Sales Tax In Ga

Sales tax is an essential component of the tax system in the state of Georgia, United States. It is a tax levied on the sale of goods and services and is a significant source of revenue for the state government and local municipalities. The sales tax system in Georgia is unique and differs from many other states, offering a fascinating insight into the intricacies of taxation and its impact on businesses and consumers alike.
Understanding the Georgia Sales Tax Structure
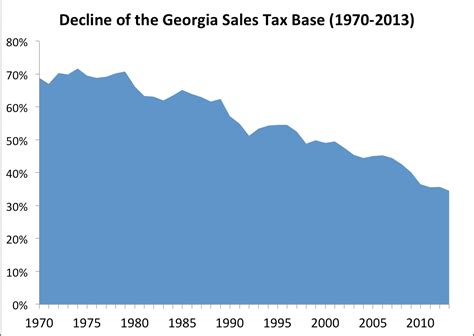
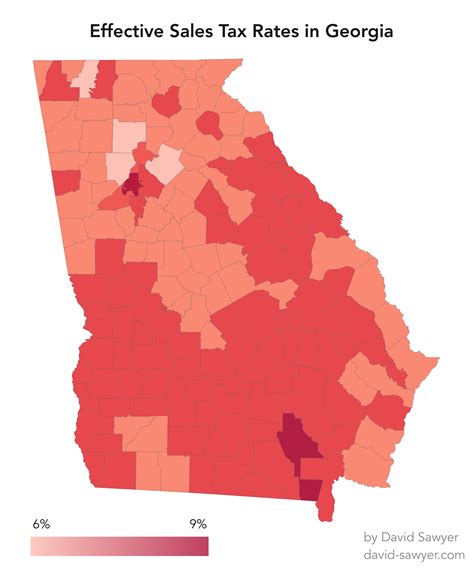
The sales tax in Georgia is primarily a state-level tax, with a base rate of 4% applicable to most tangible personal property and certain services. However, it is important to note that Georgia’s sales tax is a combined state and local tax, which means that local jurisdictions can impose additional sales taxes on top of the state rate. This results in a combined sales tax rate that varies across the state.
For instance, the city of Atlanta has a local sales tax rate of 3.5%, which is added to the state rate, resulting in a combined sales tax of 7.5% for most purchases within the city limits. This is a common scenario in Georgia, where local governments have the authority to levy additional taxes to fund specific projects or services.
Categories of Sales Taxable Items
Georgia’s sales tax is applicable to a wide range of goods and services, but certain categories are exempt. These include prescription medications, certain medical equipment, and groceries. Additionally, the state offers sales tax holidays, during which specific items are exempt from sales tax for a limited period. These holidays often coincide with back-to-school shopping and energy-efficient appliance purchases, providing a temporary tax relief for consumers.
Here's a table outlining the categories of items subject to sales tax in Georgia, along with the applicable rates:
| Category | State Rate | Local Rate (Average) | Combined Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tangible Personal Property | 4% | 2.5% | 6.5% |
| Preparatory Schools | 4% | 2.5% | 6.5% |
| Elective Cosmetic Surgery | 4% | 2.5% | 6.5% |
| Short-Term Lodging | 5% | 1.5% | 6.5% |
Compliance and Filing Requirements

Businesses operating in Georgia have specific compliance and filing obligations when it comes to sales tax. They are required to register with the Georgia Department of Revenue and obtain a sales and use tax certificate. This certificate allows businesses to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state and local governments.
The frequency of sales tax filing depends on the business's sales volume. Larger businesses with higher sales may be required to file and remit sales tax monthly, while smaller businesses may file quarterly or semi-annually. The state offers online filing and payment options through its Georgia Tax Center, simplifying the process for businesses.
Penalties and Interest
Failure to comply with sales tax regulations in Georgia can result in penalties and interest charges. Late filing or non-payment of sales tax can incur a penalty of up to 5% of the unpaid tax, and an additional 1% interest charge per month on the outstanding amount. It is crucial for businesses to stay informed about their sales tax obligations to avoid these penalties.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The sales tax system in Georgia has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers. For businesses, particularly those with physical stores, the varying local sales tax rates can present a challenge when it comes to pricing and compliance. However, it also provides an opportunity for businesses to promote their locations in areas with lower sales tax rates, potentially attracting more customers.
For consumers, the sales tax can influence purchasing decisions. While a higher sales tax rate may deter some consumers from making large purchases, it can also encourage them to shop during sales tax holidays or explore online shopping options where sales tax may be lower or non-existent.
Sales Tax and Economic Development
Georgia’s sales tax structure also plays a role in the state’s economic development strategies. Local governments often use the additional sales tax revenue to fund infrastructure projects, public transportation, and other community initiatives. This can enhance the quality of life for residents and potentially attract new businesses and investment.
Moreover, the sales tax system can influence the location choices of businesses. Areas with lower sales tax rates may become more attractive for business expansion or relocation, especially for retail and hospitality sectors that are directly impacted by sales tax.
Future Considerations and Reforms
As Georgia’s economy continues to evolve, there are ongoing discussions and proposals for sales tax reforms. Some of these reforms aim to simplify the tax system, reduce administrative burdens on businesses, and ensure a fair distribution of tax revenue across the state.
One proposed reform is the streamlined sales tax, which would standardize the sales tax rates and rules across the state, making it easier for businesses to comply and for consumers to understand. Another consideration is the potential expansion of sales tax to include more services, which could provide a more stable revenue source for the state and reduce the reliance on property taxes.
Conclusion
Georgia’s sales tax system is a complex but crucial component of the state’s tax structure. It impacts businesses, consumers, and the overall economic landscape. As the state continues to grow and evolve, the sales tax system will likely undergo reforms to adapt to changing economic conditions and technological advancements. Understanding the intricacies of sales tax in Georgia is essential for businesses operating within the state, as well as for consumers making purchasing decisions.
How often do businesses need to file sales tax returns in Georgia?
+The frequency of sales tax filing depends on the business’s sales volume. Larger businesses may file monthly, while smaller businesses file quarterly or semi-annually.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Georgia, and what items are typically included?
+Yes, Georgia offers sales tax holidays, often for back-to-school shopping and energy-efficient appliances. These holidays provide a temporary tax relief for consumers on specific items.
Can local governments in Georgia increase the sales tax rate above the state rate?
+Yes, local governments in Georgia have the authority to impose additional sales taxes, which can result in varying combined sales tax rates across the state.