State Of Mi Income Tax Rate
The income tax system in Michigan is a fundamental component of the state's revenue generation strategy, playing a pivotal role in funding essential public services and infrastructure. The state's income tax structure, with its progressive nature, ensures a balanced approach to taxation, catering to different income levels. Understanding the intricacies of Michigan's income tax rates is crucial for both residents and businesses, as it directly impacts their financial planning and contributions to the state's economy.
Understanding Michigan’s Income Tax Structure
Michigan’s income tax system operates on a progressive scale, meaning that higher incomes are taxed at higher rates. This approach aims to distribute the tax burden fairly across different income groups. The state’s income tax is levied on wages, salaries, and other forms of income, including investment gains and retirement benefits.
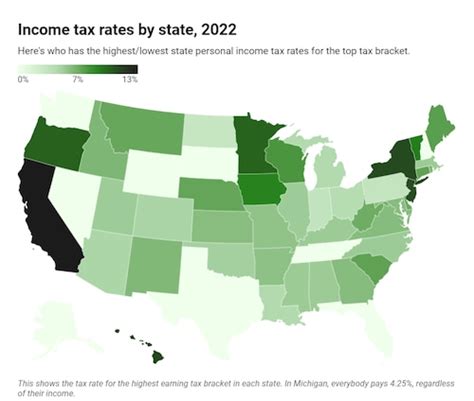
The current income tax rate in Michigan is 4.25%, which is applicable to all income levels. However, it's important to note that this is a flat rate, and Michigan does not have a graduated income tax system like some other states. This means that regardless of your income bracket, the tax rate remains the same.
Despite the flat rate, Michigan offers various tax credits and deductions that can reduce the overall tax liability for individuals and businesses. These incentives are designed to encourage economic growth, promote investment, and provide relief to specific demographic groups.
| Income Tax Rate | Applicable Income Range |
|---|---|
| 4.25% | All Income Levels |

Taxable Income and Exemptions
Michigan law exempts certain types of income from state income tax, including Social Security benefits and military pensions. Additionally, the state provides tax credits for low-income individuals and families, as well as credits for certain business activities, such as investing in Michigan’s film industry or conducting research and development.
Local Income Taxes
In addition to the state income tax, Michigan residents may also be subject to local income taxes. These are typically levied by cities and counties to fund local projects and services. The rates and structures of these local taxes can vary significantly, so it’s essential for individuals and businesses to be aware of the specific tax requirements in their local jurisdictions.
The Impact of Income Tax on Michigan’s Economy

The income tax plays a critical role in Michigan’s economic landscape. It serves as a primary source of revenue for the state government, enabling it to invest in public education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and other vital services. The stability and predictability of the income tax system contribute to Michigan’s economic health and its ability to attract and retain businesses.
Moreover, the tax revenue generated helps to address social and economic inequalities by funding initiatives aimed at improving the lives of Michigan's residents. This includes programs focused on education, healthcare access, and economic development in underserved communities.
Income Tax and Economic Growth
The flat income tax rate in Michigan can be advantageous for businesses, as it provides a stable and predictable tax environment. This simplicity can make the state an attractive destination for new businesses and entrepreneurs, fostering economic growth and job creation. However, it’s essential to consider the overall tax burden, including local taxes and other business-related expenses, when evaluating the state’s economic climate.
Comparison with Other States
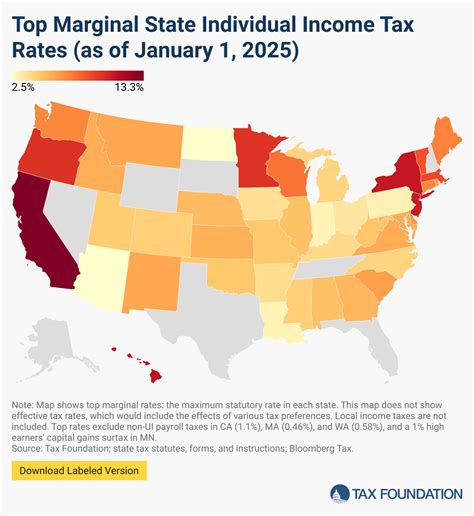
When compared to other states, Michigan’s income tax rate is relatively moderate. Some states have higher tax rates, while others, like Florida and Texas, have no income tax at all. This variation in tax structures across states can significantly impact an individual’s or business’s financial planning and decision-making when considering relocation or expansion.
| State | Income Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Michigan | 4.25% |
| California | 1 - 13.3% |
| Texas | 0% |
| Florida | 0% |
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
The income tax system in Michigan is subject to ongoing debates and potential reforms. As the state’s economic landscape evolves, there may be calls for adjustments to the tax rate or structure to better align with changing economic conditions and the needs of Michigan’s residents and businesses.
One potential area of reform could be the introduction of a graduated income tax system, which would tax higher incomes at higher rates. This approach could generate additional revenue for the state, allowing for increased investment in public services and infrastructure. However, such a change would require careful consideration to ensure it does not discourage economic growth or lead to an exodus of high-income earners.
Potential Tax Reform Scenarios
Some proposed reforms include introducing multiple tax brackets, similar to the federal income tax system, with rates ranging from 3% to 5% for different income levels. This could provide a more progressive tax structure while still maintaining a competitive tax environment. Other proposals focus on expanding tax credits and deductions to provide relief to specific industries or demographic groups.
Impact on Residents and Businesses
Changes to the income tax system can have a significant impact on residents and businesses. While tax reforms may bring about benefits like improved public services or targeted support for specific industries, they can also lead to increased tax burdens for certain groups. It’s essential for policymakers to carefully consider the potential consequences of any proposed changes to ensure they benefit the state as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Michigan’s income tax rate compare to other states?
+Michigan’s income tax rate of 4.25% is relatively moderate compared to some states. States like California have higher rates, while others like Texas and Florida have no income tax. This variation can influence individual and business decisions regarding relocation or expansion.
Are there any tax credits or deductions available in Michigan?
+Yes, Michigan offers various tax credits and deductions to reduce tax liability. These include credits for low-income individuals, families, and businesses engaging in specific activities like film production or research and development.
What types of income are exempt from Michigan’s income tax?
+Certain types of income are exempt from Michigan’s income tax, including Social Security benefits and military pensions. The state also exempts income from certain investments and specific types of retirement benefits.
How do local income taxes impact overall tax liability in Michigan?
+In addition to the state income tax, Michigan residents may be subject to local income taxes levied by cities and counties. These local taxes can vary significantly, and it’s essential to consider them when assessing the overall tax burden in a specific jurisdiction.
What potential reforms are being considered for Michigan’s income tax system?
+Potential reforms include introducing a graduated income tax system with multiple tax brackets or expanding tax credits and deductions to provide targeted relief. These reforms aim to balance revenue generation with the needs of Michigan’s residents and businesses.