Sales And Use Tax Texas

Texas, known for its diverse economy and thriving business environment, has a unique approach to sales and use taxes that can be intriguing to understand. Sales and use taxes are an essential part of the state's revenue generation and impact various sectors and consumers. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the specifics of sales and use tax in Texas, exploring its intricacies, applications, and implications.
Understanding Sales and Use Tax in Texas

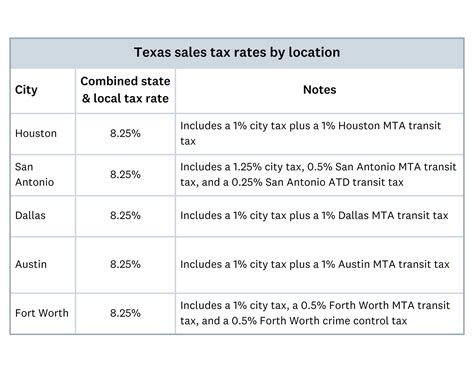
Sales tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services. It is a key revenue source for many states, including Texas. The state of Texas imposes a 6.25% sales tax rate, which is among the higher rates in the country. However, this base rate can vary at the local level, with additional taxes added by cities, counties, and special purpose districts, resulting in a combined rate that can be higher.
The use tax, on the other hand, is a lesser-known counterpart to sales tax. It is applied to purchases made outside of Texas but used or stored within the state. This ensures that even if a transaction occurs outside the state, the state still receives its fair share of tax revenue. Use tax is particularly relevant for online purchases, where consumers may not pay sales tax at the time of purchase but are still required to remit use tax to the state.
Sales and Use Tax Application
Texas sales and use tax applies to a wide range of goods and services. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Taxable Items
- Tangible Personal Property: This includes items like clothing, electronics, furniture, and vehicles. Any physical goods purchased within the state are generally subject to sales tax.
- Services: Certain services are also taxable in Texas. Examples include repair services, installation, and certain professional services like accounting or legal advice.
- Digital Products: Texas imposes sales tax on the sale of digital goods and services, including software downloads, streaming services, and digital publications.
Tax Exemptions
While sales and use tax applies to a broad range of items, there are certain exemptions. These can include:
- Food and Groceries: In Texas, food for human consumption is generally exempt from sales tax.
- Prescription Drugs: Pharmaceuticals and medical devices are exempt from sales tax.
- Certain Manufacturing Processes: Some manufacturing-related purchases may be exempt or partially exempt, depending on the specific use.
- Educational Materials: Books, textbooks, and certain educational supplies are often exempt from sales tax.
Remote Sellers and Marketplace Facilitators
With the rise of e-commerce, Texas has implemented laws to ensure that remote sellers and marketplace facilitators collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state. This means that even if a seller does not have a physical presence in Texas, they may still be required to collect and remit sales tax if they meet certain thresholds of sales or transactions in the state.
Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with sales and use tax regulations is crucial for businesses operating in Texas. Here’s an overview of the compliance process:
Registration
Any business making taxable sales or purchases in Texas must register with the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts. This includes both in-state and out-of-state businesses that have nexus in the state.
Tax Calculation and Remittance
Businesses are responsible for calculating the applicable sales tax rate based on the location of the sale and the nature of the transaction. This information is then used to remit the appropriate amount of tax to the state on a regular basis, typically monthly or quarterly.
Record-Keeping
Proper record-keeping is essential for sales tax compliance. Businesses must maintain records of sales, purchases, and tax payments to ensure accuracy and facilitate audits. This includes keeping track of exempt sales, tax-exempt certificates, and any applicable tax rates.
Audits and Enforcement
The Texas Comptroller’s office conducts audits to ensure compliance with sales and use tax regulations. These audits can be complex and time-consuming, so it’s crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records and understand their tax obligations.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Sales and use tax has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers in Texas. Here are some key considerations:
Business Impact
- Competitive Advantage: For businesses, understanding and effectively managing sales tax can provide a competitive edge. Proper tax calculation and compliance can help avoid penalties and ensure a positive relationship with the state.
- Nexus Considerations: Businesses must carefully consider their nexus in Texas, as even remote sellers can be subject to sales tax collection requirements.
- Tax Planning: Businesses can leverage tax planning strategies to optimize their tax obligations. This includes understanding tax exemptions, utilizing tax software, and staying updated on tax law changes.
Consumer Impact
- Price Transparency: Consumers in Texas should be aware of the sales tax rate when making purchases. Understanding the tax rate can help them budget and compare prices accurately.
- Use Tax Awareness: Consumers should also be aware of their responsibility to pay use tax on out-of-state purchases. Failing to pay use tax can result in penalties and interest.
- Exemptions and Savings: Consumers can take advantage of tax exemptions, such as those on groceries and prescription drugs, to save money.
Texas Sales and Use Tax in Practice

To illustrate the application of sales and use tax in Texas, let’s consider a few real-world examples:
Example 1: Online Retailer
An online retailer based in California sells a laptop to a customer in Texas. The laptop is shipped directly to the customer’s address in Texas. In this scenario, the online retailer is considered a remote seller and is responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax to Texas, even though they do not have a physical presence in the state.
Example 2: Local Business
A local furniture store in Houston, Texas, sells a dining set to a customer. The store calculates the sales tax based on the combined state and local tax rates, which may vary depending on the customer’s location within Houston. The store collects the sales tax from the customer and remits it to the appropriate tax authority.
Example 3: Use Tax Scenario
A Texas resident purchases a smartphone online from an out-of-state retailer. The retailer does not collect sales tax at the time of purchase. In this case, the Texas resident is responsible for paying use tax on the smartphone. They can either self-report and remit the use tax to the state or wait for the state to contact them for payment.
Future Implications and Trends
Sales and use tax in Texas is likely to evolve with changing economic landscapes and technological advancements. Here are some potential future trends and implications:
- Online Sales Tax Collection: With the continued growth of e-commerce, the state may implement more stringent measures to ensure compliance with sales tax collection by remote sellers.
- Tax Simplification: Texas may explore options to simplify its sales tax system, potentially reducing the complexity for businesses and consumers.
- Digital Economy: As the digital economy expands, Texas may need to adapt its tax laws to address new business models and technologies, such as the sharing economy and blockchain-based transactions.
- Economic Development: Sales tax revenue plays a crucial role in funding various state initiatives and infrastructure projects. The state may continue to explore ways to optimize its tax system to support economic development and attract businesses.
Conclusion
Sales and use tax in Texas is a complex yet essential aspect of the state’s economic landscape. It impacts businesses, consumers, and the state’s revenue generation. By understanding the intricacies of sales and use tax, businesses can ensure compliance, optimize their tax obligations, and contribute to the state’s economic growth. Consumers, on the other hand, can make informed purchasing decisions and understand their tax responsibilities.
How often must businesses remit sales tax in Texas?
+Businesses typically remit sales tax on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on their sales volume and type of business.
Are there any penalties for non-compliance with sales tax regulations in Texas?
+Yes, penalties for non-compliance can include fines, interest, and even criminal charges in severe cases. It is crucial for businesses to stay compliant to avoid these consequences.
How can businesses stay updated on sales tax law changes in Texas?
+Businesses can subscribe to notifications from the Texas Comptroller’s office, which regularly publishes updates and changes to tax laws. Additionally, staying informed through industry publications and tax professional networks can be beneficial.