Tax Deduction For Car Loan Interest

Understanding the intricacies of tax deductions can be a complex task, especially when it comes to specific scenarios like car loan interest. Many individuals who have taken out car loans might be curious about whether they are eligible for any tax benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of tax deductions related to car loan interest, exploring the criteria, limitations, and potential benefits. By the end of this article, you'll have a clearer understanding of whether and how you can maximize your tax savings in relation to your car loan.
Navigating Tax Deductions for Car Loan Interest: A Comprehensive Guide
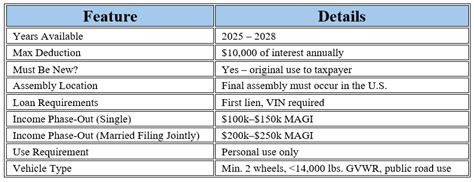
The concept of tax deductions for car loan interest is often misunderstood and can vary greatly depending on your jurisdiction and the purpose for which the car is used. Whether you're a business owner, an employee, or a self-employed individual, the rules and eligibility can differ. Let's explore the specifics and provide clarity on this often-confusing topic.
Eligibility and Criteria for Deductions
When it comes to tax deductions for car loan interest, the eligibility criteria can be quite strict. Generally, the deduction is only applicable if the car is used primarily for business purposes. This means that if your car is primarily used for personal reasons, with only occasional business use, you might not qualify for this deduction. Let's take a closer look at the specific eligibility requirements.
Firstly, it's important to understand the definition of business use. This typically refers to using your vehicle for work-related tasks, such as visiting clients, traveling to meetings, or making deliveries. If your car is primarily used for these purposes, you may be eligible for a tax deduction on the interest paid on your car loan. However, if the car is mainly used for commuting to and from your workplace, it is considered a personal expense and is not deductible.
For instance, let's consider a scenario where Jane, a sales representative, uses her car to travel to different client sites throughout the week. She keeps detailed records of her mileage and the purpose of each trip. In this case, Jane can claim a tax deduction for the interest on her car loan, as the primary use of her vehicle is for business purposes.
On the other hand, if John, an office worker, takes out a car loan to purchase a vehicle for his daily commute, he cannot claim a tax deduction for the interest. Even if he occasionally uses the car for work-related errands, the primary purpose of the vehicle is personal transportation, rendering it ineligible for the deduction.
It's worth noting that the definition of primary use can vary depending on the jurisdiction. Some countries or states may have specific thresholds or guidelines to determine whether a vehicle is primarily used for business. For example, in certain regions, if a car is used for business purposes more than 50% of the time, it may be considered primarily for business.
| Vehicle Use | Tax Deduction Eligibility |
|---|---|
| Business Use (50%+) | Eligible for Deduction |
| Personal Use (Majority) | Ineligible for Deduction |
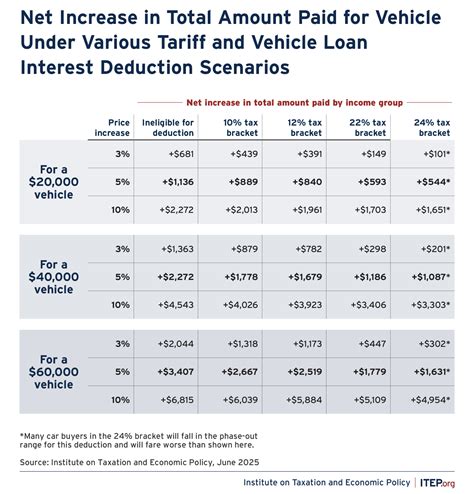
Calculating the Deduction Amount
If you meet the eligibility criteria and can demonstrate that your car is primarily used for business purposes, the next step is to calculate the deductible amount. The deduction is typically calculated based on the interest paid on your car loan during the tax year. However, there may be additional factors to consider, depending on your jurisdiction's tax laws.
