State Income Tax Wisconsin
When it comes to managing personal finances, understanding the intricacies of state income taxes is crucial. Wisconsin, known for its rich history, vibrant cities, and diverse landscapes, has a unique tax system that impacts its residents and businesses. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of Wisconsin's state income tax, exploring its history, rates, deductions, and everything in between. Join us as we navigate the financial landscape of this beautiful state, ensuring you have the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding your tax obligations.
A Historical Perspective on Wisconsin's Income Tax

The journey of Wisconsin's state income tax dates back to the early 20th century. It was in 1911 that the state first imposed an income tax, making it one of the early adopters of this form of taxation in the United States. The primary aim was to generate revenue for state-wide initiatives and infrastructure development, reflecting a growing need for sustainable funding sources.
Over the years, the income tax system in Wisconsin has undergone several revisions and amendments, adapting to the changing economic landscape and societal needs. One notable reform occurred in 1978, when the state implemented a new tax structure, introducing brackets and rates that are still in use, albeit with periodic adjustments.
Fast forward to the present, and Wisconsin's income tax system stands as a well-established and integral part of its fiscal framework. It not only provides a stable source of revenue for the state but also influences the financial planning and decision-making of its residents and businesses.
Understanding Wisconsin's Income Tax Rates

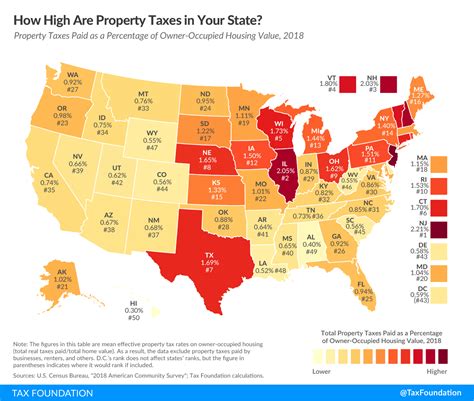
Wisconsin employs a progressive income tax system, which means that the tax rate you pay increases as your income rises. This approach aims to ensure fairness, where those with higher incomes contribute a larger share to the state's revenue. As of the 2023 tax year, there are four income tax brackets in Wisconsin, each with its respective tax rate:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 - $12,300 (Single) / 0 - $18,450 (Married Filing Jointly) | 3.62% |
| $12,301 - $32,200 (Single) / $18,451 - $48,600 (Married Filing Jointly) | 4.85% |
| $32,201 - $159,600 (Single) / $48,601 - $239,400 (Married Filing Jointly) | 5.84% |
| Over $159,600 (Single) / Over $239,400 (Married Filing Jointly) | 6.98% |
These brackets and rates are subject to change annually, often adjusted to account for inflation and economic factors. It's crucial for Wisconsin taxpayers to stay updated on any modifications to ensure accurate tax filings.
Deductions and Credits: Maximizing Your Tax Savings
Wisconsin offers a range of deductions and credits that can help reduce your taxable income and, consequently, the amount of tax you owe. Here are some of the key deductions and credits available to Wisconsin taxpayers:
Standard Deduction
Every taxpayer is entitled to a standard deduction, which reduces your taxable income by a set amount. As of the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction for single filers is $2,450, while for married couples filing jointly, it's $4,900. If you don't qualify for itemized deductions, taking the standard deduction is a straightforward way to lower your tax liability.
Itemized Deductions
If your eligible expenses exceed the standard deduction, you might consider itemizing your deductions. Common itemized deductions in Wisconsin include medical expenses, charitable contributions, mortgage interest, and state and local taxes. By itemizing, you can potentially lower your taxable income and save on taxes.
Tax Credits
Wisconsin provides various tax credits to support specific groups and promote certain behaviors. For instance, the state offers a credit for seniors and people with disabilities, helping to offset the cost of living for these vulnerable populations. Additionally, there's a credit for child and dependent care expenses, encouraging parents to work or attend school while having their children cared for.
Other Deductions and Credits
Wisconsin also offers deductions for education expenses, such as tuition and fees, which can be a significant relief for students and their families. Moreover, there are credits for renewable energy systems and energy-efficient home improvements, incentivizing residents to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
Filing Your Wisconsin State Income Tax Return
Filing your Wisconsin state income tax return is a straightforward process, thanks to the Wisconsin Department of Revenue's user-friendly website and resources. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the filing process:
- Gather Your Documents: Before you begin, ensure you have all the necessary documents, including your W-2 forms, 1099s, and any other income statements. You'll also need records of your deductions and credits.
