Property Tax Detroit

Property taxes are a significant aspect of Detroit's financial landscape, impacting homeowners, businesses, and the city's overall revenue generation. With a unique historical context and a dynamic present, understanding property taxes in Detroit is crucial for anyone interested in the city's real estate market, economic development, or local governance.
The Complex Landscape of Detroit's Property Taxes

Detroit's property tax system is intricate, reflecting the city's rich history, diverse neighborhoods, and ongoing economic transformation. It involves a unique interplay of local, state, and federal regulations, creating a dynamic tax environment.
The city's property tax rates are among the highest in the country, influenced by factors such as the Headlee Amendment, which limits the growth of property tax rates, and Proposal A, which shifted some of the burden of funding public schools from local property taxes to the state.
Tax Rates and Assessments: Understanding the Basics
In Detroit, property taxes are calculated based on the assessed value of the property and the applicable tax rate. The assessed value is determined by the city's assessor, who considers factors like property size, location, and recent sales of comparable properties.
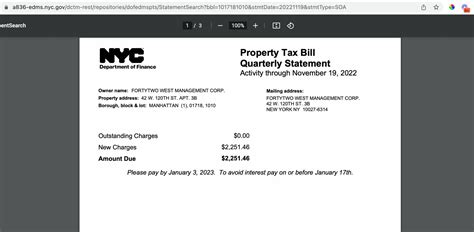
The tax rate, expressed as mills, is set annually by the city and other taxing authorities, such as the Detroit Public Schools and the Detroit Water and Sewerage Department. A mill represents $1 of tax for every $1,000 of assessed property value. For instance, if your property has an assessed value of $100,000 and the tax rate is 40 mills, your annual property tax would be $4,000.
| Taxing Authority | Millage Rate (FY 2023) |
|---|---|
| City of Detroit | 17.50 |
| Detroit Public Schools | 21.55 |
| Wayne County | 12.00 |
| Detroit Community College | 2.00 |
| Detroit Water and Sewerage Department | 45.00 |
| Total Effective Millage | 100.05 |
These rates are subject to change annually and can vary based on the specific location of the property within the city.
The Impact of Property Taxes on Detroit's Economy
Property taxes are a vital source of revenue for Detroit, funding essential city services, infrastructure development, and public education. They contribute to the city's overall economic health, influencing investment, real estate trends, and the cost of living.
High property taxes can be a double-edged sword. While they provide necessary funding, they can also pose challenges for homeowners, especially those on fixed incomes or with lower property values. Conversely, they may deter potential homebuyers or businesses from investing in the city.
The city has implemented various initiatives to mitigate these challenges, including tax abatement programs and incentives to encourage economic development and homeownership.
Navigating Property Tax Appeals and Exemptions
Homeowners in Detroit have the right to appeal their property tax assessments if they believe the assessed value is incorrect. The process involves submitting an appeal to the Detroit Tax Tribunal, which will review the case and make a determination.
Detroit also offers several tax exemption programs to eligible homeowners. For instance, the Homestead Property Tax Credit provides a credit based on income, and the Principal Residence Exemption (PRE) exempts the primary residence from the non-homestead tax, reducing the overall tax burden.
Comparative Analysis: Detroit vs. Other Major Cities
When compared to other major U.S. cities, Detroit's property tax rates are significantly higher. For instance, New York City's effective tax rate is approximately 2.24%, while Detroit's is closer to 3.33%. This disparity can influence real estate decisions and investment strategies.
However, it's important to note that property taxes are just one aspect of the city's overall tax structure. Detroit's income and sales taxes are relatively low, which can offset the high property tax rates for some residents and businesses.
Future Outlook and Potential Reforms

The future of property taxes in Detroit is closely tied to the city's ongoing economic recovery and redevelopment efforts. As the city continues to attract investment and residents, property values are likely to increase, potentially leading to higher tax revenues.
However, the city must also consider the impact of these rising values on its residents. Implementing strategies to ensure property taxes remain equitable and do not disproportionately burden lower-income homeowners will be crucial.
Potential reforms could include adjusting tax rates to reflect property values more dynamically, introducing additional tax relief programs, or exploring alternative revenue streams to reduce the reliance on property taxes.
The Role of Technology and Data in Tax Administration
Advancements in technology and data analytics offer opportunities to improve the accuracy and efficiency of Detroit's property tax system. Implementing digital tools for assessment and tax administration can enhance transparency, reduce administrative burdens, and improve taxpayer experiences.
For instance, using GIS (Geographic Information System) technology can aid in more precise property assessments, while digital platforms can streamline the tax payment and appeal processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average property tax rate in Detroit?
+The average property tax rate in Detroit is approximately 3.33%, which is calculated based on the total effective millage rate and the average assessed property value in the city.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I appeal my property tax assessment in Detroit?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>To appeal your property tax assessment in Detroit, you need to file an appeal with the Detroit Tax Tribunal. This process typically involves submitting documentation to support your claim, such as recent property sales in your neighborhood or an appraisal report. The Tribunal will then review your case and make a decision.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any tax exemption programs for Detroit homeowners?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, Detroit offers several tax exemption programs to eligible homeowners. These include the Homestead Property Tax Credit, which provides a credit based on income, and the Principal Residence Exemption (PRE), which exempts the primary residence from the non-homestead tax. Additionally, veterans and senior citizens may be eligible for specific tax relief programs.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How do property taxes in Detroit compare to other major U.S. cities?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Detroit's property tax rates are generally higher compared to many other major U.S. cities. For example, New York City's effective tax rate is around 2.24%, while Detroit's is closer to 3.33%. However, it's important to consider the overall tax structure, as Detroit has relatively low income and sales taxes.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What role does technology play in Detroit's property tax system?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Technology plays a significant role in Detroit's property tax system by enhancing accuracy and efficiency. GIS technology, for instance, aids in precise property assessments, while digital platforms streamline tax payment and appeal processes, making the system more transparent and user-friendly.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>