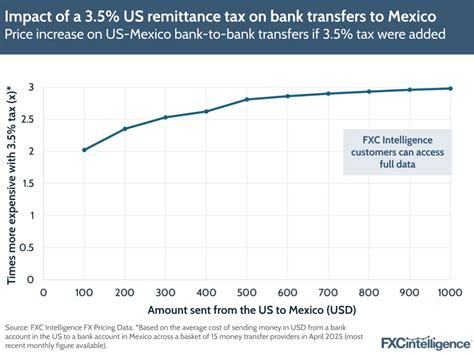
The rise of the digital economy poses challenges for tax systems. Multinational tech companies, for instance, often have complex structures that make it difficult to determine their tax liabilities. Governments are exploring new ways to tax digital services and e-commerce to ensure a fair tax burden.
Sustainable Development Goals
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aim to eradicate poverty, promote sustainable economic growth, and address climate change. Taxes and transfers will play a crucial role in achieving these goals. For instance, carbon taxes can be used to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while generating revenue for sustainable development initiatives.
Conclusion
Taxes and transfers are the pillars of modern economic systems, shaping the financial landscape and influencing the lives of individuals and businesses. By understanding their intricate workings and impacts, we can appreciate their role in promoting economic growth, reducing inequality, and achieving social goals. As we navigate an ever-changing world, the study and adaptation of tax and transfer policies will remain a critical aspect of economic policy-making.
How do taxes influence economic growth and investment decisions?
+Taxes can have a significant impact on economic growth and investment decisions. Lower tax rates can stimulate economic activity by incentivizing businesses to invest and expand. This, in turn, can lead to job creation and increased productivity. Additionally, tax policies can influence where businesses choose to locate, as lower tax rates can make a region more attractive for investment.
What are some common challenges in administering transfer programs?
+Administering transfer programs can be complex and challenging. Some common issues include determining eligibility criteria, ensuring efficient delivery of benefits, and preventing fraud and abuse. Moreover, the administrative costs of running these programs can be significant, which may reduce the overall impact of the transfers.
How do taxes and transfers affect income inequality?
+Taxes and transfers play a crucial role in addressing income inequality. Progressive tax systems, where higher-income earners pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes, can help reduce income inequality by redistributing wealth. Similarly, transfer programs provide financial support to those in need, helping to alleviate poverty and promote social equity.