- Choose Your Filing Method: Wisconsin offers both online and paper filing options. The e-System is a secure, user-friendly platform for electronic filing, while paper filers can access the necessary forms on the Department of Revenue's website.
- Complete Your Return: Whether you're filing online or on paper, carefully fill out all the required information. Ensure accuracy, as errors can lead to delays or penalties.
- Review and Submit: Before finalizing your return, review it thoroughly to ensure all the information is correct. Once satisfied, submit your return electronically or mail your paper return to the address provided by the Department of Revenue.
- Payment Options: If you owe taxes, you can pay online, by mail, or in person at a participating financial institution. Ensure you make your payment by the due date to avoid late fees and penalties.
Staying Informed: Resources for Wisconsin Taxpayers
Staying updated on the latest tax laws, rates, and regulations is essential for Wisconsin taxpayers. Here are some valuable resources to help you navigate the world of Wisconsin taxes:
- Wisconsin Department of Revenue: The official website of the Wisconsin Department of Revenue provides a wealth of information, including tax forms, publications, and guidelines. It's a go-to resource for any tax-related queries.
- Tax Workshops and Seminars: The Department of Revenue often conducts workshops and seminars to educate taxpayers on various tax topics. These events can be an excellent way to learn about new tax laws and regulations.
- Tax Preparation Assistance: If you need help preparing your tax return, the Department of Revenue offers free tax preparation assistance through its Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) and Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE) programs. These services are especially beneficial for low- to moderate-income individuals and seniors.
- Tax Publications and Guides: The Department of Revenue publishes a range of guides and publications to assist taxpayers. These resources cover various tax topics, providing clear and concise information to help you understand your tax obligations.
Future Outlook: Implications for Wisconsin Taxpayers
As Wisconsin continues to evolve economically and socially, its tax system is likely to undergo further changes and reforms. Here are some potential future implications for Wisconsin taxpayers:
Economic Growth and Tax Revenues
Wisconsin's economy is expected to grow, driven by sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and healthcare. This growth could lead to increased tax revenues, potentially allowing for tax rate reductions or the expansion of tax credits and deductions.
Tax Reform and Simplification
With the ever-changing economic landscape, there may be calls for tax reform to make the system more efficient and equitable. Simplifying the tax code and reducing complexities could benefit taxpayers, making the filing process less burdensome.
Social and Environmental Initiatives
Wisconsin's commitment to social welfare and environmental sustainability is likely to continue. This could lead to the expansion of tax credits and deductions related to these initiatives, such as incentives for renewable energy adoption and support for community development projects.
Conclusion
Understanding Wisconsin's state income tax system is crucial for both individuals and businesses operating within the state. By grasping the historical context, current tax rates, and available deductions and credits, taxpayers can make informed decisions and effectively manage their tax obligations. As Wisconsin continues to evolve, staying updated on tax laws and regulations will ensure compliance and help maximize tax savings.
Frequently Asked Questions
When is the deadline for filing Wisconsin state income tax returns?
+
The deadline for filing Wisconsin state income tax returns typically aligns with the federal deadline, which is April 15th. However, if this date falls on a weekend or a holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day.
Can I file my Wisconsin state income tax return electronically?
+
Yes, Wisconsin offers an electronic filing system called the e-System. This platform is secure and user-friendly, making it a convenient option for taxpayers. Electronic filing often results in faster processing and refund times.
Are there any special tax credits or deductions for senior citizens in Wisconsin?
+
Yes, Wisconsin offers a credit for seniors and people with disabilities. This credit can help offset the cost of living for these vulnerable populations. The amount of the credit depends on your income and other factors.
What is the difference between the standard deduction and itemized deductions in Wisconsin?
+
The standard deduction is a set amount that reduces your taxable income, and it’s available to all taxpayers. Itemized deductions, on the other hand, allow you to subtract specific expenses from your taxable income, but only if they exceed the standard deduction amount. Common itemized deductions include medical expenses, charitable contributions, and state and local taxes.
How can I get help with my Wisconsin state income tax return if I have questions or need assistance?
+
The Wisconsin Department of Revenue offers various resources and assistance programs. You can visit their website for tax forms, publications, and guidelines. Additionally, they provide free tax preparation assistance through the Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) and Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE) programs. These programs are especially beneficial for low- to moderate-income individuals and seniors.