Taxes In Spain

Spain, a vibrant and diverse country in the heart of Europe, boasts a rich cultural heritage and a thriving economy. When it comes to taxes, understanding the Spanish system is crucial for both residents and businesses. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of taxes in Spain, providing an in-depth analysis of the tax landscape and its implications.
The Spanish Tax System: An Overview
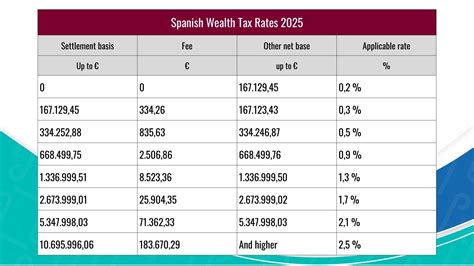
Spain’s tax system is designed to support the country’s fiscal needs and promote economic growth. It is characterized by a combination of direct and indirect taxes, with a focus on progressive taxation. The Spanish Tax Agency (Agencia Tributaria) oversees the administration and collection of taxes, ensuring compliance with the country’s fiscal regulations.
Direct Taxes
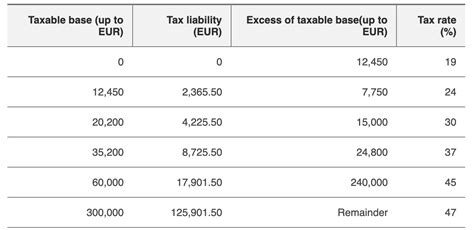
Direct taxes in Spain primarily consist of income tax and corporate tax. The Income Tax on Individuals (Impuesto sobre la Renta de las Personas Físicas or IRPF) is the primary source of tax revenue for the government. The tax rate varies depending on an individual’s income bracket, with higher earners facing higher tax rates. The IRPF system aims to promote social equity by taxing wealthier individuals at a higher rate.
Corporate tax, known as the Corporation Tax (Impuesto sobre Sociedades or IS), applies to businesses and companies operating in Spain. The standard corporate tax rate is set at 25%, but there are various incentives and deductions available to encourage investment and business growth. Start-ups and small businesses often benefit from reduced tax rates and simplified tax regimes.
Indirect Taxes
Indirect taxes in Spain include the Value Added Tax (VAT or Impuesto sobre el Valor Añadido - IVA) and various excise duties. The VAT is applied to most goods and services and is a significant source of revenue for the government. The standard VAT rate is 21%, but reduced rates of 10% and 4% apply to specific products and services, such as tourism-related activities and basic necessities.
Excise duties are levied on specific products like tobacco, alcohol, and fuels. These taxes are designed to discourage consumption of harmful substances and generate revenue for the government. The rates for excise duties vary depending on the product and its classification.
Real Estate Taxes
Spain has a comprehensive system of taxes related to real estate. The Property Transfer Tax (Impuesto sobre Transmisiones Patrimoniales - ITP) applies to the purchase of properties, with rates varying between 6% and 10% depending on the region. Additionally, there is the Property Tax (Impuesto sobre Bienes Inmuebles - IBI), which is an annual tax levied on property ownership. The IBI rates are set by local authorities and can vary significantly across different municipalities.
Tax Obligations for Residents and Non-Residents

Tax obligations in Spain differ for residents and non-residents. Residents, defined as individuals living in Spain for more than 183 days a year, are subject to tax on their worldwide income. Non-residents, on the other hand, are typically taxed only on income generated within Spain.
Tax Residence Status
Spain offers a Non-Resident Taxpayer Number (NRTN or Número de Identificación Fiscal - NIF) for non-residents who need to file tax returns or engage in certain financial activities. Obtaining a NRTN is crucial for non-residents to comply with their tax obligations and avoid penalties.
Residents, on the other hand, are assigned a Tax Identification Number (TIN or Número de Identificación Fiscal - NIF) which serves as their unique tax identifier. This number is essential for tax filing, banking, and various administrative processes.
Tax Returns and Deadlines
Tax returns in Spain are due annually. The deadline for filing income tax returns is typically around the end of June, although this can vary slightly depending on the region. Businesses and self-employed individuals have different deadlines, usually falling between July and October.
Late filing or non-compliance with tax obligations can result in penalties and interest charges. It is essential to stay informed about the latest tax regulations and deadlines to avoid any legal issues.
Tax Benefits and Incentives
Spain offers a range of tax benefits and incentives to attract investment and support certain industries. These include tax breaks for research and development, green energy initiatives, and cultural activities. The government also provides incentives for foreign investors, such as reduced tax rates and simplified tax procedures.
Regional Variations
It’s important to note that Spain’s tax system allows for some regional variations. Certain taxes, like the Property Transfer Tax and Property Tax, are managed by regional governments, resulting in different rates and regulations across different communities. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for individuals and businesses operating in multiple regions.
| Tax | Rate/Bracket | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Income Tax (IRPF) | 24-45% | Progressive tax rate based on income brackets. |
| Corporate Tax (IS) | 25% | Standard rate, with incentives for start-ups and small businesses. |
| VAT (IVA) | 21%, 10%, 4% | Standard, reduced, and super-reduced rates for different products and services. |
| Property Transfer Tax (ITP) | 6-10% | Varies by region, applied to property purchases. |
| Property Tax (IBI) | Varies by municipality | Annual tax on property ownership, set by local authorities. |
FAQs
What is the tax rate for non-residents in Spain?
+Non-residents are generally taxed at a flat rate of 24% on income earned in Spain. However, there are exceptions and specific circumstances that may apply, so it’s best to consult with a tax advisor for personalized guidance.
Are there any tax breaks for expats moving to Spain?
+Yes, Spain offers the “14% Tax Regime” for expats who meet certain criteria. This regime provides a reduced tax rate of 14% on foreign-sourced income for the first five years of residency. It’s a significant incentive for individuals considering a move to Spain.
How often do I need to file tax returns in Spain as a resident?
+As a resident, you are typically required to file an annual tax return by the end of June each year. However, the exact deadline can vary slightly, so it’s important to stay updated with the latest tax regulations.
Are there any tax incentives for investing in renewable energy projects in Spain?
+Absolutely! Spain offers tax benefits for investments in renewable energy, including reduced tax rates and accelerated depreciation. These incentives aim to encourage the development of clean energy projects and promote sustainability.
Can I apply for tax residency in Spain if I spend less than 183 days a year there?
+The 183-day rule is a general guideline, but there are other factors that can influence tax residency. If you maintain strong connections to Spain, such as owning property or having a significant presence there, you may still be considered a tax resident even if you spend less than 183 days in the country.