Maryland Income Tax Rate
In the state of Maryland, income tax is an important source of revenue for the government, and it plays a significant role in funding various public services and infrastructure. Understanding the Maryland income tax rate is crucial for residents and businesses alike, as it directly impacts their financial planning and overall economic stability.
Understanding Maryland’s Income Tax Structure

Maryland employs a progressive income tax system, which means that higher income levels are subject to higher tax rates. This approach aims to distribute the tax burden fairly among residents and encourages economic growth by providing tax relief to those with lower incomes.
The Maryland income tax rate is determined by the state's legislature and is subject to periodic revisions to adapt to economic changes and budgetary needs. As of my last update in January 2023, the state had six tax brackets with corresponding tax rates ranging from 2% to 5.75%. These rates apply to taxable income, which is calculated after various deductions and exemptions.
Tax Brackets and Rates
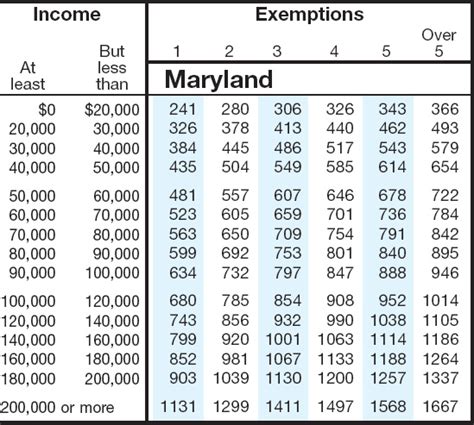
Here’s a breakdown of the current income tax brackets and rates in Maryland:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Taxable Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.00% | $0 - $1,000 |
| 2 | 3.00% | $1,001 - $2,000 |
| 3 | 4.00% | $2,001 - $3,000 |
| 4 | 4.75% | $3,001 - $100,000 |
| 5 | 5.00% | $100,001 - $250,000 |
| 6 | 5.75% | Over $250,000 |

It's important to note that these tax brackets and rates are subject to change, and it is recommended to refer to the most recent tax guidelines provided by the Maryland Comptroller's Office for accurate and up-to-date information.
Deductions and Exemptions
Maryland offers several deductions and exemptions to reduce the taxable income of individuals and businesses. These deductions can significantly impact the overall tax liability and provide financial relief to taxpayers. Some common deductions include:
- Standard Deduction: All Maryland taxpayers are entitled to a standard deduction, which reduces their taxable income. The standard deduction amount varies based on filing status.
- Personal Exemptions: Maryland residents are allowed a personal exemption amount for themselves and their dependents, which further reduces taxable income.
- Itemized Deductions: Taxpayers can choose to itemize their deductions, which includes expenses such as medical costs, state and local taxes, mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and more.
- Business Deductions: Businesses operating in Maryland can deduct various expenses, including advertising costs, rent, utilities, and employee compensation.
Impact of Income Tax on Residents and Businesses
The Maryland income tax rate directly affects the financial planning and decision-making processes of residents and businesses within the state. Here are some key implications:
Financial Planning for Residents
For Maryland residents, understanding the income tax structure is essential for budgeting and saving. The progressive tax system means that as income increases, so does the tax rate. This encourages individuals to plan their finances strategically, especially when considering investments, retirement savings, and other financial goals.
Residents can benefit from taking advantage of deductions and exemptions to minimize their taxable income. For example, contributing to tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as IRAs or 401(k) plans, can reduce taxable income and provide long-term financial benefits.
Impact on Businesses
Maryland’s income tax structure also has significant implications for businesses operating within the state. The tax rates and deductions can influence business decisions, including expansion plans, hiring practices, and investment strategies.
Businesses can optimize their tax liability by carefully managing their expenses and taking advantage of available deductions. For instance, investing in research and development, hiring employees, and contributing to charitable causes can all lead to tax deductions and potentially lower the overall tax burden.
Economic Development and Growth
The income tax structure in Maryland plays a vital role in the state’s economic development and growth. The progressive tax system ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their earnings, which helps fund public services and infrastructure projects. This, in turn, creates a positive cycle of economic growth and development.
The state's tax policies can also attract businesses and investors by offering incentives and tax breaks for specific industries or economic activities. These initiatives aim to boost employment opportunities, stimulate economic growth, and enhance the overall competitiveness of Maryland's business environment.
Future Implications and Considerations
The income tax rate in Maryland is a dynamic aspect of the state’s fiscal policy, and it is subject to ongoing evaluation and potential revisions. Here are some key considerations and future implications:
Budgetary Needs and Economic Changes
The state’s budgetary requirements and economic conditions can influence the income tax rate. In times of economic prosperity, the state may have surplus revenues, which could lead to tax rate adjustments or the introduction of new tax brackets. Conversely, during economic downturns, the state may need to adjust tax rates to ensure adequate revenue generation.
Tax Policy Reforms
Maryland, like many other states, regularly reviews its tax policies to ensure fairness, efficiency, and competitiveness. Tax reform initiatives may aim to simplify the tax system, reduce complexity, or introduce new incentives to promote economic growth. Residents and businesses should stay informed about any proposed tax policy changes that could impact their financial planning.
Impact on Tax Burden
Changes in the income tax rate can directly affect the tax burden on individuals and businesses. While higher tax rates can increase the overall tax liability, they also contribute to funding essential public services and infrastructure projects. On the other hand, lower tax rates may provide relief to taxpayers but could potentially impact the state’s revenue generation and ability to fund critical programs.
Comparison with Other States
When considering the Maryland income tax rate, it is essential to compare it with other states to understand its competitiveness and potential impact on businesses and residents. Different states have varying tax structures, rates, and incentives, which can influence business location decisions and individual migration patterns.
How often are Maryland’s income tax rates updated?
+Maryland’s income tax rates are subject to periodic updates, typically determined by the state legislature. While there is no fixed schedule, updates are usually made in response to economic changes, budgetary needs, or tax policy reforms. It is advisable to refer to the Maryland Comptroller’s Office for the most recent tax guidelines.
Are there any tax incentives for specific industries in Maryland?
+Yes, Maryland offers various tax incentives and credits to promote economic growth and development. These incentives are often targeted at specific industries, such as biotechnology, cybersecurity, and renewable energy. Businesses should consult the Maryland Department of Commerce or a tax professional to explore available incentives.
Can residents of Maryland claim tax credits or refunds?
+Absolutely! Maryland residents may be eligible for various tax credits and refunds, including the Maryland Homestead Tax Credit, Property Tax Credit, and various income tax credits. It is important to review the state’s tax guidelines and consult a tax professional to determine eligibility and claim the applicable credits.