Sale Tax In Florida

Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the Sales Tax system in the vibrant state of Florida. As a hub of tourism and economic activity, Florida's sales tax regulations play a pivotal role in shaping its business landscape and impacting residents and visitors alike. This article aims to demystify the intricacies of sales tax in Florida, offering a comprehensive guide for both businesses and individuals.
Understanding Florida’s Sales Tax

Florida’s sales tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale or lease of goods and certain services within the state. It is a critical revenue stream for the state government, contributing to infrastructure development, education, and other public services. The sales tax rate varies across different jurisdictions, including the state, counties, and municipalities, creating a complex tax landscape.
At the state level, Florida imposes a uniform sales tax rate, currently set at 6%. This rate is applicable to most retail sales, with certain exceptions and exemptions outlined in the Florida Statutes. However, it's essential to note that local governments, counties, and cities can impose additional sales taxes, often referred to as local option taxes, to fund specific projects or initiatives.
Local Sales Tax Variations
Florida’s local sales tax structure adds a layer of complexity. Each county in Florida has the authority to levy an additional sales tax, typically ranging from 0% to 2.5%. For instance, while some counties like Monroe and Miami-Dade impose the maximum additional tax rate, others like Dixie and Liberty counties have no additional tax. This means that the total sales tax rate can vary significantly across the state, impacting businesses and consumers differently.
| County | Local Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Alachua | 1.5% |
| Broward | 1.5% |
| Miami-Dade | 2.5% |
| Orange | 1.5% |
| Palm Beach | 1.5% |
| Pinellas | 1.5% |
Exemptions and Special Considerations
Florida’s sales tax system also includes various exemptions and special considerations. Certain goods and services are exempt from sales tax, such as prescription drugs, non-prepared foods, and certain agricultural products. Additionally, there are special tax rates for specific industries, like tourism and entertainment, which have a significant impact on Florida’s economy.
For instance, the Tourist Development Tax, often referred to as the resort tax, is an additional sales surtax levied on the sales of short-term accommodations, such as hotels, motels, and vacation rentals. This tax, which varies by county, is used to fund tourism-related projects and promotions, further contributing to Florida's thriving tourism industry.
Sales Tax Registration and Compliance
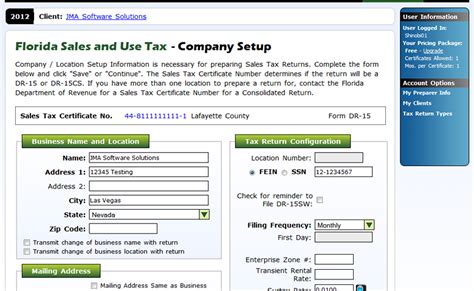
For businesses operating in Florida, sales tax compliance is a critical aspect of financial management. The Florida Department of Revenue mandates that all businesses selling taxable goods or services must register for a sales tax permit and collect the appropriate sales tax from customers. This process involves understanding the tax rates applicable to your business location and ensuring accurate tax collection and remittance.
Registration Process
To register for a sales tax permit in Florida, businesses typically need to provide basic information about their operations, including the business name, address, and the type of goods or services sold. The registration process can be completed online through the Florida Department of Revenue’s official website, offering a convenient and efficient way to obtain the necessary permits.
Once registered, businesses are issued a unique sales tax permit number, which must be displayed prominently at the point of sale. This number is crucial for identifying the business during tax audits and for proper tax reporting.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
Businesses are responsible for collecting the appropriate sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This involves calculating the applicable tax rate, which can be complex given Florida’s varying tax rates, and ensuring the tax is added to the final bill or purchase price. Accurate record-keeping is essential to track sales tax collected, as businesses must remit these funds to the state and local governments on a regular basis.
The frequency of sales tax remittance varies based on the business's sales volume and tax liability. Most businesses are required to remit sales tax monthly or quarterly, with the due dates determined by the Florida Department of Revenue. Late remittances can result in penalties and interest, underscoring the importance of timely and accurate tax payments.
Impact on Consumers
Florida’s sales tax structure has a direct impact on consumers, influencing their purchasing decisions and overall spending. For tourists and visitors, the varying sales tax rates across counties can be a surprise, especially when planning a trip or making significant purchases. Understanding these rates can help consumers budget effectively and compare prices across different locations.
Price Transparency and Comparison
Given the diverse sales tax landscape in Florida, price transparency becomes crucial. Consumers should be aware of the sales tax rates in the areas they are shopping in to make informed decisions. Comparing prices between different counties or even different stores within the same county can help identify the best deals, especially for high-value purchases.
Online tools and resources, such as sales tax calculators and business directories, can provide valuable insights into the applicable sales tax rates. These tools allow consumers to estimate the total cost of their purchases, including sales tax, aiding in financial planning and budget management.
Consumer Rights and Protections
Florida’s sales tax regulations also protect consumers by ensuring fair and transparent pricing. Businesses are required to display sales tax rates clearly and accurately, preventing any confusion or misleading practices. Consumers have the right to request a detailed breakdown of the sales tax charged, ensuring they are not overcharged.
Additionally, Florida's sales tax system provides certain exemptions and discounts for specific consumer groups. For instance, senior citizens and veterans may be eligible for reduced sales tax rates on certain items, further enhancing consumer protection and fairness.
Future Implications and Trends
As Florida’s economy continues to evolve, the sales tax landscape is likely to undergo changes and adaptations. The state’s growing emphasis on tourism and e-commerce presents unique challenges and opportunities for sales tax regulation.
E-Commerce and Online Sales
The rise of e-commerce has transformed the sales tax landscape, especially in Florida, a state known for its thriving online business ecosystem. With remote sellers now required to collect and remit sales tax, even if they don’t have a physical presence in the state, the tax collection process has become more complex. This shift ensures a level playing field for both online and brick-and-mortar businesses, preventing unfair competitive advantages.
Potential Reforms and Initiatives
Looking ahead, there are discussions and proposals for sales tax reforms in Florida. These initiatives aim to simplify the tax structure, reduce compliance burdens, and enhance fairness. Some proposed changes include standardizing sales tax rates across counties, introducing a statewide flat tax rate, or exploring alternative tax systems, such as a value-added tax (VAT) or a consumption tax.
Furthermore, with the increasing focus on sustainable development and environmental initiatives, there is a growing interest in exploring green taxes and incentives. This could involve sales tax exemptions or reductions for environmentally friendly products and services, encouraging consumers and businesses to adopt more sustainable practices.
Conclusion

Florida’s sales tax system is a dynamic and intricate component of the state’s economic framework. From local variations in tax rates to special considerations for specific industries, understanding and navigating this system is essential for businesses and consumers alike. As Florida continues to evolve, so too will its sales tax regulations, shaping the future of business and consumer interactions in the Sunshine State.
What is the current state sales tax rate in Florida?
+The current state sales tax rate in Florida is 6%.
Are there any counties in Florida with no additional sales tax?
+Yes, counties like Dixie and Liberty have no additional sales tax beyond the state rate.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in Florida?
+Businesses typically remit sales tax monthly or quarterly, depending on their sales volume and tax liability.
Are there any consumer groups eligible for sales tax discounts in Florida?
+Yes, senior citizens and veterans may be eligible for reduced sales tax rates on certain items.
How is Florida adapting to the rise of e-commerce in its sales tax regulations?
+Florida now requires remote sellers to collect and remit sales tax, ensuring fair competition between online and offline businesses.



