Progressive Tax Meaning
Understanding the concept of a progressive tax is essential in the world of finance and economics. Progressive taxation is a fundamental principle in many tax systems, including those of numerous countries around the world. This system aims to distribute the tax burden equitably, taking into account an individual's or entity's ability to pay. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of progressive taxation, exploring its definition, purpose, and impact on society.
The Essence of Progressive Taxation

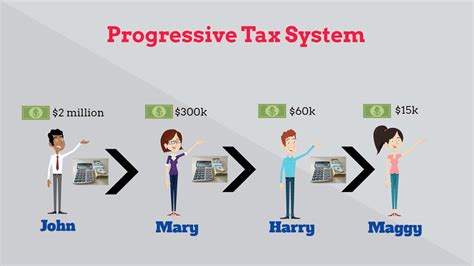
At its core, a progressive tax system is designed to impose higher tax rates on higher levels of income or wealth. In simpler terms, it means that as an individual’s income increases, so does the proportion of their income that is subject to taxation. This approach stands in contrast to regressive or proportional tax systems, which we will discuss later.
The underlying philosophy behind progressive taxation is rooted in the concept of social equity and redistribution of wealth. By taxing those with higher incomes at a higher rate, the government aims to reduce income inequality and provide a more balanced society. This system acknowledges that individuals with higher earnings have a greater capacity to contribute to the common good through taxes, which can then be used to fund public services and support those in need.
How Progressive Taxation Works
Progressive tax systems employ a tiered structure, dividing income into different brackets, each with its own tax rate. As an individual’s income rises, they move into higher tax brackets, resulting in a higher percentage of their income being taxed.
For instance, consider a simplified example where there are three tax brackets: 10%, 20%, and 30%. An individual earning up to a certain amount (let's say $50,000) would be taxed at the 10% rate. Once their income surpasses that threshold, they enter the next bracket and are taxed at 20% on the income above $50,000. If their income continues to rise, they may enter the highest bracket, where they are taxed at 30% on the income exceeding a certain limit, such as $100,000.
| Tax Bracket | Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Bracket 1 | Up to $50,000 | 10% |
| Bracket 2 | $50,001 - $100,000 | 20% |
| Bracket 3 | Above $100,000 | 30% |

This progressive structure ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their earnings to the government, while those with lower incomes are taxed at a lower rate, easing their financial burden.
The Benefits and Considerations of Progressive Taxation
Social Justice and Equity
One of the primary advantages of progressive taxation is its ability to promote social justice. By taxing higher-income individuals at a higher rate, the system aims to narrow the gap between the rich and the poor, fostering a more equitable society. This approach recognizes that wealth is not evenly distributed and that those with greater resources should contribute more to support public services and social programs.
Revenue Generation
Progressive taxation is often seen as an effective tool for generating substantial revenue for the government. Higher-income earners, who are typically in a better financial position, can afford to pay more taxes, providing a stable source of income for the government to fund various initiatives and programs.
Potential Drawbacks and Challenges
While progressive taxation has its merits, it is not without its criticisms and challenges. Some argue that it may discourage high-income earners from working harder or investing, as they face higher tax rates. Additionally, determining the appropriate tax rates and brackets can be complex and subject to political influence, leading to potential inefficiencies or unfairness.
Alternative Tax Systems: Regressive and Proportional Taxation
Regressive Taxation
In contrast to progressive taxation, regressive tax systems impose a higher tax burden on lower-income individuals relative to their income. This means that as income decreases, the proportion of income taken as tax increases. While this system may seem unfair, it is often applied to certain goods or services, such as sales taxes or excise duties, which affect lower-income individuals more significantly.
Proportional Taxation
Proportional taxation, also known as flat taxation, applies the same tax rate to all income levels. In this system, an individual earning 50,000 and an individual earning 100,000 would both be taxed at the same rate, regardless of their income bracket. While this approach is simpler to administer, it does not consider an individual’s ability to pay, which can lead to a heavier tax burden on lower-income earners.
The Impact of Progressive Taxation on Society

Progressive taxation has far-reaching implications for society as a whole. By redistributing wealth, it can lead to improved social mobility, as more resources are available to support education, healthcare, and other essential services. It can also encourage investment in public infrastructure and stimulate economic growth, as the government has the means to fund development projects.
Moreover, progressive taxation can foster a sense of social responsibility among higher-income earners, who understand that their contributions are helping to build a stronger and more resilient society. This can lead to increased civic engagement and a more cohesive community.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does progressive taxation differ from proportional taxation?
+Progressive taxation imposes higher tax rates on higher income levels, while proportional taxation applies the same tax rate to all income levels. Progressive taxation aims to reduce income inequality, while proportional taxation treats all income earners equally.
Are there any disadvantages to progressive taxation?
+One potential disadvantage is that it may discourage high-income earners from working harder or investing, as they face higher tax rates. Additionally, determining the appropriate tax rates and brackets can be complex and may lead to inefficiencies.
How does progressive taxation impact the economy as a whole?
+Progressive taxation can have a positive impact on the economy by generating revenue for the government to fund essential services and infrastructure. It can also promote social mobility and encourage investment, leading to economic growth.