In most cases, the deduction is calculated as a percentage of the total interest paid. This percentage is determined by the proportion of business use of the vehicle. For example, if your car is used for business purposes 70% of the time, you can claim a deduction for 70% of the interest paid on your car loan.
Let's illustrate this with an example. Suppose Sarah has a car loan with an annual interest of $3,000. She uses her car for business purposes 60% of the time. In this case, Sarah can claim a tax deduction of $1,800 ($3,000 x 60%). This deduction can help reduce her taxable income and potentially lower her overall tax liability.
However, it's important to note that there may be limits or caps on the amount you can deduct. These limits are often set by tax authorities to prevent excessive deductions. For instance, some countries may have a maximum deduction amount per year or a limit based on the vehicle's value or depreciation.
Additionally, it's worth considering any other expenses related to your vehicle, such as fuel, maintenance, and insurance. In some jurisdictions, these expenses may also be deductible, further reducing your taxable income.
Documenting and Filing Your Deduction
To claim the tax deduction for car loan interest, you'll need to properly document and file your claim with the relevant tax authority. This process can vary depending on your country's tax system, so it's essential to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements.
Generally, you'll need to keep detailed records of your vehicle's use, including mileage logs, trip purposes, and any other relevant information. These records should be accurate and up-to-date, as they may be requested during an audit or review.
When filing your tax return, you'll need to include the appropriate forms or sections that relate to vehicle expenses and interest deductions. It's crucial to follow the instructions carefully and ensure that all the required information is provided. In some cases, you may need to attach supporting documentation, such as bank statements or loan agreements.
Working with a tax professional or using tax preparation software can be beneficial, as they can guide you through the process and ensure that your deduction claim is accurate and compliant with the latest tax regulations.
Maximizing Your Tax Benefits
Understanding the eligibility criteria and calculation methods is just the first step. To truly maximize your tax benefits, there are a few additional strategies you can consider.
- Optimize Your Business Use: If you're on the cusp of meeting the primary use criteria, consider optimizing your business trips. This could involve combining multiple errands into one trip or exploring opportunities for business travel that align with your profession.
- Track Your Mileage: Accurate mileage tracking is essential. Invest in a reliable mileage tracking app or logbook to ensure you have precise records. This can help maximize your deduction and provide solid evidence during tax audits.
- Explore Other Deductions: Don't limit yourself to just car loan interest deductions. Research and explore other potential deductions related to your vehicle, such as fuel costs, maintenance, and insurance. These additional deductions can further reduce your taxable income.
- Stay Updated on Tax Laws: Tax laws and regulations can change frequently. Stay informed about any updates or amendments to the tax code that may impact your deductions. This ensures you're aware of any changes and can adjust your strategies accordingly.
Conclusion

Tax deductions for car loan interest can provide a significant advantage for those who meet the eligibility criteria. By understanding the requirements, accurately calculating the deduction, and properly documenting your claim, you can potentially reduce your taxable income and save on taxes. Remember, it's essential to stay informed, keep detailed records, and explore all available deductions to maximize your tax benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I deduct the entire interest on my car loan, regardless of its use?
+
No, the deduction for car loan interest is generally limited to business use. If your vehicle is primarily used for personal purposes, the interest is not deductible. The deduction is calculated based on the proportion of business use.
Are there any limits to the amount I can deduct for car loan interest?
+
Yes, there may be limits or caps on the deduction amount. These limits can vary by jurisdiction and may be based on factors such as the vehicle’s value, depreciation, or annual maximum deductions. It’s important to check the specific regulations in your country.
Can I deduct the interest on a car loan if I use the car for both business and personal purposes?
+
Yes, as long as the primary use of the vehicle is for business purposes. You can calculate the deduction based on the proportion of business use. For example, if you use the car 60% for business, you can deduct 60% of the interest paid.
What records do I need to keep to support my deduction claim for car loan interest?
+
It’s crucial to maintain accurate records of your vehicle’s use, including mileage logs, trip purposes, and any other relevant information. These records should be detailed and up-to-date to support your deduction claim and provide evidence during tax audits.



